Abstract
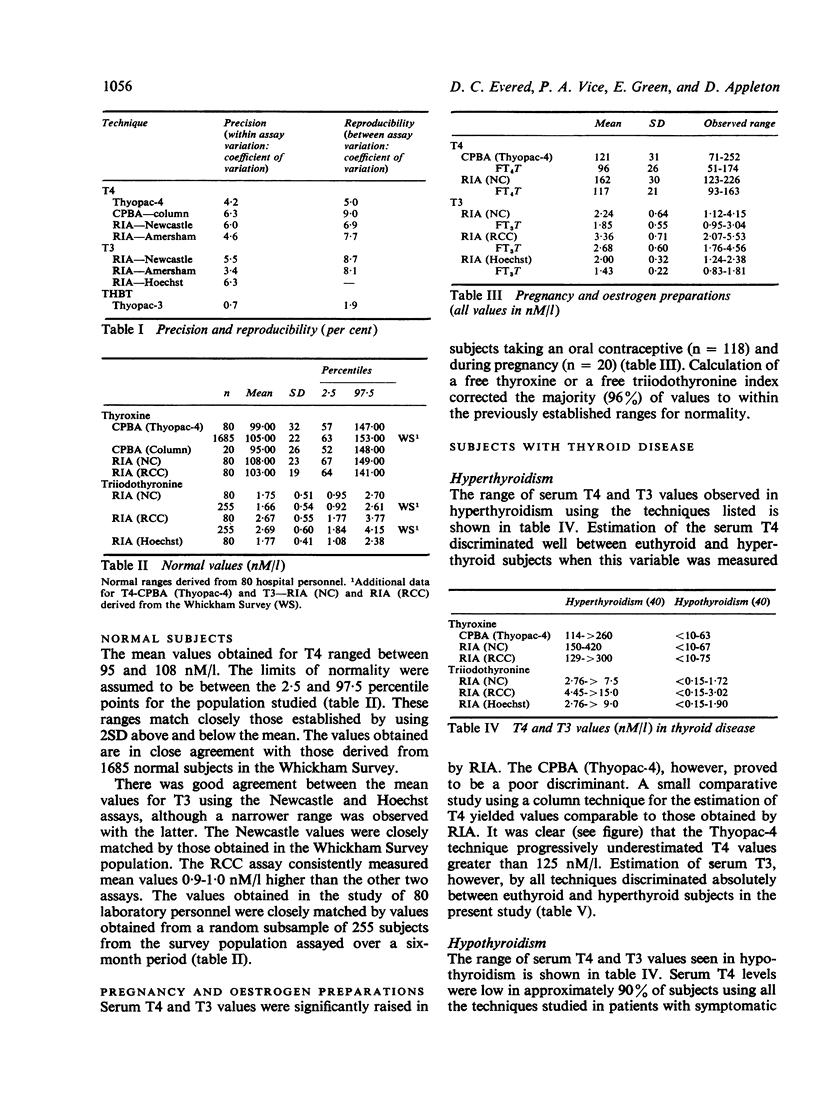
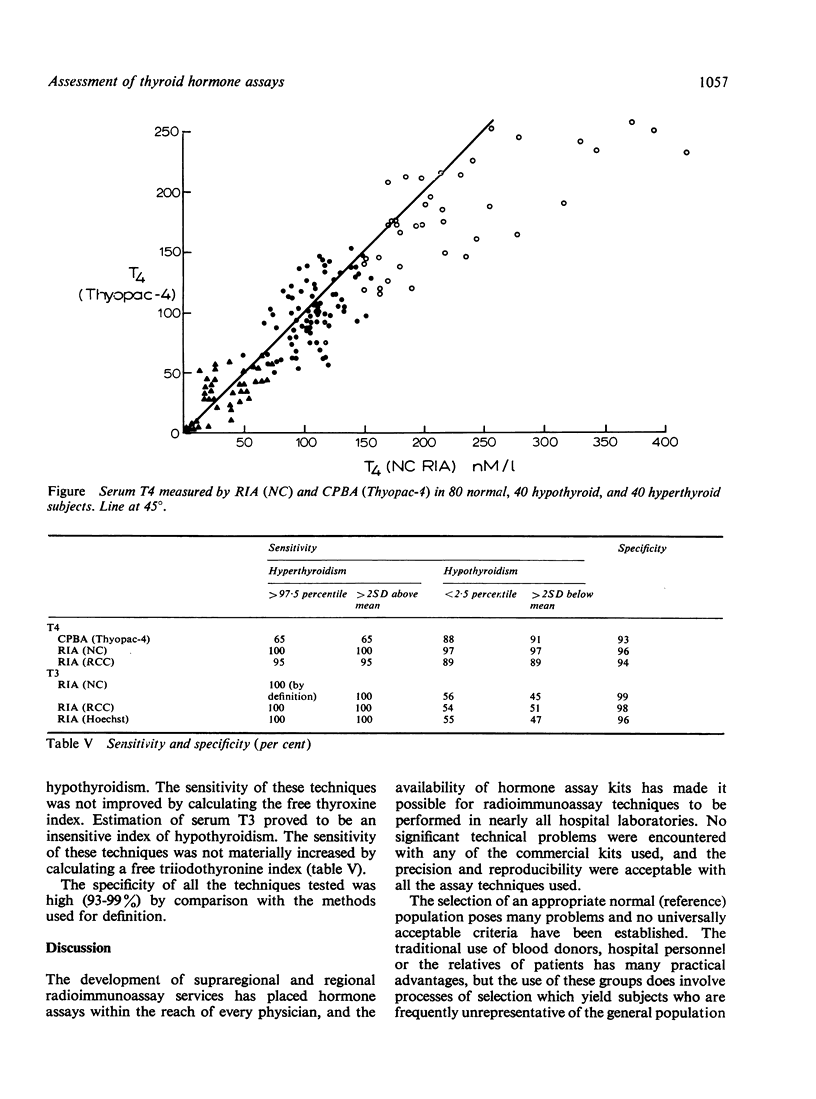
Four techniques for estimating serum T4 and three for estimating serum T3 have been investigated and found to be satisfactory in routine use. Normal ranges for each techniques have been established. Estimation of serum T3 by the commerical kits tested appears to have a high discriminant value in the diagnosis of hyperthyroidism, although the diagnostic definition used inevitably enhances the apparent sensitivity of these techniques. Estimation of serum T4 will identify the majority of patients with symptomatic hypothyroidism. The low sensitivity of T3 in the diagnosis of thyroid failure is confirmed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britton K. E., Quinn V., Brown B. L., Ekins R. P. A strategy for thyroid function tests. Br Med J. 1975 Aug 9;3(5979):350–352. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5979.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr W. A., Black E. G., Griffiths R. S., Hoffenberg R. Serum triiodothyronine and reverse triiodothyronine concentrations after surgical operation. Lancet. 1975 Dec 27;2(7948):1277–1279. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90612-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter J. N., Eastman C. J., Corcoran J. M., Lazarus L. Effect of severe, chronic illness on thyroid function. Lancet. 1974 Oct 26;2(7887):971–974. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evered D. C., Ormston B. J., Smith P. A., Hall R., Bird T. Grades of hypothyroidism. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 17;1(5854):657–662. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5854.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evered D. Diseases of the thyroid gland. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Nov;3(3):425–450. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(74)80035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R., Amos J., Ormston B. J. Radioimmunoassay of human serum thyrotrophin. Br Med J. 1971 Mar 13;1(5749):582–585. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5749.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesch R. D., Evered D. Radioimmunoassay of triiodothyronine in unextracted human serum. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 17;1(5854):645–648. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5854.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligson H., Seligson D. Measurement of thyroxine by competitive protein binding. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Apr;38(1):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalet S. M., Beardwell C. G., Lamb A. M., Gowland E. Value of routine serum-triiodothyronine estimation in diagnosis of thyrotoxicosis. Lancet. 1975 Nov 22;2(7943):1008–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90293-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


