 An unprecedented diastereoselective and enantioselective catalytic direct aldol reaction generating β-hydroxy-α-amino acid derivatives with alkyl-substituted adjacent quaternary-tertiary stereocenters.
An unprecedented diastereoselective and enantioselective catalytic direct aldol reaction generating β-hydroxy-α-amino acid derivatives with alkyl-substituted adjacent quaternary-tertiary stereocenters.
Abstract
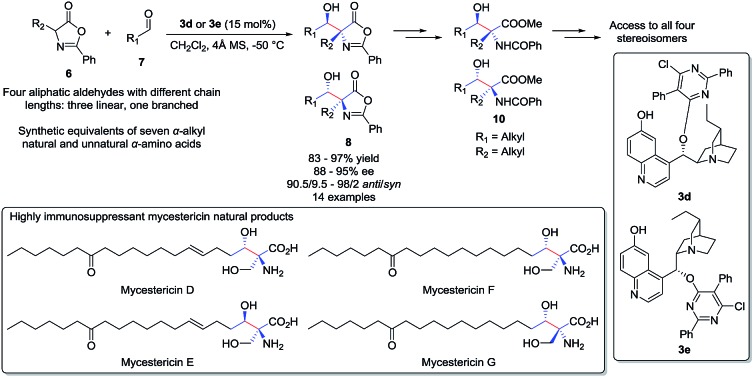
An unprecedented highly diastereoselective and enantioselective aldol reaction of α-alkyl azlactones and aliphatic aldehydes was achieved with cinchona alkaloid catalysts. To our knowledge, this reaction provides the first useful catalytic asymmetric access toward β-hydroxy-α-amino acids bearing alkyl substituents, which are structural motifs embedded in many natural products.
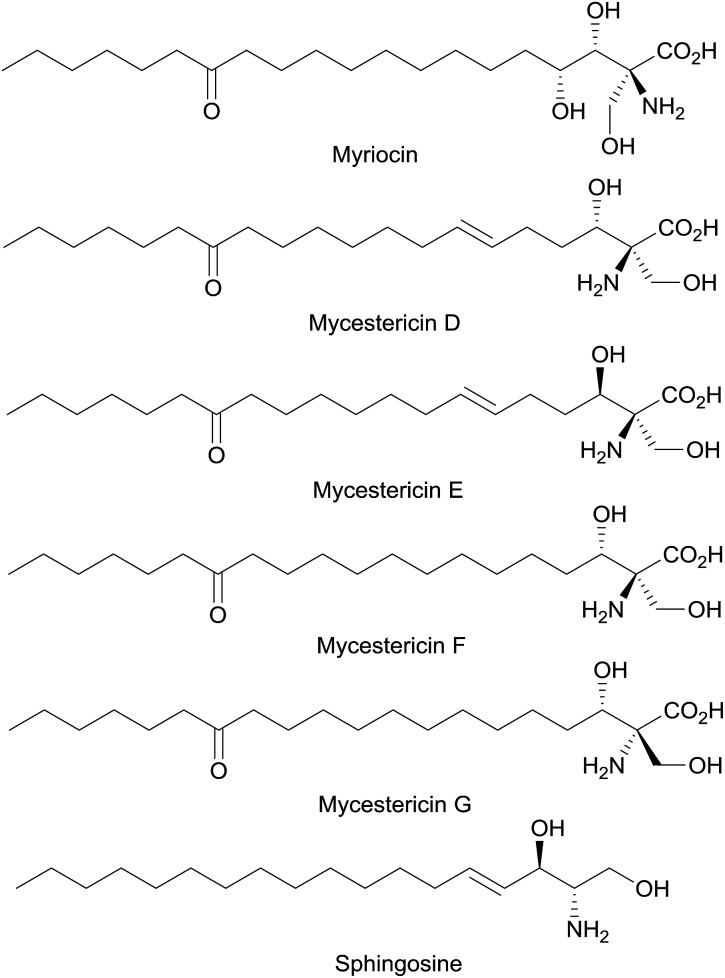
Optically active β-hydroxy-α-amino acids are an important class of amino acids as they are structural motifs in many biologically active natural products such as vancomycin,1 katanosins,2 cyclosporin,3 myriocin,4a,b mycestericins,4c,d sphingosine and threonine (Fig. 1). Furthermore, these amino acids are also useful chiral building blocks in organic synthesis as precursors to β-lactams,5 β-halo-α-amino acids,6 and aziridines.7 A variety of catalytic asymmetric approaches for the synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids has been reported.8–14 In a pioneering study,8a Ito, Hayashi and coworkers reported a gold-catalyzed highly diastereoselective and enantioselective aldol reaction for the generation of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids containing tertiary α-carbons. Since then other groups have also reported asymmetric direct aldol reactions with chiral transition-metal catalysts,8c–h organocatalysts9 and aldolases10 for the synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids and their derivatives. In addition, Sharpless asymmetric aminohydroxylation,11 transition-metal-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation,12 palladium-catalyzed allylic alkylation13 and chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed addition to oxocarbenium ion14 have been utilized to achieve the same goal.
Fig. 1. Mycestericins: potent immunosuppressant natural products.
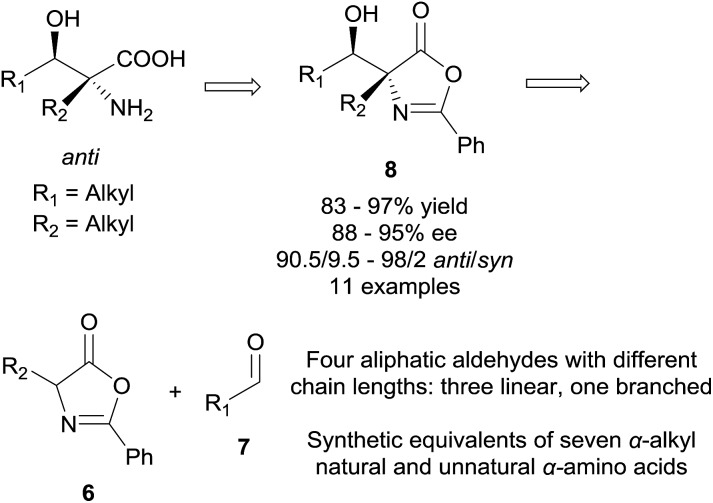
We became interested in the development of catalytic asymmetric synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids because biologically interesting natural products such as mycestericins contain a chiral β-hydroxy-α-amino acid motif that could not be constructed from existing catalytic asymmetric aldol reactions. In particular this motif presents both a tertiary β-stereocenter and a quaternary α-stereocenter with alkyl substituents. In principle, an efficient catalytic asymmetric aldol reaction of α-alkyl enolates or the equivalents with aliphatic aldehydes could provide a direct access to this structural motif.15 However, to our knowledge, such an asymmetric transformation was not available. Herein, we report the first efficient catalytic asymmetric direct aldol reaction of α-alkyl azlactones 6 and aliphatic aldehydes 7 (Scheme 1), which provides, to our knowledge, the first useful asymmetric catalytic access toward β-hydroxy-α-amino acids bearing alkyl substituents at both the tertiary β-stereocenter and the quaternary α-stereocenter. The high anti-diastereoselectivity in combination with a broad substrate scope allows the reaction to complement existing methods to form a general strategy for the asymmetric synthesis of β-hydroxy-α-amino acids.
Scheme 1. Reaction design.
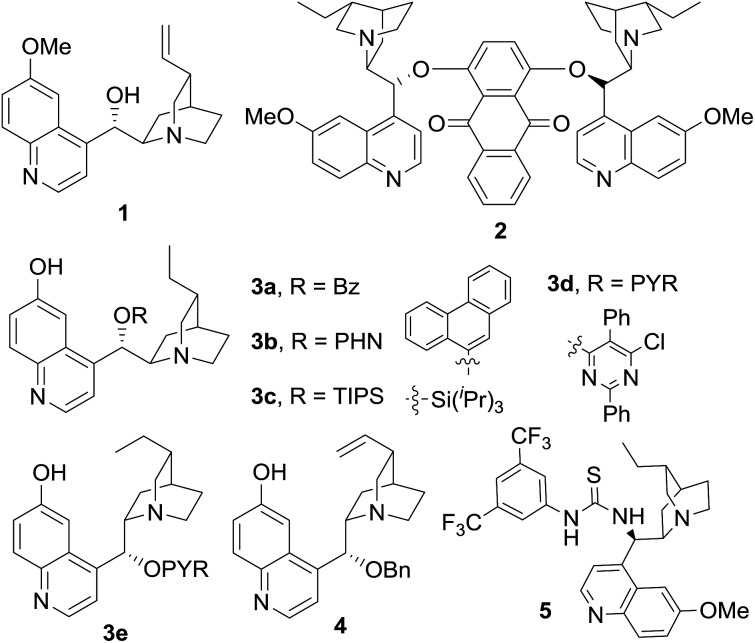
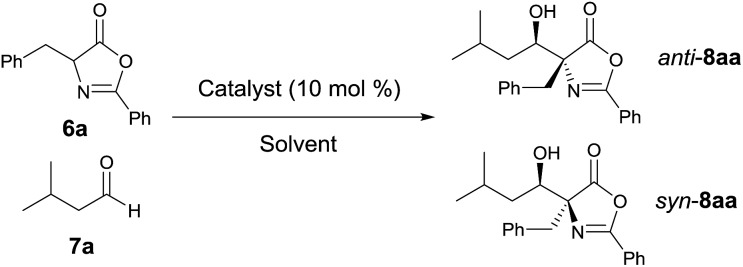
We initiated our study by reacting azlactone 6a and aldehyde 7a in the presence of a stoichiometric amount of triethylamine. After considerable experiments, we found that a reaction could be reasonably fast and clean at –20 °C in chloroform. We next investigated the possibility of promoting an asymmetric variant of this reaction with cinchona alkaloid-derived catalysts (Fig. 2). Upon first screening of a series cinchona alkaloid derivatives, (entries 1–9, Table 1), we identified the 6′-OH cinchona alkaloid 3d as the most promising catalyst in terms of affording high diastereoselectivity and enantioselectivity (entry 6, Table 1). Catalyst 3e, the pseudo-enantiomer of 3d, gave comparable results with an expected reverse sense of asymmetric induction (entry 7, Table 1). Following these results, we carried out the 3d-promoted aldol reaction in a variety of solvents with azlactone 6a at a significantly decreased concentration of 0.5 M (entry 10–15). We found that the reaction at the reduced concentration proceeded in higher diastereo- and enantioselectivity (entry 10 vs. 6). Moreover, the reaction in dichloromethane occurred in a slightly higher diastereoselectivity than and the same enantioselectivity as the reaction in chloroform (entries 11–10, Table 1). Both the diastereoselectivity and enantioselectivity afforded by catalyst 3d could be improved significantly when the reaction was performed at significantly reduced temperature and concentration (entry 16 vs. 11), although a higher catalyst loading and an extended reaction time were required for the reaction to proceed to completion. Importantly, under these conditions, a highly diastereoselective and enantioselective aldol reaction was established to generate the desired aldol product 8aa in 92% isolated yield, 94% ee and 97.5/2.5 anti/syn ratio. It should be noted that no product resulted from the self-aldol reaction by aldehyde 7a was detected by NMR analysis.
Fig. 2. Cinchona alkaloid catalysts.
Table 1. Catalytic asymmetric aldol reaction of azlactone 6a and aldehyde 7a a .
| |||||||
| Entry | Catalyst | Solvent | Temp (°C) | Time | Conv. c (%) | ee c d (%) | anti/syn c |
| 1 | 1 | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | >95 | 29/22 | 43.5/56.5 |
| 2 | 2 | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | 93 | 43/12 | 40.5/59.5 |
| 3 | 3a | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | >95 | 57/25 | 81/19 |
| 4 | 3b | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | >95 | 51/19 | 73/27 |
| 5 | 3c | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | 92 | –7/18 | 71/29 |
| 6 | 3d | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | >95 | 75/13 | 88/12 |
| 7 | 3e | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | >95 | –73/16 | 90/10 |
| 8 | 4 | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | 91 | –64/–6 | 82/18 |
| 9 | 5 | CHCl3 (2 M) | –20 | 15 h | >95 | –71/22 | 66/34 |
| 10 | 3d | CHCl3 (0.5 M) | –20 | 34 h | 95 | 86/–11 | 91/9 |
| 11 | 3d | CH2Cl2 (0.5 M) | –20 | 34 h | 93 | 86/–39 | 93.5/6.5 |
| 12 | 3d | PhCH3 (0.5 M) | –20 | 34 h | 80 | 48/–28 | 80/20 |
| 13 | 3d | THF (0.5 M) | –20 | 34 h | >95 | 50/–28 | 79.5/20.5 |
| 14 | 3d | Et2O (0.5 M) | –20 | 34 h | >95 | 53/–28 | 83/17 |
| 15 | 3d | CH3CN (0.5 M) | –20 | 34 h | >95 | 72/–18 | 88/12 |
| 16 e , f | 3d | CH2Cl2 (0.1 M) | –50 | 88 h | >95 (92) b | 94/ND | 97.5/2.5 |
aReactions were carried out with 0.1 mmol of 6a and 0.15 mmol of 7a.
bIsolated yield.
cDetermined by chrial HPLC analysis.
dee (anti/syn).
e10 mg of 4 Å molecular sieves were added.
f15 mol% of 3d.
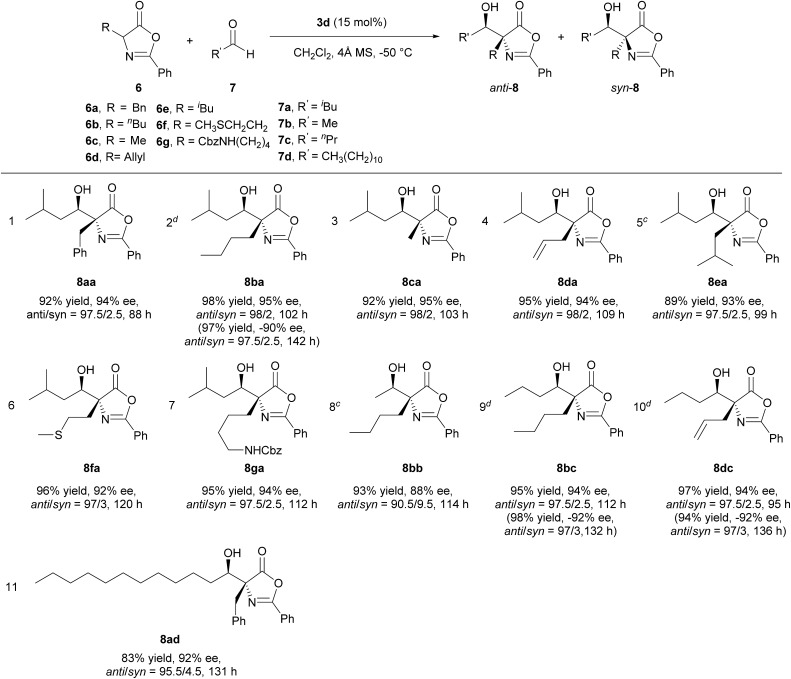
Applying the optimized reaction conditions for the model reaction, we investigated the substrate scope of this asymmetric aldol reaction (Table 2). The reactions of aldehyde 7a and azlactones 6a–g bearing different α-alkyl substituents gave consistently excellent yields, enantioselectivity and anti-selective diastereoselectivity (entries 1–7, Table 2). The catalyst could also accommodate variations in aliphatic aldehydes as shown by its high efficiency in the promotion of asymmetric aldol reactions involving a series of aliphatic aldehydes (entries 8–11, Table 2). The tolerance of aldehyde 7d, which bears a linear C12 alkyl chain, is noteworthy. With catalyst 3e, the reaction provide equally efficient access to the other enantiomer of the aldol product, as shown in the formation of aldol adduct ent-8ba, ent-8bc and ent-8dc (entries 2, 9, 10, Table 2). As detailed in the ESI,† the relative and absolute configurations of aldol products 8 were determined by 1D NOESY experiment and a modified Mosher's method, respectively.16
Table 2. Scope of reaction a b e .
|
aUnless noted, reactions were carried out with 0.1 mmol of 6, 0.15 mmol of 7, 0.015 mmol of 3d, 10 mg of 4 Å molecular sieves in 1 mL of dichloromethane.
bee value and anti/syn ratio determined by chiral HPLC analysis.
c0.2 mmol of 7b.
dResults in parentheses obtained using 3e (15 mol%) as catalyst.
eSee ESI for determination of relative and absolute configurations.
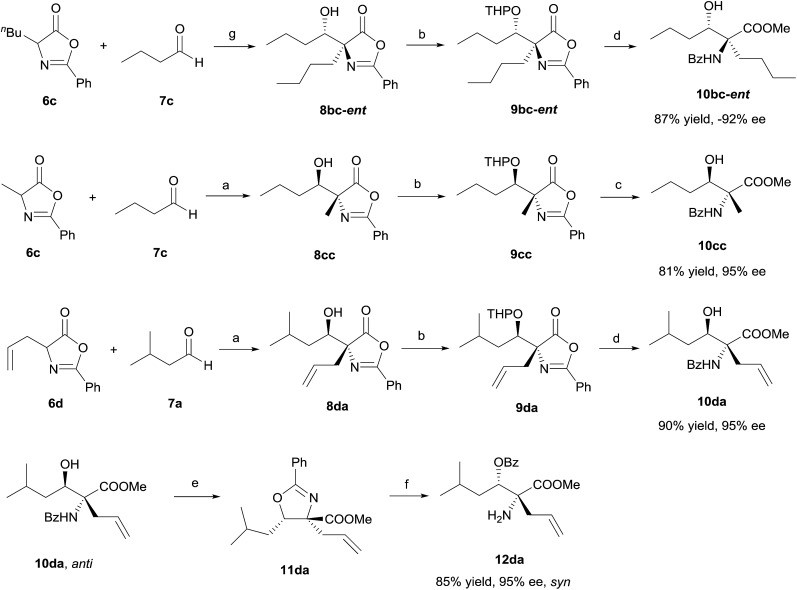
To demonstrate the potential synthetic utility of the chiral aldol adduct 8, ring opening transformations converting 8 into useful β-hydroxy-α-amino acid derivative 10 must be developed. We found that 8 were liable toward retro-aldol initiated decompositions under a variety of reaction conditions. After extensive experimental explorations, we were able to establish a high yield, three-step protocol to convert 8 into β-hydroxy-α-aminoester 10 (Scheme 2). Critical to the development of this useful conversion was the experimental discovery that the THP protected β-hydroxy-α-alkylazlactones 9, unlike 8, is inert toward retro-aldol decompositions.17 It should be noted that the four-step enantioselective preparations of β-hydroxy-α-aminoester 10 from azlactones 6 and aldehydes 7 require only a single purification for the isolation of 10, both intermediates 8 and 9 were used for the next step without subjecting to purifications. To establish enantioselective access to all four stereoisomers of β-hydroxy-α-amino acid derivative 10, we developed a one-pot conversion of anti-β-hydroxy-α-amino acid 10da into the corresponding syn-β-hydroxy-α-amino acid syn-12da involving the treatment of anti-10da with thionyl chloride followed by HCl in THF (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2. Transformation of aldol product 8. Reagents and conditions: (a) 3d (15 mol%), CH2Cl2, 4 Å MS, –50 °C; (b) PPTS, DHP, CH2Cl2, rt; then K2CO3, Na2SO4, MeOH, rt; (c) 2 N HCl, MeOH, rt; (d) HCl in MeOH (∼1.25 M), rt; (e) SOCl2, THF, rt; (f) 2 N HCl, THF, rt; (g) 3e (15 mol%), CH2Cl2, 4 Å MS, –50 °C. PPTS = pyridinum-p-toluenesulfonate; DHP = 3,4-dihydro-2-H-pyran.
Conclusions
In summary, we have developed a highly enantioselective and diastereoselective direct aldol reaction of α-alkyl azlactones with aliphatic aldehydes catalyzed by cinchona alkaloid catalysts 3d and 3e. To our knowledge, this is the first efficient asymmetric direct aldol reaction of azlactones and aliphatic aldehydes. Providing an efficient catalytic asymmetric access to β-hydroxy-α-amino acids bearing alkyl substituents at both the tertiary β-stereocenter and the quaternary α-stereocenter, this new catalytic asymmetric aldol reaction should find applications in natural product synthesis and medicinal chemistry.18
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the generous financial support from National Institutes of General Medical Sciences (GM-61591).
Footnotes
†Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental procedures and characterization for new compounds are provided. See DOI: 10.1039/c5sc02116b
References
- (a) Williams D. H. Acc. Chem. Res. 1984;17:364. [Google Scholar]; (b) Harris C. M., Kopecka H., Harris T. M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983;105:6915. [Google Scholar]; (c) Nagarajan R., Schabel A. A., Occolowitz J. L., Counter F. T., Ott J. L. J. Antibiot. 1988;41:1431. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.1430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (a) Kato T., Hinoo H., Terui Y., Kikuchi J., Shoji J. J. Antibiot. 1988;41:719. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Shoji J., Hinoo H., Matsumoto K., Hattori T., Yoshida T., Matsuura S., Kondo E. J. Antibiot. 1988;41:713. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.41.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Carr S. A., Block E., Costello C. E. J. Org. Chem. 1985;50:2854. [Google Scholar]
- (a) Schreiber S. L. Science. 1991;251:283. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Evans D. A., Weber A. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986;108:6757. [Google Scholar]
- (a) Fujita T., Inoue K., Yamamoto S., Ikumoto T., Sasaki S., Toyama R., Chiba K., Hoshino Y., Okumoto T. J. Antibiot. 1994;47:208. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.47.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Fujita T., Inoue K., Yamamoto S., Ikumoto T., Sasaki S., Toyama R., Chiba K., Hoshino Y., Okumoto T. J. Antibiot. 1994;47:216. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.47.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Sasaki S., Hashimoto R., Kiuchi M., Inoue K., Ikumoto T., Hirose R., Chiba K., Hoshino Y., Okumoto T., Fujita T. J. Antibiot. 1994;47:420. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.47.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Fujita T., Hamamichi N., Kiuchi M., Matsuzaki T., Kitao Y., Inoue K., Hirose R., Yoneta M., Sasaki S., Chiba K. J. Antibiot. 1996;49:846. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.49.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (a) Lotz B. T., Miller J. J. Org. Chem. 1993;58:618. [Google Scholar]; (b) Miller M. J. Acc. Chem. Res. 1986;19:49. [Google Scholar]
- Pansare S. V., Vederas J. C. J. Org. Chem. 1987;52:4804. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner D. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1994;33:599. [Google Scholar]
- For selected examples, see: ; (a) Ito Y., Sawamura M., Hayashi T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986;108:6405. [Google Scholar]; (b) Ito Y., Sawamura M., Shirakawa E., Hayashizaki K., Hayashi T. Tetrahedron. 1988;44:5253. [Google Scholar]; (c) Evans D. A., Janey J. M., Magomedov N., Tedrow J. S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2001;40:1884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Kobayashi J., Nakamura M., Mori Y., Yamashita Y., Kobayashi S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:9192. doi: 10.1021/ja047597t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Willis M. C., Cutting G. A., Piccio V. J.-D., Durbin M. J., John M. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005;44:1543. doi: 10.1002/anie.200462125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Sladojevich F., Trabocchi A., Guarna A., Dixon D. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011;133:1710. doi: 10.1021/ja110534g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Yoshino T., Morimoto H., Lu G., Matsunaga S., Shibasaki M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:17082. doi: 10.1021/ja908571w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Trost B. M., Miege F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014;136:3016. doi: 10.1021/ja4129394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For selected examples, see: ; (a) Horikawa M., Busch-Peterson J., Corey E. J. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999;40:3843. [Google Scholar]; (b) Ooi T., Taniguchi M., Kameda M., Maruoka K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002;41:4542. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20021202)41:23<4542::AID-ANIE4542>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Ooi T., Kameda M., Taniguchi M., Maruoka K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:9685. doi: 10.1021/ja048865q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Thayumanavan R., Tanaka F., Barbas III C. F. Org. Lett. 2004;6:3541. doi: 10.1021/ol0485417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Li L., Klauber K. G., Seidel D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:12248. doi: 10.1021/ja804838y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Chen W.-B., Wu Z.-J., Hu J., Cun L.-F., Zhang X.-M., Yuan W.-C. Org. Lett. 2011;13:2472. doi: 10.1021/ol200724q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For selected examples, see: ; (a) Vassilev V. P., Uchiyama T., Kajimoto T., Wong C.-H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36:4081. [Google Scholar]; (b) Kimura T., Vassilev V. P., Shen G.-J., Wong C.-H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997;119:11734. [Google Scholar]; (c) Gutierrez M. L., Garrabou X., Agosta E., Servi S., Parella T., Joglar J., Clapés P. Chem.–Eur. J. 2008;14:4647. doi: 10.1002/chem.200800031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Hernandez K., Zelen I., Petrillo G., Usón I., Wandtke C. M., Bujons J., Joglar J., Parella T., Clapés P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015;54:3013–3017. doi: 10.1002/anie.201411484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For selected examples, see: ; (a) Tao B., Schlingloff G., Sharpless K. B. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:2507. [Google Scholar]; (b) Morgan A., Masse C. E., Panek J. S. Org. Lett. 1999;1:1949. doi: 10.1021/ol9903032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Park H., Cao B., Joullié M. M. J. Org. Chem. 2001;66:7223. doi: 10.1021/jo010482c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For selected examples, see: ; (a) Noyori R., Ikeda T., Ohkuma T., Widhalm M., Kitamura M., Takaya H., Akutagawa S., Sayo N., Saito T., Taketomi T., Kumobayashi H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989;111:9134. [Google Scholar]; (b) Kuwano R., Okuda S., Ito Y. J. Org. Chem. 1998;63:3499. [Google Scholar]; (c) Mordant C., Dünkelmann P., Ratovelomanana-Vidal V., Genet J. P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004:3017. doi: 10.1039/b401631a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Mordant C., Dünkelmann P., Ratovelomanana-Vidal V., Genet J. P. Chem. Commun. 2004:1296. doi: 10.1039/b401631a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Makino K., Goto T., Hiroki Y., Hamada Y. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004;43:882. doi: 10.1002/anie.200353072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Makino K., Hiroki Y., Hamada Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005;127:5784. doi: 10.1021/ja0432113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (a) Trost B. M., Ariza X. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1997;36:2635. [Google Scholar]; (b) Trost B. M., Lee C. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998;120:6818. [Google Scholar]; (c) Trost B. M., Lee C. B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001;123:12191. doi: 10.1021/ja0118338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada M., Tanaka H., Sorimachi K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:3430. doi: 10.1021/ja8090643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For total synthesis of Mycestericin D, E, F and G, see: ; (a) Shibata K., Shingu K., Vassilev V. P., Nishide K., Fujita T., Node M., Kajimoto T., Wong C.-H. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996;37:2791. [Google Scholar]; (b) Fujita T., Hamamichi N., Matsuzaki T., Kitao Y., Kiuchi M., Node M., Hirose R. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36:8599. [Google Scholar]; (c) Nishide K., Shibata K., Fujita T., Kajimoto T., Wong C.-H., Node M. Heterocycles. 2000;52:1191. [Google Scholar]; (d) Iwabuchi Y., Furukawa M., Esumi T., Hatakeyama S. Chem. Commun. 2001:2030. doi: 10.1039/b106471c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Berhal L., Takechi S., Kumagai N., Shibasaki M. Chem.–Eur. J. 2011;17:1915. doi: 10.1002/chem.201002874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Fairhurst N. W. G., Mahon M. F., Munday R. H., Carbery D. R. Org. Lett. 2012;14:756. doi: 10.1021/ol203300k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Please see ESI for details
- Miyashita M., Yoshikoshi A., Grieco P. A. J. Org. Chem. 1977;42:3772. [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. R., Pearce C. J., Oberlies N. H. J. Nat. Prod. 2011;74:900. doi: 10.1021/np2000528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.