Abstract
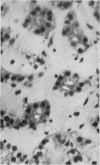
The histology of the parathyroids from 88 cases of primary hyperparathyroidism has been reviewed in a search for local amyloid deposits.
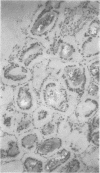
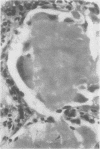
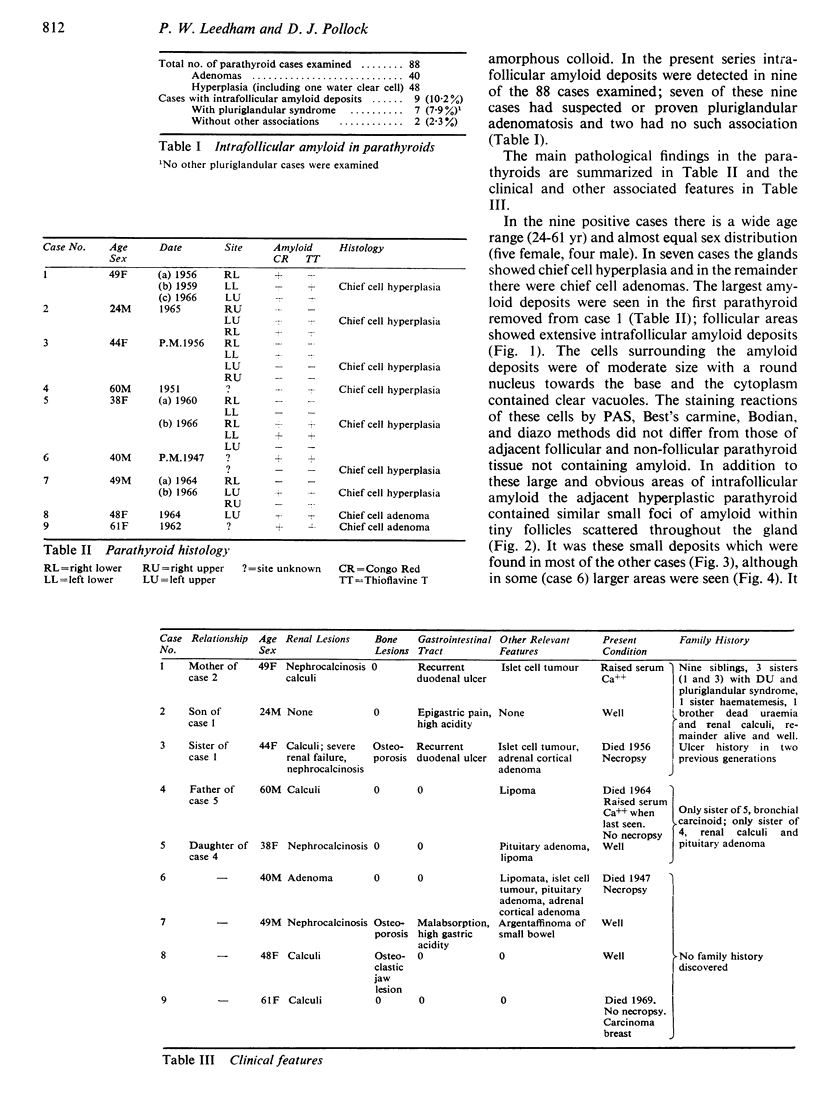
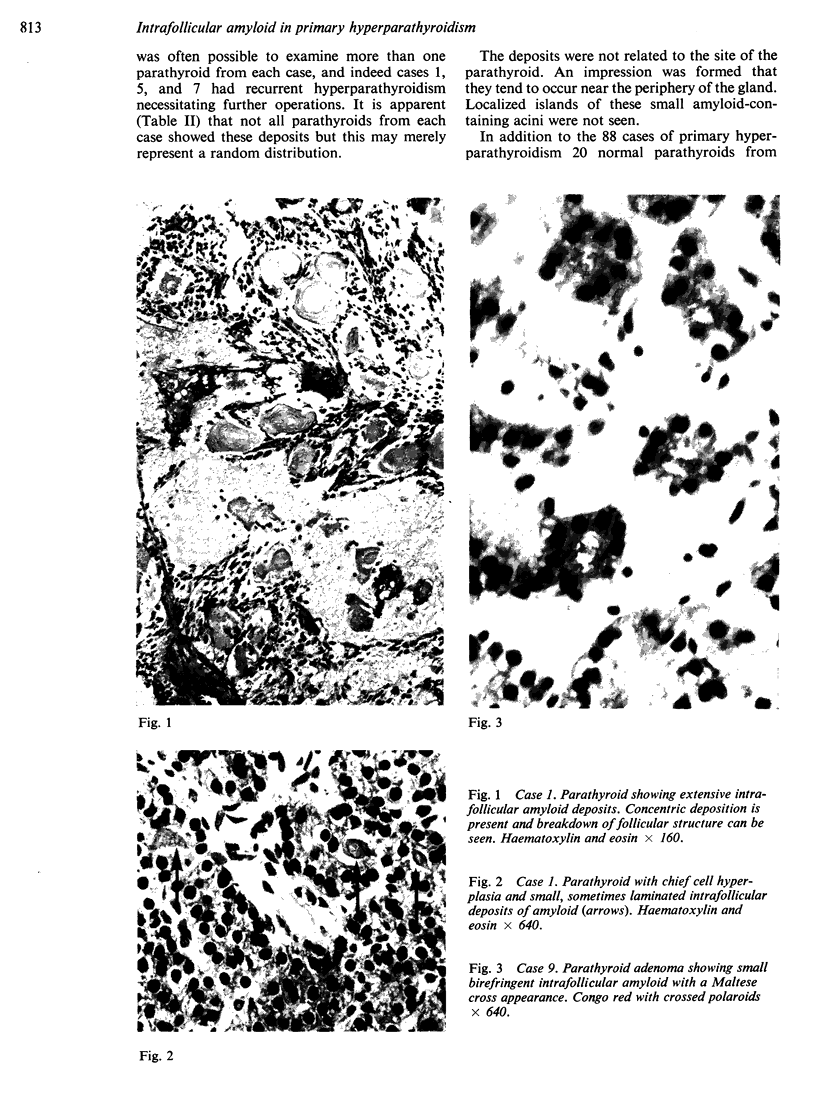
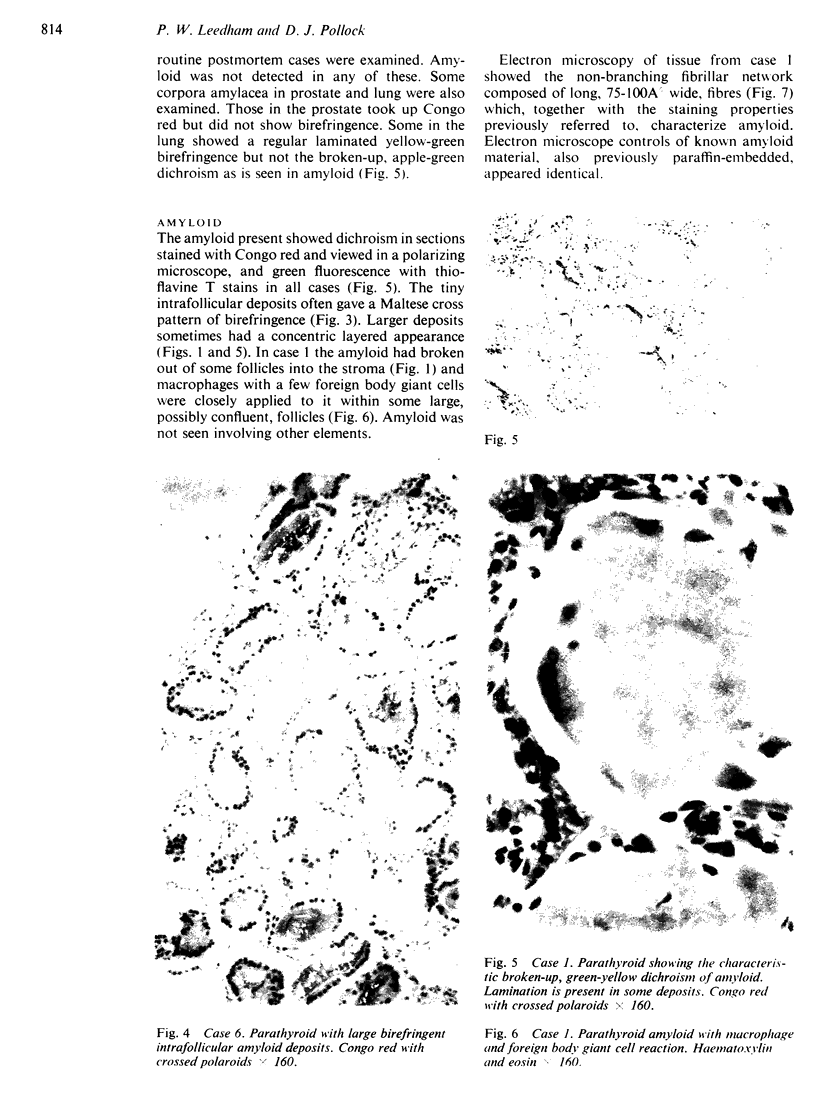
Characteristic intrafollicular amyloid deposits of varying extent were found in nine cases. The case histories of these show that seven had suspected or proven pluriglandular adenomatosis but that the remainder had no such associations. The material studied shows no correlation with systemic primary or secondary amyloidosis.
The significance of these findings is discussed in relation to the pluriglandular syndrome, peptide hormones, medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, and calcitonin secretion. It is suggested that amyloid in this context may be a `marker' for secretion of a peptide closely related to calcitonin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBORES-SAAVEDRA J., ROSE G. G., IBANEZ M. L., RUSSELL W. O., GREY C. E., DMOCHOWSKI L. THE AMYLOID IN SOLID CARCINOMA OF THE THYROID GLAND. STAINING CHARACTERISTICS, TISSUE CULTURE, AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS. Lab Invest. 1964 Jan;13:77–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALLARD H. S., FAME B., HARTSOCK R. J. FAMILIAL MULTIPLE ENDOCRINE ADENOMA-PEPTIC ULCER COMPLEX. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Jul;43:481–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COPE O., KEYNES W. M., ROTH S. I., CASTLEMAN B. Primary chief-cell hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands: a new entity in the surgery of hyperparathyroidism. Ann Surg. 1958 Sep;148(3):375–388. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195809000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COPP D. H., CAMERON E. C., CHENEY B. A., DAVIDSON A. G., HENZE K. G. Evidence for calcitonin--a new hormone from the parathyroid that lowers blood calcium. Endocrinology. 1962 May;70:638–649. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-5-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTLER R. E., REISS E., ACKERMAN L. V. FAMILIAL HYPERPARATHYROIDISM. A KINDRED INVOLVING ELEVEN CASES, WITH A DISCUSSION OF PRIMARY CHIEF-CELL HYPERPLASIA. N Engl J Med. 1964 Apr 23;270:859–865. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196404232701701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S. Amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 1967 Sep 7;277(10):522–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196709072771006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S. Preliminary chemical analysis of partially purified amyloid fibrils. Am J Pharm Sci Support Public Health. 1966 Jan;15(1 Pt 1):66–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J., Raisz L. G. Thyrocalcitonin: inhibitor of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science. 1965 Dec 10;150(3702):1465–1467. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3702.1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galante L., Gudmundsson T. V., Matthews E. W., Tse A., Williams E. D., Woodhouse N. J., MacIntyre I. Thymic and parathyroid origin of calcitonin in man. Lancet. 1968 Sep 7;2(7567):537–538. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Licea A., Hartmann W. H., Yardley J. H. Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Ultrastructural evidence of its origin from the parafollicular cell and its possible relation to carcinoid tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Apr;49(4):512–520. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.4.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAZARD J. B., HAWK W. A., CRILE G., Jr Medullary (solid) carcinoma of the thyroid; a clinicopathologic entity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Jan;19(1):152–161. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-1-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR M. A., FOSTER G. V., MACINTYRE I. FURTHER EVIDENCE FOR CALCITONIN. A RAPID-ACTING HORMONE WHICH LOWERS PLASMA-CALCIUM. Lancet. 1963 Sep 7;2(7306):480–482. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL A. H., SLOPER J. C. Pluriglandular adenomatosis of the pituitary, parathyroid and pancreatic islet cells associated with lipomatosis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1954 Jul;68(1):225–229. doi: 10.1002/path.1700680127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON A. S. Multiple familial parathyroid adenomata. Proc R Soc Med. 1960 Nov;53:903–903. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., Abdel-Bari W. Granules and thyrocalcitonin-like activity in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):523–529. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S. Fine structure of two amyloid-forming medullary carcinomas of thyroid. Cancer. 1968 Mar;21(3):406–425. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196803)21:3<406::aid-cncr2820210310>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTA E. A., YERRY R., SCOTT R. F. Amyloidosis of functioning islet cell adenomas of the pancreas. Am J Pathol. 1962 Nov;41:623–631. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G. The cytochemistry of the thyroid C cells and their relationship to calcitonin. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Apr 19;164(996):478–487. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyrah L. N., Hodgkinson A., Anderson C. K. Primary hyperparathyroidism. Br J Surg. 1966 Apr;53(4):245–316. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800530402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH S. I. Pathology of the parathyroids in hyperparathyroidism. Discussion of recent advances in the anatomy and pathology of the parathyroid glands. Arch Pathol. 1962 Jun;73:495–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens L. E., Bloomer H. A., Castleton K. B. Familial hyperparathyroidism. Arch Surg. 1967 Apr;94(4):524–531. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330100088014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Melvin E. W. Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Studies of thyrocalcitonin in plasma and tumor extracts. N Engl J Med. 1968 Aug 8;279(6):279–283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808082790602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubiana M., Milhaud G., Coutris G., Lacour J., Parmentier C., Bok B. Medullary carcinoma and thyrocalcitonin. Br Med J. 1968 Oct 12;4(5623):87–89. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5623.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERDAHL L. O., WOOLNER L. B., BLACK B. M. Multiple endocrine adenomas; report of 8 cases in which the parathyroids, pituitary and pancreatic islets were involved. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1953 Jan;13(1):20–47. doi: 10.1210/jcem-13-1-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERMER P. ENDOCRINE ADENOMATOSIS AND PEPTIC ULCER IN A LARGE KINDRED. INHERITED MULTIPLE TUMORS AND MOSAIC PLEIOTROPISM IN MAN. Am J Med. 1963 Aug;35:205–212. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLNER L. B., KEATING F. R., Jr, BLACK B. M. Tumors and hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands; a review of the pathological findings in 140 cases of primary hyperparathyroidism. Cancer. 1952 Nov;5(6):1069–1088. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195211)5:6<1069::aid-cncr2820050603>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams E. D., Brown C. L., Doniach I. Pathological and clinical findings in a series of 67 cases of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Mar;19(2):103–113. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams E. D. Histogenesis of medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Mar;19(2):114–118. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.2.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. A., Bowser E. N., Henderson W. J. Mode of hypocalcemic action of glucagon in the rat. Endocrinology. 1969 Sep;85(3):538–541. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-3-537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]