Abstract
The antibacterial activity of the four possible combinations of the three drugs, colistin, sulphamethoxazole, and trimethoprim, has been investigated with Gram-negative bacteria. All of the strains examined, with the exception of the strains of Proteus, were sensitive to colistin.
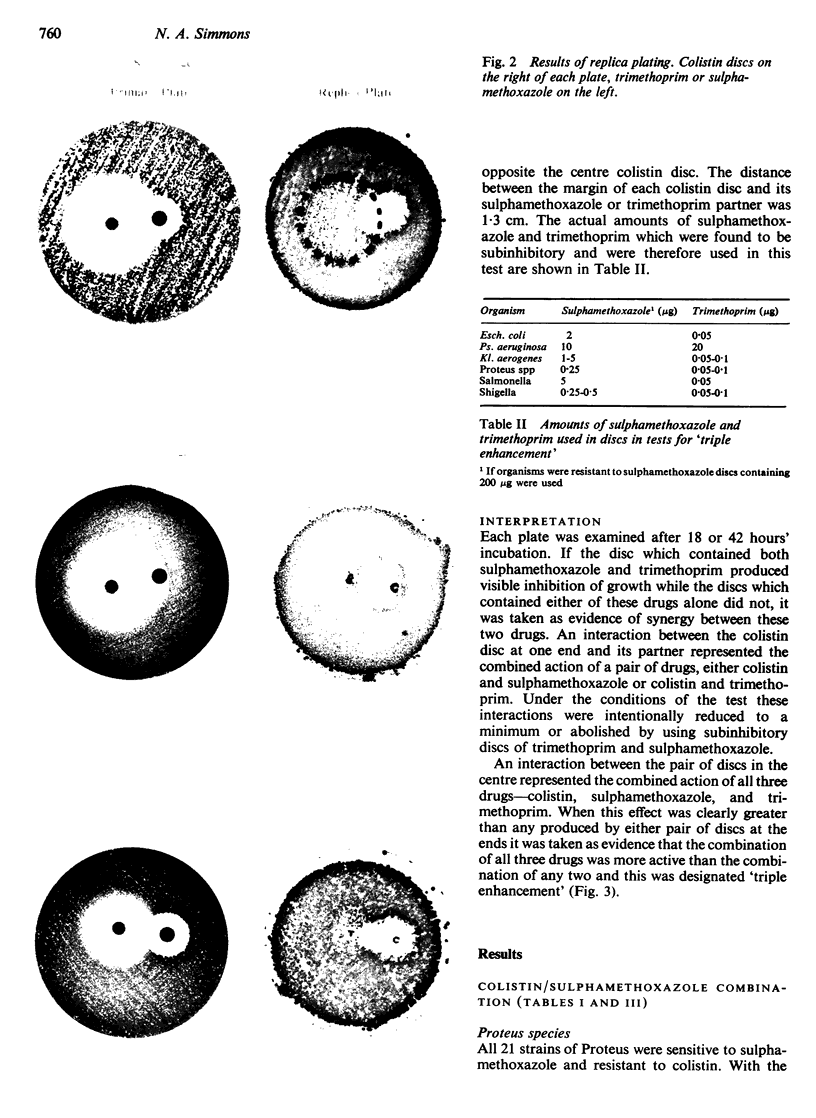
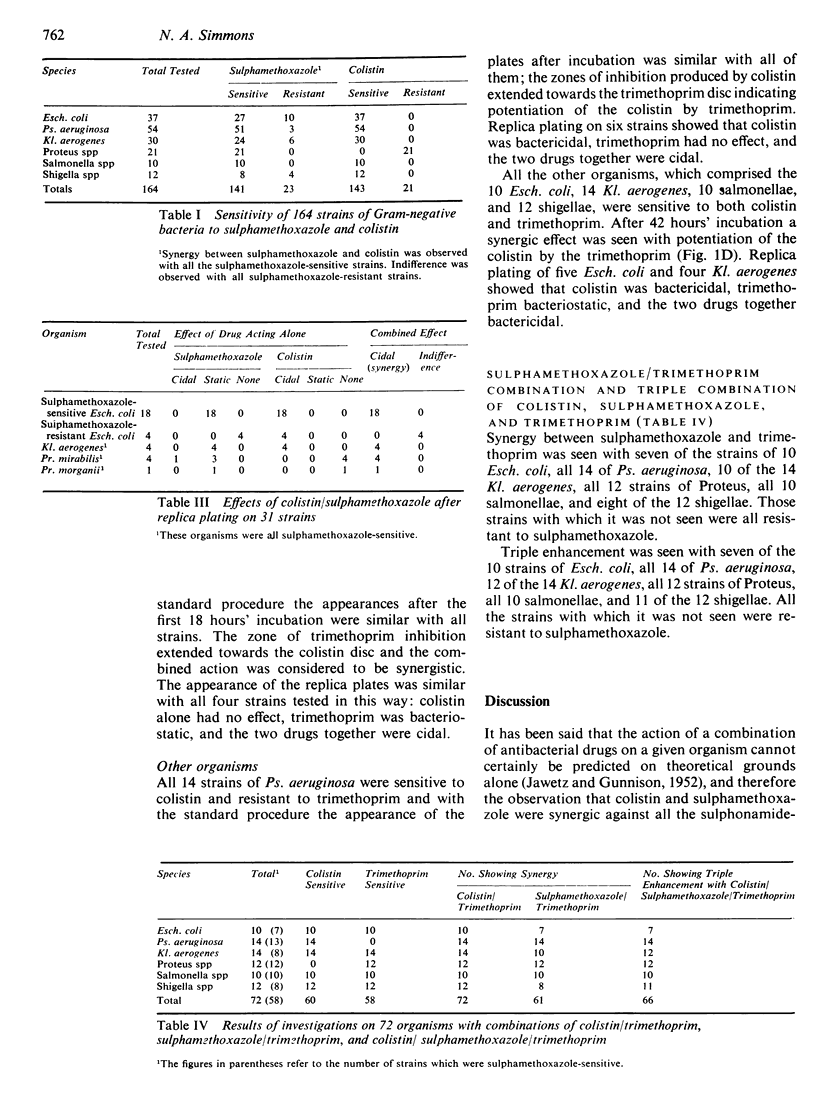
The combination of colistin and sulphamethoxazole was synergic against all 141 sulphamethoxazole-sensitive bacteria out of a total of 164 organisms against which it was tested. The sensitive strains comprised 27 of the 37 Esch. coli, 51 of the 54 Ps. aeruginosa, 24 of the 30 Kl. aerogenes, eight of the 12 shigellae, and all 21 Proteus and 10 salmonellae tested. The combined effect was indifference against the remaining 23 organisms which were resistant to sulphamethoxazole.
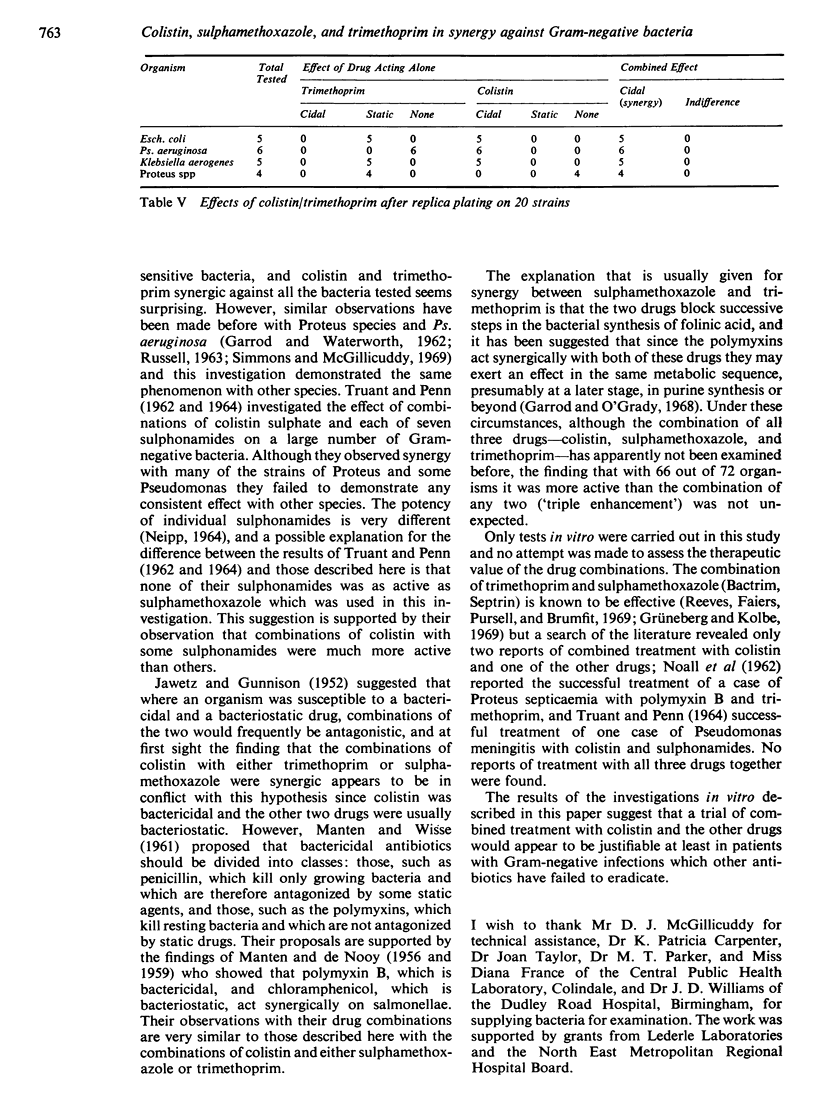
The combination of colistin and trimethoprim was synergic against all 72 organisms against which it was tested, which comprised 10 Esch. coli, 14 Ps. aeruginosa, 14 Kl. aerogenes, 12 Proteus spp, 10 salmonellae, and 12 shigellae. The combination of sulphamethoxazole and trimethoprim was synergic against 61 of the same 72 organisms; the exceptions were three Esch. coli, four Kl. aerogenes, and four shigellae, all of which were sulphamethoxazole resistant.
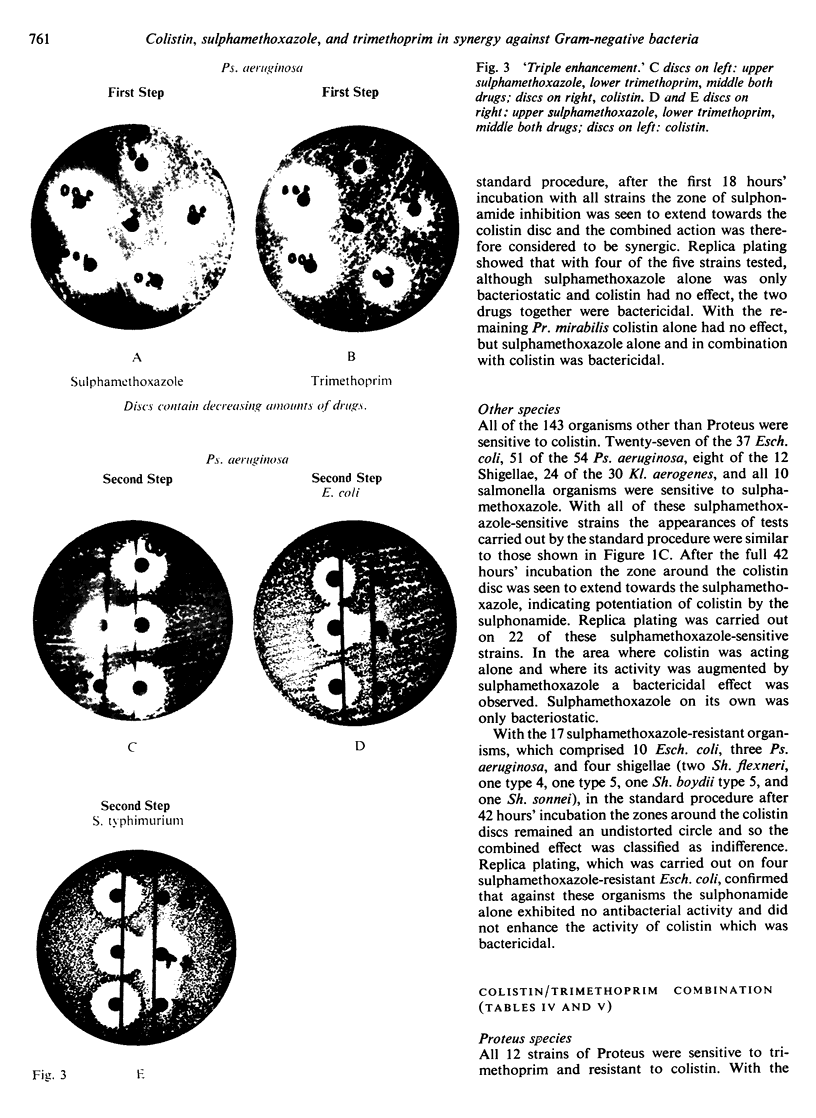
The combination of all three drugs—colistin, sulphamethoxazole, and trimethoprim—was more active than combinations of any two against 66 of the 72 organisms. The exceptions were three strains of Esch. coli, two of Kl. aerogenes, and one shigella, all of which were sulphamethoxazole resistant.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DE NOOY J. A., MANTEN A. The activity of some antibiotic combinations on Salmonella. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1956;22(3):231–236. doi: 10.1007/BF02538332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Trimethoprim: laboratory and clinical studies. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):202–209. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., HILSON G. R. Combined agar diffusion and replica plating techniques in the study of antibacterial substances. J Clin Pathol. 1954 Feb;7(1):37–44. doi: 10.1136/jcp.7.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., HILSON G. R., JEWELL P. Laboratory aspects of combined antibiotic treatment. Br Med J. 1953 Dec 12;2(4849):1298–1300. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4849.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P., WATERWORTH P. M. Methods of testing combined antibiotic bactericidal action and the significance of the results. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Jul;15:328–338. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.4.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grüneberg R. N., Kolbe R. Trimethoprim in the treatment of urinary infections in hospital. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 1;1(5643):545–547. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5643.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEN A., WISSE M. J. Antagonism between antibacterial drugs. Nature. 1961 Nov 18;192:671–672. doi: 10.1038/192671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEN A., de NOOY J. Some further observations on synergism between chloramphenicol and polymyxin B in relation to Salmonella bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1959;25:183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF02542845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noall E. W., Sewards H. F., Waterworth P. M. Successful Treatment of a Case of Proteus Septicaemia. Br Med J. 1962 Oct 27;2(5312):1101–1102. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5312.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL F. E. SYNERGISM BETWEEN SULPHONAMIDE DRUGS AND ANTIBIOTICS OF THE POLYMYXIN GROUP AGAINST PROTEUS SP. IN VITRO. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jul;16:362–366. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.4.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Faiers M. C., Pursell R. E., Brumfitt W. Trimethoprim--sulphamethoxazole: comparative study in urinary infection in hospital. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 1;1(5643):541–544. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5643.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons N. A. Potentiation of inhibitory activity of colistin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa by sulphamethoxazole and sulphamethizole. Br Med J. 1969 Sep 20;3(5672):693–696. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5672.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]