Abstract
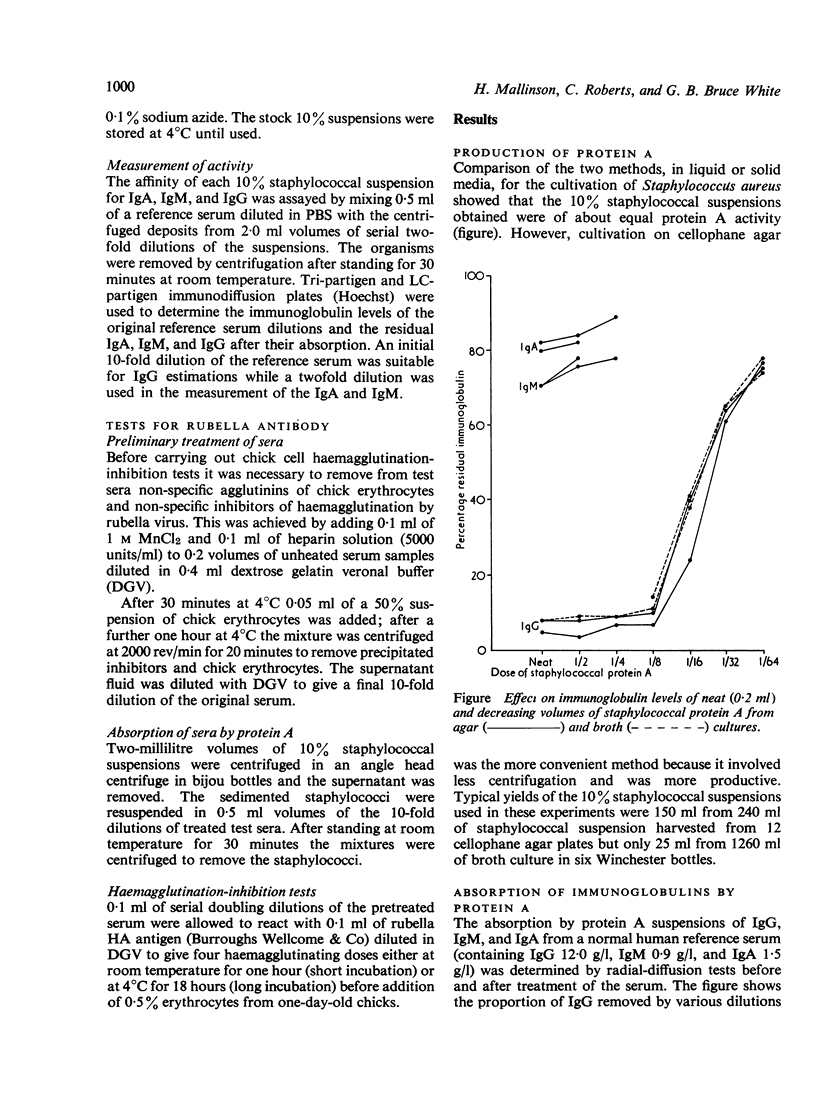
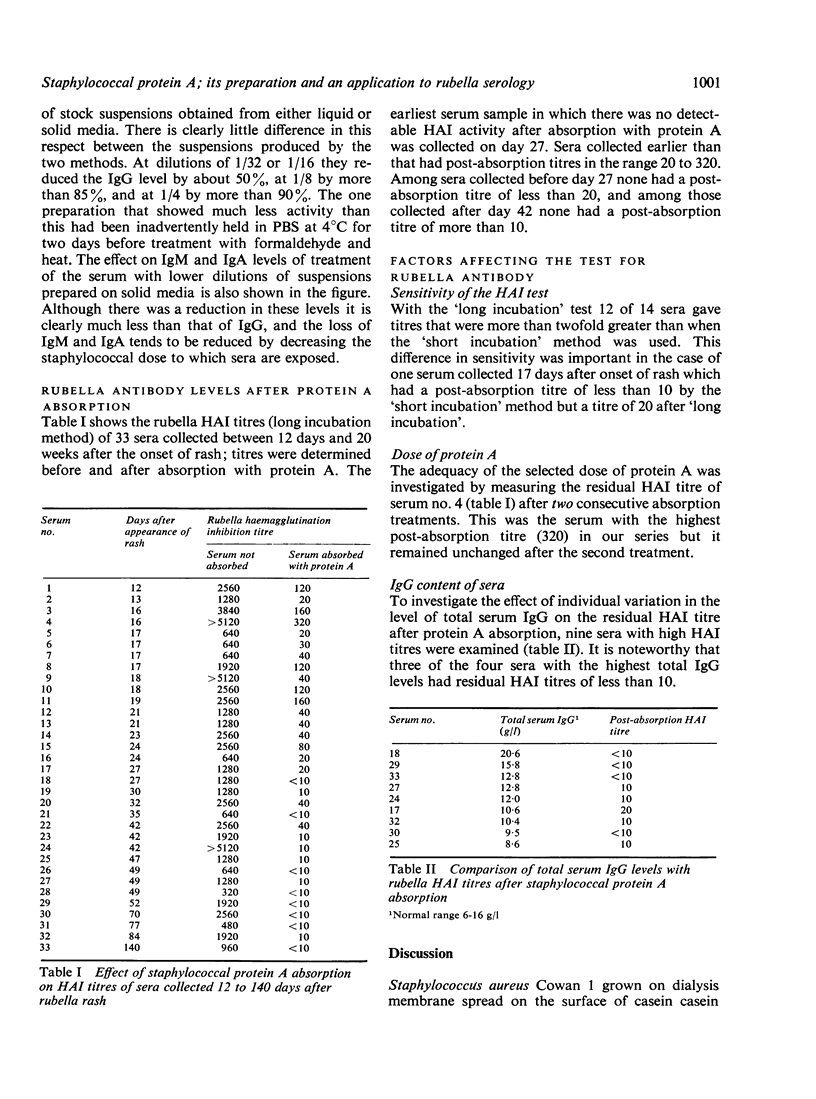
Good yields of staphylococcal protein A are obtained by growing the staphylococcus Cowan type 1 on cellophane agar. The activity of these preparations in removing immunoglobulin G (IgG) from human serum can be readily measured by the Mancini radial-diffusion technique and the correct in-use dilution determined. Treatment with protein A of sera from women with a history of rubella may help in the identification of those having specific antibody in the IgM and IgA fractions. This relatively simple procedure may have worthwhile application in the diagnosis of rubella.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankerst J., Christensen P., Kjellén L., Kronvall G. A rountine diagnostic test for IgA and IgM antibodies to rubella virus: absorption of IgG with Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):268–273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvidson S., Holme T., Wadström T. Influence of cultivation conditions on the production of extracellular proteins by Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(3):399–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G. A rapid slide-agglutination method for typing pneumococci by means of specific antibody adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):187–190. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Dossett J. H., Quie P. G., Williams R. C. Occurrence of protein a in staphylococcal strains: quantitative aspects and correlation to antigenic and bacteriophage types. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.10-15.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


