Abstract
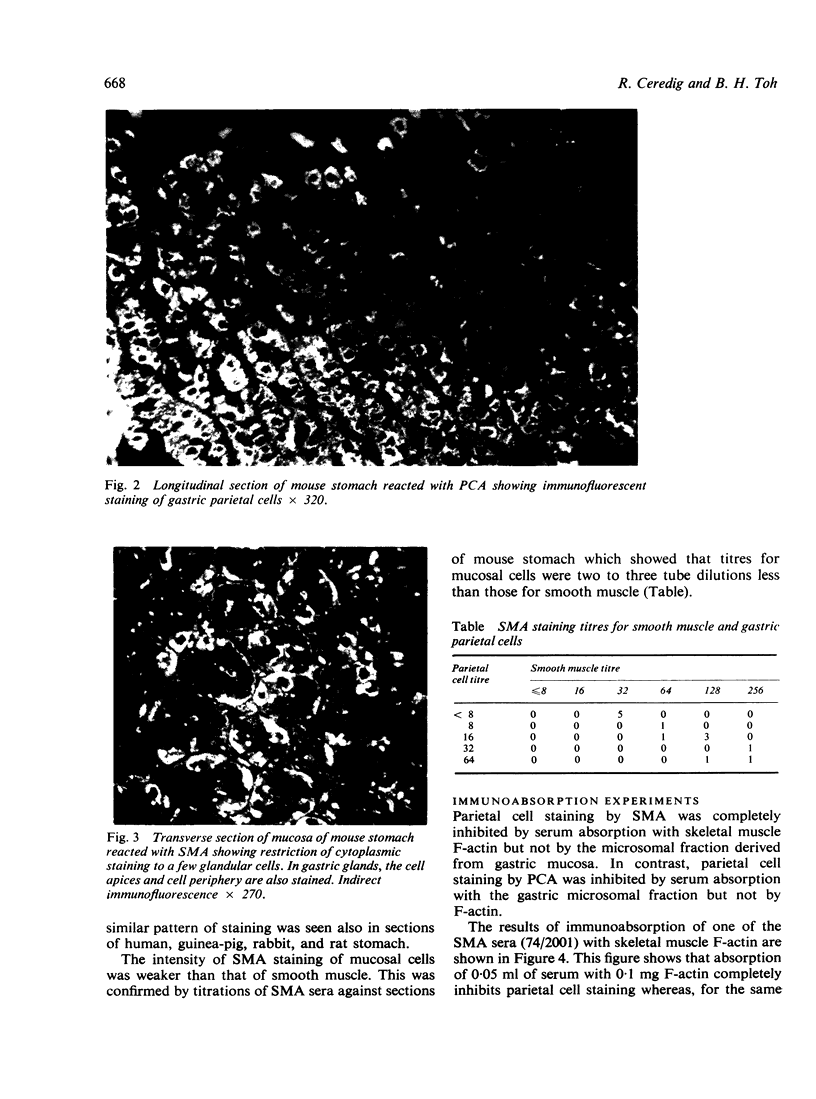
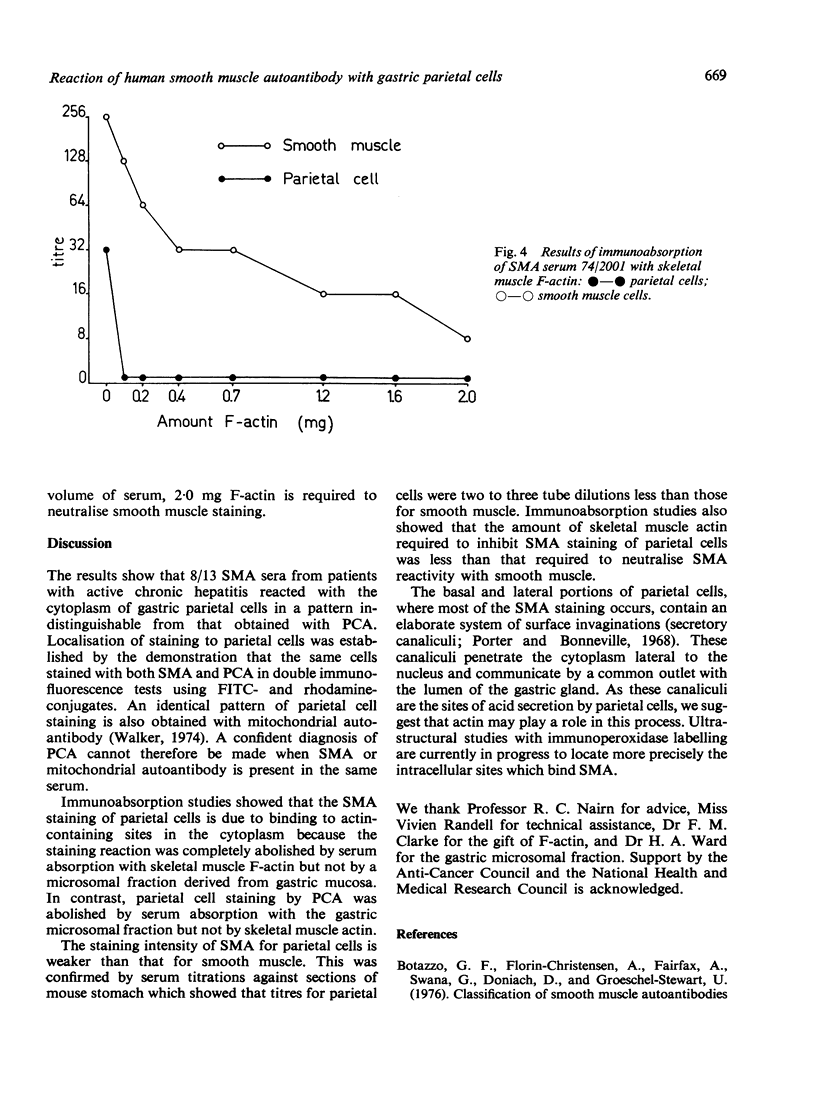
Thirteen smooth muscle antibody (SMA) sera obtained from patients with active chronic hepatitis were examined for immunofluorescence reactivity with gastric mucosal cells. Eight out of 13 sera stained the cytoplasm of gastric parietal cells in a pattern indistinguishable from that obtained with parietal cell autoantibody (PCA). The staining reaction was localised to parietal cells by the demonstration that the same cells stained with both SMA and PCA in double immunofluorescent tests. The SMA staining intensity for parietal cells was weaker than that for smooth muscle. Specificity of the staining reaction for actin was established by the observation that parietal cell staining by SMA was inhibition by serum absorption with skeletal muscle F-actin but not by a microsomal fraction derived from gastric mucosa.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Fairfax A., Swana G., Doniach D., Groeschel-Stewart U. Classification of smooth muscle autoantibodies detected by immunofluorescence. J Clin Pathol. 1976 May;29(5):403–410. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke F. M., Lovell S. J., Masters C. J., Winzor D. J. Beef muscle troponin: evidence for multiple forms of troponin-T. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 14;427(2):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doniach D., Roitt I. M., Walker J. G., Sherlock S. Tissue antibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis, active chronic (lupoid) hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis and other liver diseases and their clinical implications. Clin Exp Immunol. 1966 Jul;1(3):237–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Ryan G. B., Lamelin J. P., Vassalli P., Majno G., Bouvier C. A., Cruchaud A., Lüscher E. F. Human smooth muscle autoantibody. Its identification as antiactin antibody and a study of its binding to "nonmuscular" cells. Am J Pathol. 1973 Sep;72(3):473–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Trenchev P., Holborow E. J. Increase of contractile proteins in human cancer cells. Lancet. 1975 Oct 25;2(7939):796–797. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)80008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holborow E. J., Trenchev P. S., Dorling J., Webb J. Demostration of smooth muscle contractile protein antigens in liver and epithelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:489–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J., Glynn L. E. Antibody to smooth muscle in patients with liver disease. Lancet. 1965 Oct 30;2(7418):878–879. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidman K., Biberfeld G., Fagraeus A., Norberg R., Torstensson R., Utter G., Carlsson L., Luca J., Lindberg U. Anti-actin specificity of human smooth muscle antibodies in chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):266–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Hard G. C., Cauchi M. N., Muller H. K. Smooth-muscle-associated contractile protein in renal mesenchymal tumour cells and in transformed cells from DMN-injected rats. Br J Cancer. 1976 Nov;34(5):533–545. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Muller H. K., Cauchi M. N. Smooth muscle-associated contractile protein in human and experimental acute leukaemias. Aust N Z J Med. 1976 Oct;6(5):459–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1976.tb03035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Muller H. K., Elrick W. L. Smooth muscle associated antigen in astrocytes and astrocytomata. Br J Cancer. 1976 Feb;33(2):195–202. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh B. H., Muller H. K. Smooth muscle-associated antigen in experimental cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, keratoacanthoma, and papilloma. Cancer Res. 1975 Dec;35(12):3741–3745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. The immunology of liver disorders. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 Jun;67(6 Pt 2):566–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward H. A., Nairn R. C. Extraction of gastric parietal cell autoantigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Sep;2(5):565–571. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Mackay I. R., Irwin J. Autoimmune hepatitis. Immunofluorescence reactions with cytoplasm of smooth muscle and renal glomerular cells. Lancet. 1966 Jun 18;1(7451):1333–1335. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]