Abstract
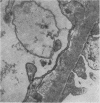
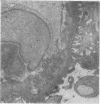
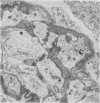
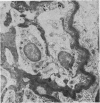
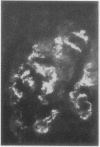
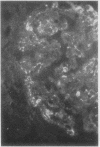
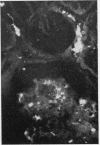
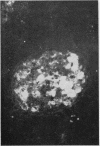
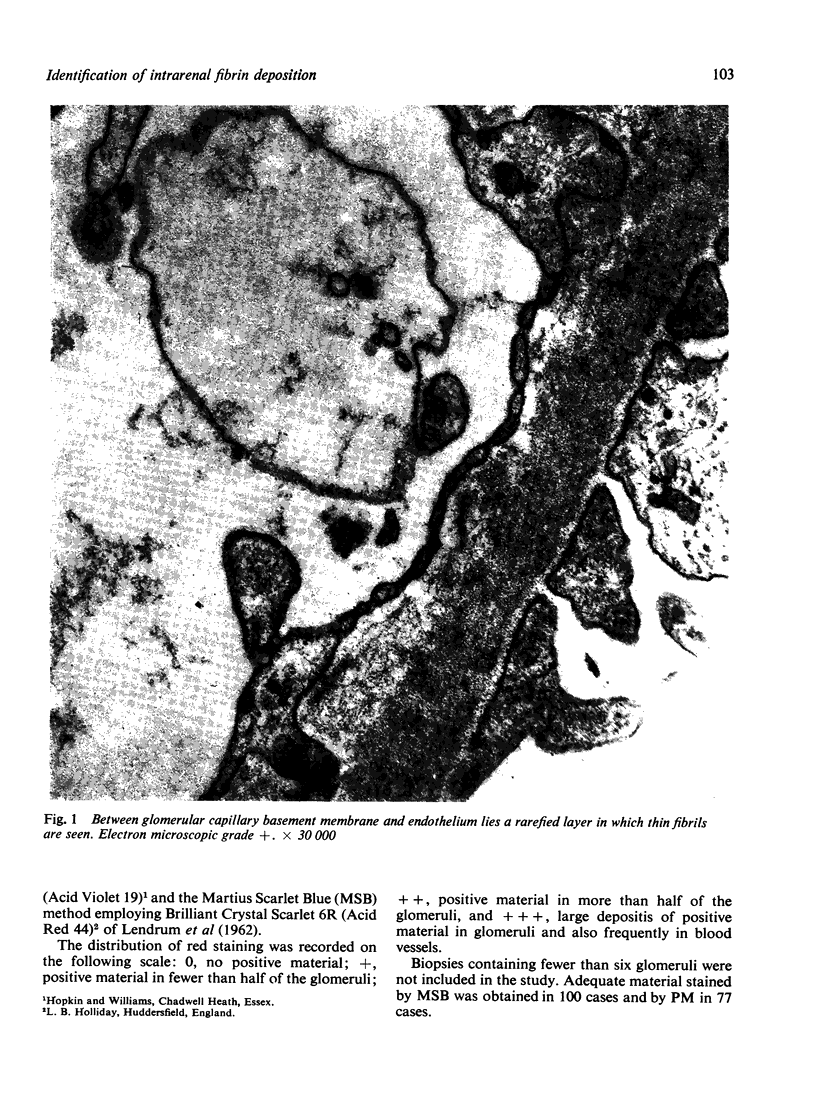
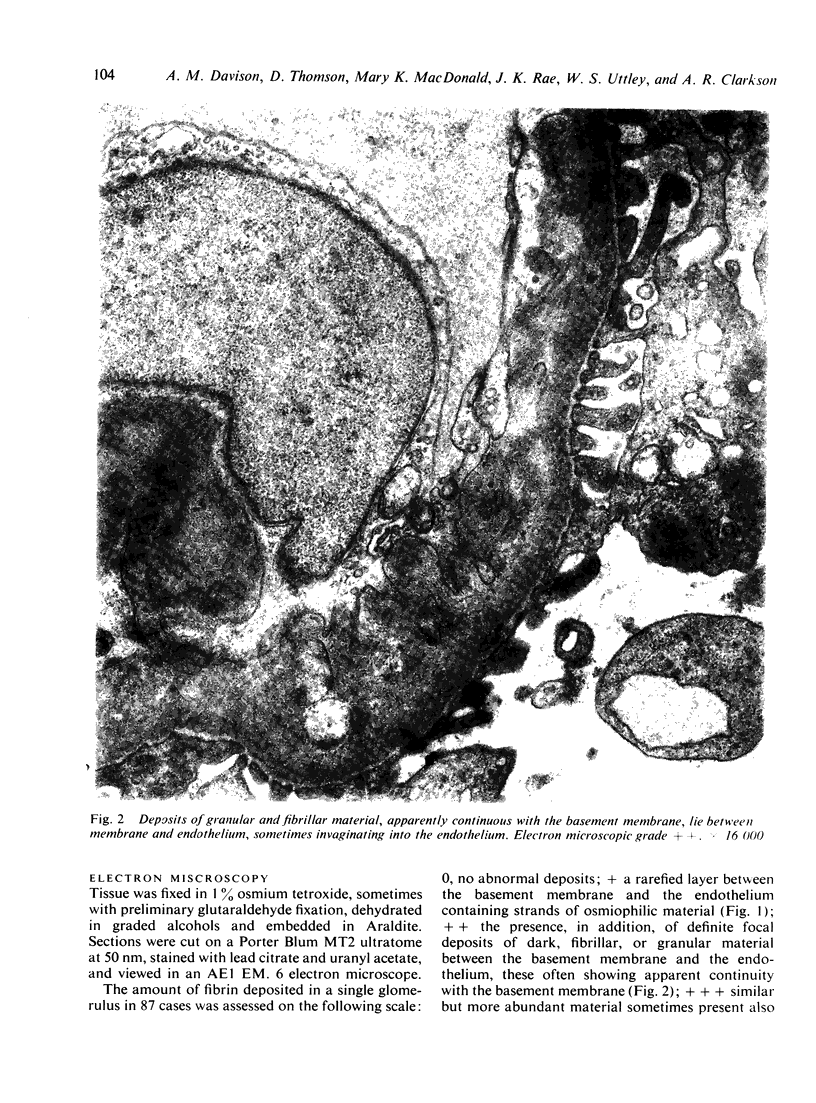
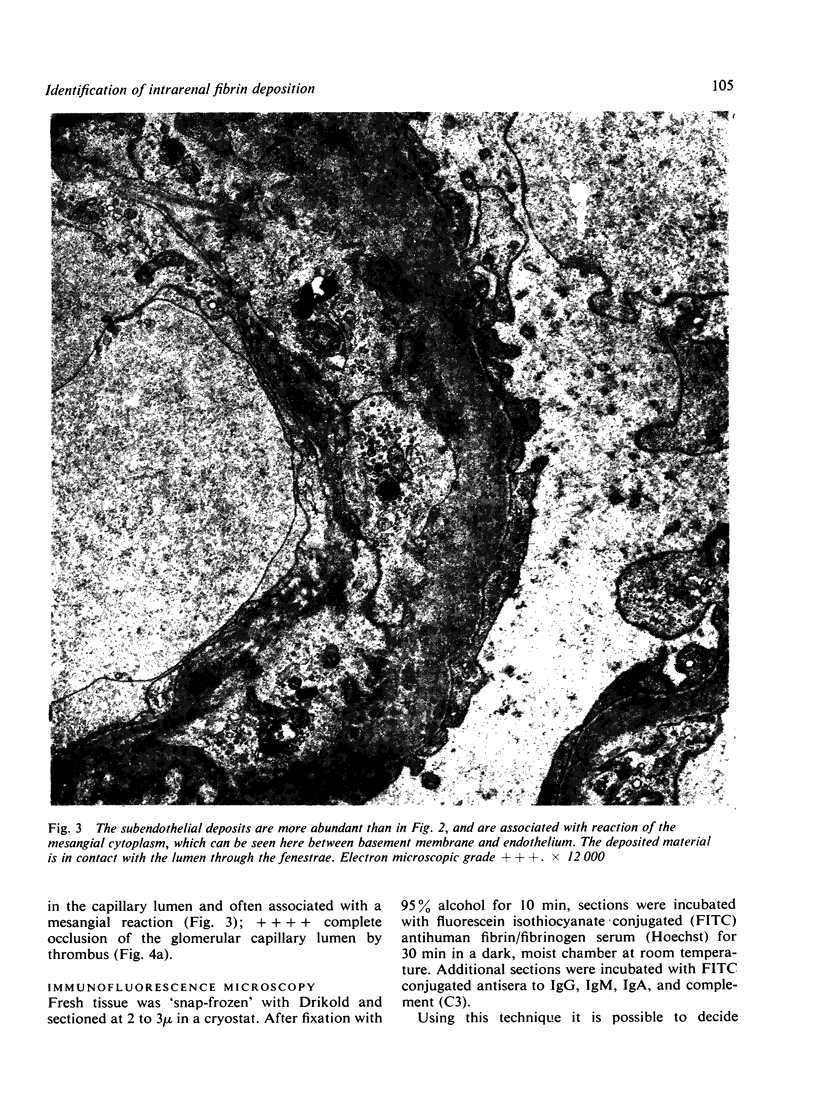
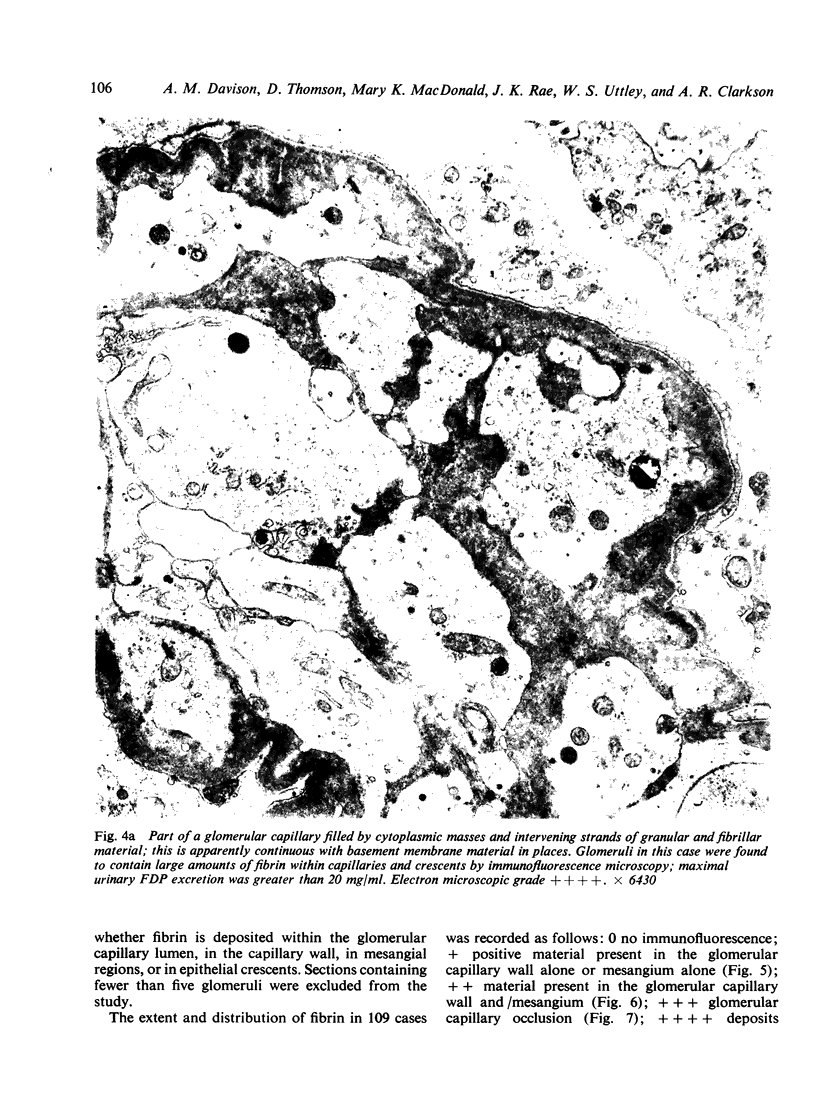
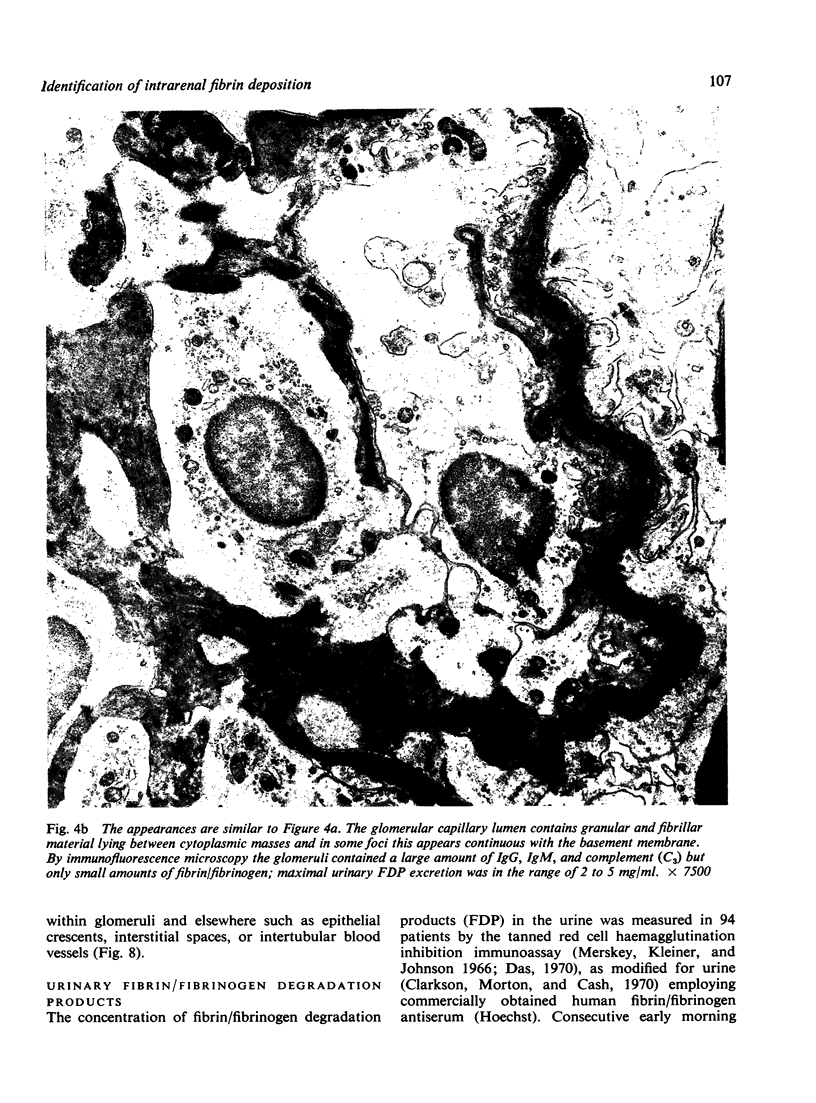
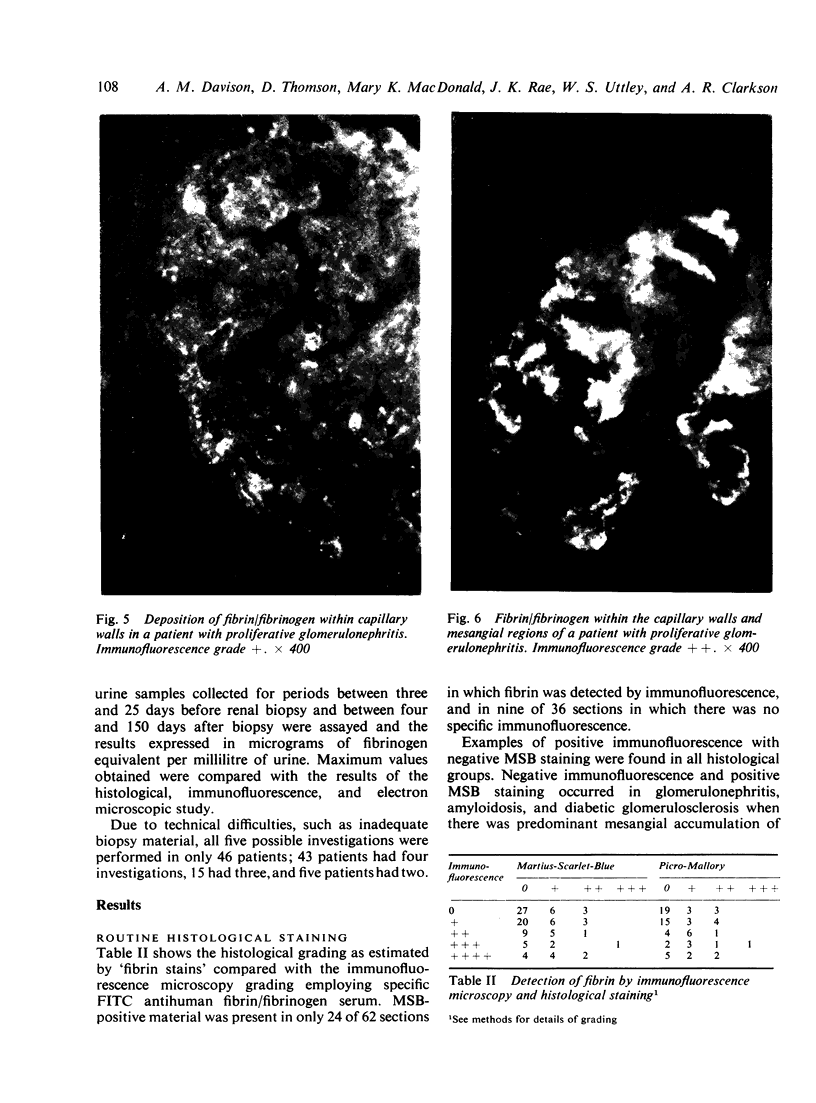
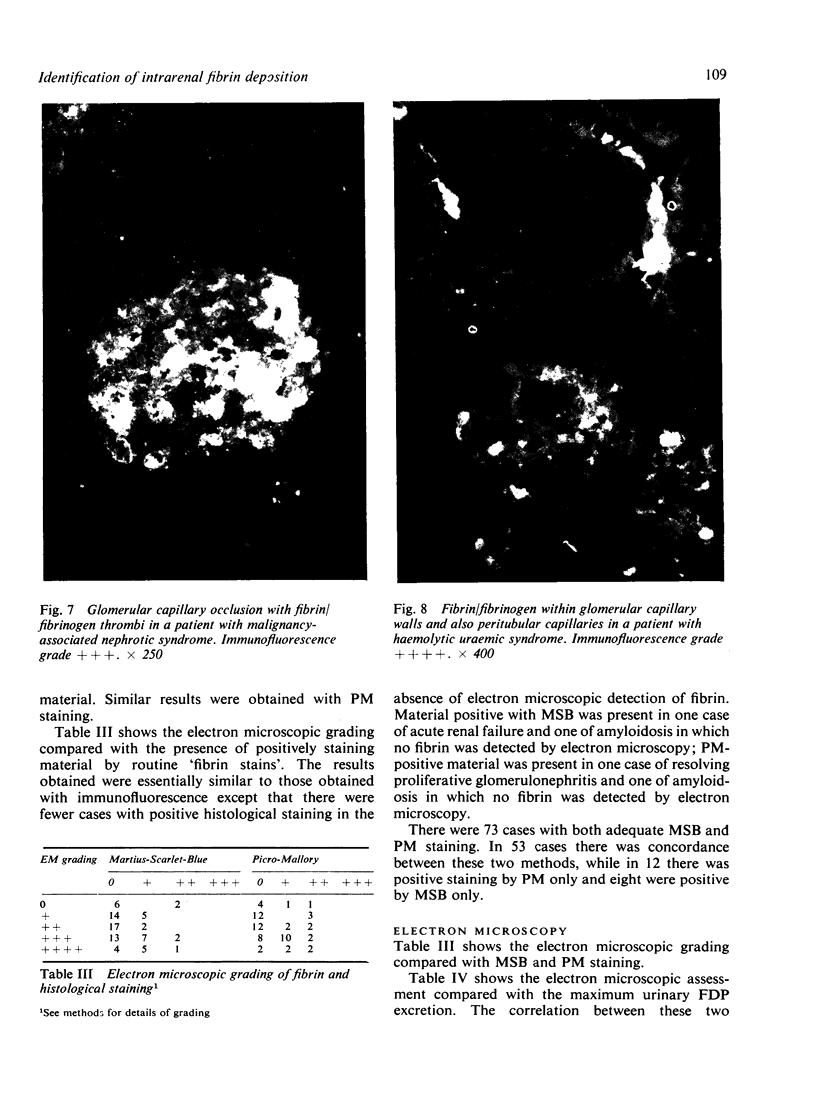
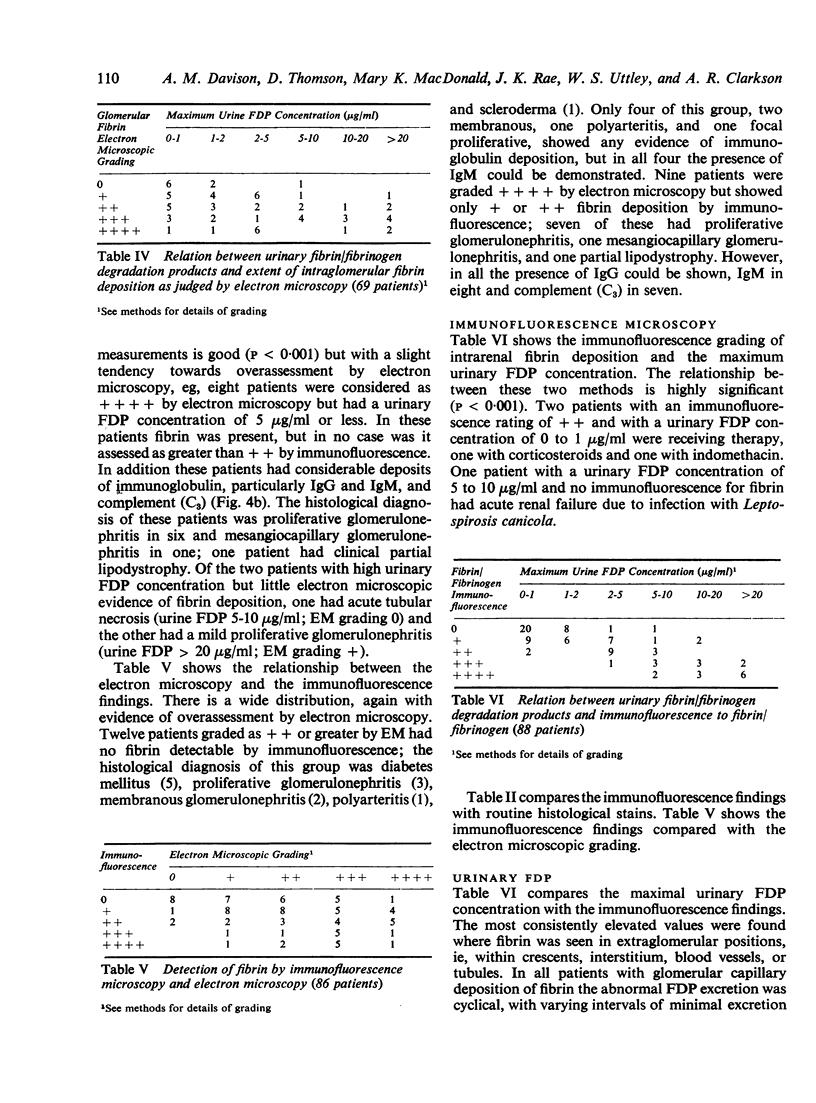
The site and extent of intrarenal fibrin deposition has been examined by routine histological staining, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy in 109 patients with a wide variety of renal diseases. The findings have been correlated with the amount of urinary fibrin/fibrinogen degradation product (FDP) excretion as measured by the tanned red cell haemagglutination inhibition immunoassay. The results show that routine histological stains (Martius Scarlet Blue and Picro Mallory) are unreliable, particularly where there is mesangial accumulation of material or where the amount of fibrin deposited is small and confined to a subendothelial position. Similarly the electron microscope may overassess the degree of fibrin deposition, particularly if this is associated with the deposition of immunoglobulins and complement. There is a close relationship between the site and extent of fibrin, as detected by immunofluorescence, and the maximal urinary FDP excretion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarkson A. R., Morton J. B., Cash J. D. Urinary fibrin-fibrinogen degradation poducts after renal homotransplantation. Lancet. 1970 Dec 12;2(7685):1220–1223. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das P. C. Assay of serum fibrin degradation products by agglutination-inhibition of coated erythrocytes. J Clin Pathol. 1970 May;23(4):299–303. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.4.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENDRUM A. C., FRASER D. S., SLIDDERS W., HENDERSON R. Studies on the character and staining of fibrin. J Clin Pathol. 1962 Sep;15:401–413. doi: 10.1136/jcp.15.5.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey R. T., Vassalli P., Gallo G., Baldwin D. S. An immunofluorescent study of pathogenic mechanisms in glomerular diseases. N Engl J Med. 1966 Mar 31;274(13):695–701. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196603312741301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Kleiner G. J., Johnson A. J. Quantitative estimation of split products of fibrinogen in human serum, relation to diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1966 Jul;28(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., SIMON G., ROUILLER C. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF GLOMERULAR LESIONS RESULTING FROM INTRAVASCULAR FIBRIN FORMATION. Am J Pathol. 1963 Oct;43:579–617. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]