Abstract
An abnormal immune response to environmental agents is generally thought to be responsible for causing chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Based on studies of experimental models and human subjects, there is increasing evidence that the response of the innate immune system is crucial for the development of this type of airway disease. Airway epithelial cells and innate immune cells represent key components of the pathogenesis of chronic airway disease and are emerging targets for new therapies. In this Review, we summarize the innate immune mechanisms by which airway epithelial cells and innate immune cells regulate the development of chronic respiratory diseases. We also explain how these pathways are being targeted in the clinic to treat patients with these diseases.
Chronic lower respiratory diseases most commonly manifest as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and they are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality throughout the world1,2. It is widely believed that an abnormal inflammatory response to environmental agents in genetically susceptible individuals is responsible for causing this type of disease. Environmental agents that may trigger asthma or COPD include allergens, tobacco and wood smoke, and microbial pathogens. Indeed, there has been considerable progress in defining how the immune system of the lungs responds to these agents.
The conventional view has been that the adaptive immune response is crucial for the type of long-term inflammation that is required to drive chronic respiratory disease. This scheme has been particularly well developed for allergic reactions, but has also been extrapolated to explain the immune responses that are induced by non-allergic stimuli3. However, an alternative view that is gaining wider acceptance is that the innate immune system also drives chronic respiratory disease (FIG. 1). This conceptual shift raises the possibility that sentinel epithelial cells and immune cells might be essential components of pathogenesis, and might represent new targets for therapeutic intervention. A particular challenge is to explain how innate immune responses, which are traditionally viewed as being transient in nature, can drive the type of long-term immune activation that is seen in the context of chronic inflammatory disease.
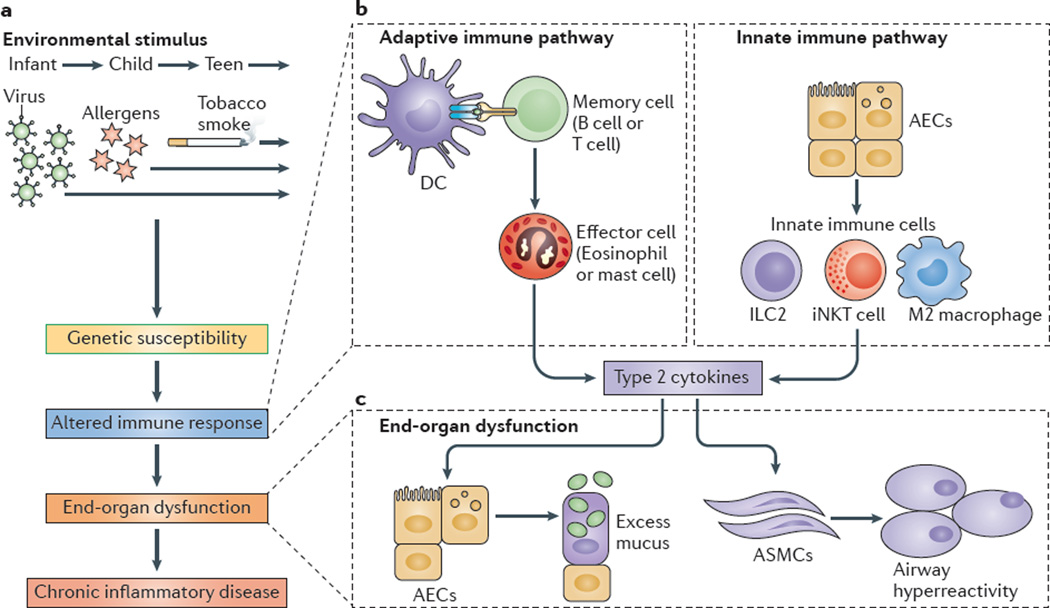
Figure 1. Adaptive and innate immune responses in chronic respiratory disease.
a | Environm ental stimuli — suchas respiratory viruses, allergens and/or tobacco smoke — may act on genetically susceptible individuals to lead to an altered immune response, end-organ dysfunction and chronic inflammatory disease. b | An altered adaptive immune response involves antigen-presenting cells, primarily dendritic cells (DCs), that process and present antigens to memory B cells and T cells that drive the activation of effector immune cells (such as eosinophils and mast cells). Additional T cell subsets that regulate the adaptive immune response include T helper 17 (TH17) cells, TH9 cells and regulatory T cells (not shown). Alternatively, an altered innate immune response can involve airway epithelial cells (AECs) that activate innate immune cells, such as invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, M2 macrophages and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs). c | Effector cells or innate immune cells then produce type 2 cytokines — for example, interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 — that act on end-organ cells, especially AECs, to produce excess mucus, and on airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) to manifest airway hyperreactivity, which, to varying degrees, are both characteristic of patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
In this Review, we summarize the innate immune mechanisms that regulate the development of chronic respiratory diseases, focusing on asthma and COPD. We describe the recent data that have uncovered how airway epithelial cells (AECs) and innate immune cells contribute to the pathogenesis of airway disease, and we then explain how these insights are being translated into therapeutic applications. We highlight the emerging data that suggest a role for respiratory viral infection as a key trigger for the initiation, exacerbation and progression of the immune responses that underlie chronic airway disease. Related to this, we also focus on how long-term reprogramming of AECs may account for how the innate immune system can drive the chronic activation of immune effector cells that mediates lifelong disease. For a more detailed discussion on specific aspects of the innate immune system, we refer the reader to other recent reviews4–9. We conclude with a perspective on how new insights into the normal and abnormal function of the innate immune system can help to explain the biological and pathological outcomes of the response to inhaled stimuli, and can provide the basis for improving treatments for one of the most common and deadly types of chronic disease in the world.
AECs in chronic respiratory disease
One of the first issues in addressing the role of the innate immune response in the development of airway disease is to define the initial responders to inhaled stimuli of disease. Airway dendritic cells (DCs) fulfil this sentinel role in the adaptive immune response, and it has been proposed that defects in DC function in response to allergen exposure or viral infection lead to asthma10. However, in the case of the innate immune response, the AECs of the lower respiratory tract may be the early responders that direct the subsequent immune response. This possibility first became apparent in studies showing that AECs might control immune cell infiltration into the airways during experimental asthma11,12. This concept has since broadened to one in which AECs monitor the external environment by using pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) to sense potentially dangerous inhaled materials13–15. Below, we describe how AEC-expressed PRRs can orchestrate the acute innate immune response to inhaled allergens and infectious viruses. We also introduce the fundamentally new concept that an airway progenitor epithelial cell (APEC) subset of AECs may drive a recurring innate immune response that leads to chronic respiratory disease16.
PRRs in acute responses of AECs
Similarly to the epithelial cells in other barrier tissues, AECs express various PRRs, including Toll-like receptors (TLRs), RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) and NOD-like receptors (NLRs)17. The roles of these various PRR groups have been studied in the AEC response to both allergens and viral infections (FIG. 2), but much of the current scheme for PRR actions (especially in vivo) is extrapolated from research on immune cells (especially antigen-presenting cells) and is likely to be modified with further study.
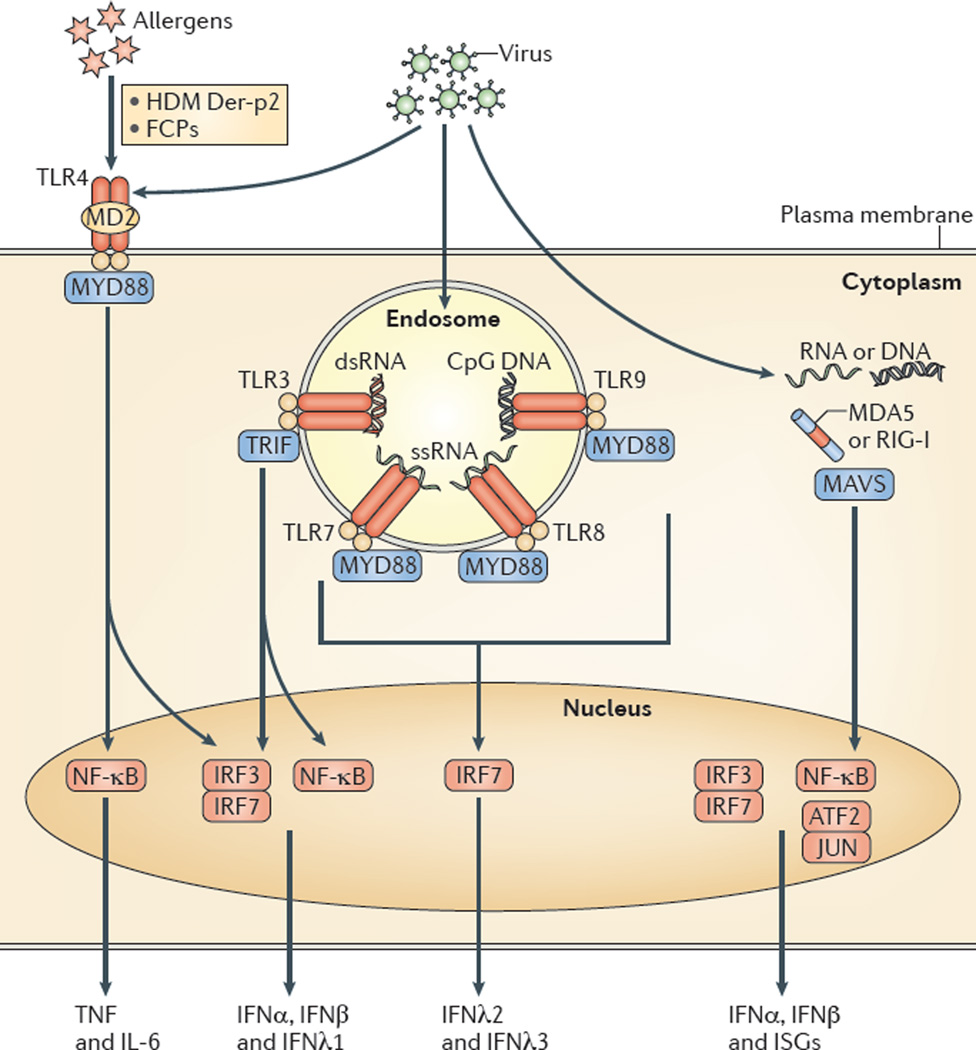
Figure 2. PRR pathways in AECs leading to airway disease.
Allergens such as Der-p2 derived from the house dust mite (HDM) Dermatophagoides farinae and fibrinogen cleavage products (FCPs) that are generated by proteases from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae can act as ligands for the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) complex. The activation of TLR4-dependent signalling leads to an allergic response that is characterized by type 2 cytokine production. Alternatively, viral infection can induce the activation of several additional TLRs (such as TLR3, TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9) in the endosome and can also activate RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) — such as melanoma differ entiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5) and retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) — in the cytosol. In each case, activation leads to downstream signalling with the eventual stimulation of transcription factors in the nucleus and consequent expression of the indicated cytokines and interferon (IFN)-stimulated genes (ISGs). dsRNA, double-stranded RNA; IL, interleukin; IRF, IFN-regulatory factor; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein; MD2, myeloid differentiation factor 2; MYD88, myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; ssRNA, single-stranded RNA; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; TRIF, TIR domain-containing adaptor protein inducing IFNβ.
Previous work on the response to allergens has concentrated on the TLR subset of PRRs. In this case, there is evidence that TLR4 participates in the recognition of aeroallergens and thereby triggers maladaptive allergic reactions. For example, house dust mite antigen from Dermatophagoides farinae and fungal protease from Aspergillus oryzae can activate TLR4 signalling that leads to allergic responses18,19. Furthermore, these signals may be delivered through the activation of TLR4 on AECs. However, it still needs to be determined whether TLR4 signalling occurs primarily in AECs or in TLR4-expressing innate immune cells, such as airway macrophages, in vivo. Moreover, the existing analysis is largely confined to experimental models in cells and mice, so it remains uncertain whether there is similar signalling in humans. It will also be important to define the pathway from TLR4 activation to the development of a type 2 immune response (BOX 1) that is typical of allergy and to determine whether this pathway shares features of type 2 responses that might be triggered by non-allergic stimuli, such as viral infections.
Box 1 | Type 2 immunity.
Type 2 immunity is generally characterized by an immune response that exhibits a distinct gene expression profile that, in particular, includes expression of the genes encoding interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5 and IL-13. Some immune stimuli drive immune responses involving T helper 2 (TH2) cells, and these reactions are therefore known as TH2-type responses. Other types of immune stimuli can cause a type 2 response that involves alternatively activated macrophages; these reactions are described as ‘M2-type responses’. Both of these responses (TH2-type and M2-type) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic airway disease. However, in some cases, studies of patients offer a limited means by which to characterize the cellular source of cytokine production. These studies must therefore primarily rely on gene expression profiles of cytokines and/or cytokine targets to categorize the immune response. In these cases, it is most appropriate to consider these conditions to represent a type 2 immune response, rather than assigning the response to TH2 cells, M2 macrophages or even type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s).
Different subsets of PRRs may participate in the immune responses to the types of viruses that are thought to commonly trigger airway disease — for example, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human rhinovirus (HRV) and influenza A virus20. TLR3, TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 can drive the response to these infections through the recognition of viral nucleic acids, primarily within intracellular endosomes. The activation of these TLRs stimulates the production of type I and type III interferons (IFNs), as well as other cytokines21,22. TLR3, which recognizes double-stranded RNA, seems to be especially relevant to the response of AECs to RSV23, HRV24,25 and influenza A virus26. TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 — which are also activated by virus-associated nucleic acids27–30 — do not seem to have a non-redundant role in the response to viral infection in vivo. The activation of TLR3 (as well as TLR7) generally promotes the acute inflammatory response to respiratory viruses, although TLR3 may attenuate the acute type 2 inflammation that develops after RSV infection in mice31–37. However, the connection between acute TLR activation and the chronic inflammation that is found in human respiratory disease remains uncertain. Nonetheless, there are ongoing efforts to develop TLR agonists, adjuvants and antagonists as therapeutics for asthma and COPD38.
RLRs — such as retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5) — also recognize viral nucleic acids39–41, but interaction of these receptors with their ligands occurs within the cytoplasm. The subsequent PRR signal travels through caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), as well as the adaptor mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein (MAVS; also known as IPS1, VISA and CARDIF), to induce IFN-regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) expression and subsequent IFN production42–44. MDA5 has been reported to sense positive-strand RNA viruses, such as HRV, whereas RIG-I recognizes negative-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, such as RSV and influenza A virus41. In contrast to some PRRs, the loss of MDA5 causes a marked compromise in host defence against mouse parainfluenza virus (also known as Sendai virus)20, suggesting that RLR-dependent recognition may have a non-redundant role in host defence against respiratory viral infection. Thus, RLRs probably have a considerable influence on the severity of infection and thereby also the likelihood of post-viral airway disease.
NLRs have more recently been recognized as a component of the epithelial response to viral infection45,46. For example, the NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome complex47 provides a signal for pro-caspase 1 activation and the subsequent processing and release of certain interleukin-1 (IL-1) family cytokines, including IL-1β and IL-18, that mediate paracrine signalling to neighbouring cells48. Initial work indicated that the NLRP3 inflammasome was an essential component of the response to viral RNA during influenza A virus infection49. However, a comprehensive analysis of NLRs found little evidence of a role for NLRP3 in allergen-challenge mouse models of asthma50, so more work is needed to define the role of NLRs in chronic airway disease.
IFN induction in acute AEC responses
A major consequence of PRR activation that could influence the development of airway disease is the induction of IFN production and IFN-mediated signalling51–54. For the signal transduction process to be effective, type I and type III IFNs must activate Janus kinase (JAK)–signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signalling pathways and thereby induce the expression of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) that control viral replication55,56. The IFN response of AECs seems to be required for adequate defence against at least some types of respiratory viruses in experimental mouse models57. Shornick et al.57 used the mouse parainfluenza virus model but presumably any type of respiratory virus that uses AECs as the primary host cell would fit this paradigm. In that context, the IFN response of AECs has been examined to investigate whether a defective or enhanced response might promote or attenuate chronic respiratory disease, respectively.
With regard to a possible defect in the IFN response being a contributory factor in chronic airway disease, some studies have found that compared with AECs from healthy controls, AECS from patients with asthma showed a deficiency in IFNβ and IFNλ production in response to HRV58–60. These observations led to a limited clinical trial of inhaled IFNβ for viral exacerbations of asthma61. Other studies suggested that abnormal IFN receptor signalling also contributes to the development of asthma62, and genetic analysis has demonstrated that ISGs are associated with susceptibility to asthma63,64. Moreover, control of viral replication and production of IFN may also be defective in AECs from patients with COPD and cystic fibrosis65–67. However, many studies found no defect in IFN-dependent control of HRV or other types of respiratory viruses (notably, RSV and influenza A virus) in AECs from patients with asthma, despite using similar cell culture techniques to the studies that did report a difference68–75. Irrespective of whether there is defective IFN production in airway disease, it may be advantageous to enhance the IFN signalling pathway as a strategy for improving antiviral defence and preventing respiratory disease61. Initial work has shown that genetic strategies in mice and screening approaches in small-molecule drug discovery can enhance IFN signalling and improve control of viral infection76–78. However, further work is required to translate these findings into clinical practice for respiratory diseases.
AEC heterogeneity
Another key aspect of the AEC response that needs to be addressed is the possible heterogeneity within the AEC population. AECs have been shown to be heterogeneous in terms of their expression of virus entry receptors79, and it is likely that subsets of AECs will have distinct roles in activating and orchestrating the innate immune response. The major populations of AECs (namely, ciliated, secretory, mucous and basal AECs) are specialized to carry out specific roles in mucociliary function, and in the response to allergic and infectious agents. As these populations vary in terms of their susceptibility to viral infection74,80, they are also likely to provide different PRR-dependent signals to the immune response. Moreover, other rare cell populations that are present in the airway epithelium — for example, pulmonary neuro-endocrine cells that are sensitive to chemical stimuli — may provide additional immune signals81. Further definition of functional AEC subsets and their roles in the innate immune response will be needed to better understand the role of the sentinel epithelial response under healthy conditions and in the context of disease.
Chronic responses of AECs
A central issue concerning the role of AECs in airway disease is how this cell population might participate in the chronic disease process. In support of an upstream role of AECs in driving inflammatory disease, there are extensive studies showing that AECs respond to allergen challenge or viral infection by producing bioactive lipids and cytokines that control the trafficking, activation and survival of immune cells. However, it has remained difficult to understand how a relatively transient AEC response can account for the persistent activation of innate immune cells that would be required for chronic airway disease.
Recent studies of a post-viral mouse model of chronic airway disease and translation of the findings into humans have provided important new insights into this issue. This post-viral mouse model relies on infection with mouse parainfluenza virus, and a distinct aspect of the model is that the characteristic features of airway disease — namely, airway inflammation, airway hyperreactivity and excessive mucus production — develop after the virus has been cleared from the lungs and persist for at least several months thereafter82. Moreover, the development of airway disease requires the activation of innate immune cells, including invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells and macrophages, that produce the IL-13 that drives airway mucus production and airway hyperreactivity83. Closer analysis of the mechanisms that drive ongoing immune activation in this model showed that IL-33 signalling through the IL-33 receptor subunit IL-1 receptor-like 1 (IL-1RL1) was required for the induction of IL-13 production and subsequent airway disease16. Moreover, increased IL-33 expression was shown to primarily occur in an inducible subset of secretory AECs, as well as in a constitutive set of surfactant protein C-expressing type 2 alveolar epithelial cells that have been shown to have a stem cell function in the lungs84,85. Together, these findings thereby raised the possibility that a renewable cell population was reprogrammed and expanded to drive chronic inflammatory disease.
This possibility was supported by studies showing a similar increase in IL-33 expression in airway tissue from patients with COPD, along with the expression of MUC5AC (which encodes mucin 5AC) and genes associated with IL-13–IL-13R signalling16. IL-33 expression was localized to a subset of airway basal cells and, in this case, IL-33-expressing basal cells were isolated and found to maintain an ex vivo programme characterized by increased progenitor cell capacity and ATP-mediated release of IL-33 (REF. 16). Given the previous work on airway basal cells as progenitor cells86, the findings reinforce the idea that APECs might provide the upstream stimulus for chronic innate immune activation that was missing from previous schemes. Together with previous results that link immune cell production of IL-13 and IL-13 signalling to mucin gene expression82,83,87,88, the latest results suggest a new scheme linking acute infection to chronic lung disease based on long-term epithelial progenitor cells as a renewable source of IL-33 (FIG. 3). Further work will be needed to better define the development of APECs into a specialized IL-33-expressing niche. It will also be important to define the control of IL-33 production, processing and receptor binding in disease to see if it follows the variations in gene expression, protein processing and genetic variation that may be linked to airway disease64,89,90. Similarly, it will be useful to define the control of IL-33 release, and its relation to other epithelial danger signals such as the levels of ATP and ATP-dependent P2Y2 purinergic receptors91–93. It will also be useful to determine whether other AEC-derived cytokines — for example, thymic stromal lympho-poietin (TSLP) — contribute to the airway disease that is triggered by allergic stimuli. In support of this idea, treating patients with asthma with TSLP-specific blocking antibodies attenuated their response to allergen challenge94.
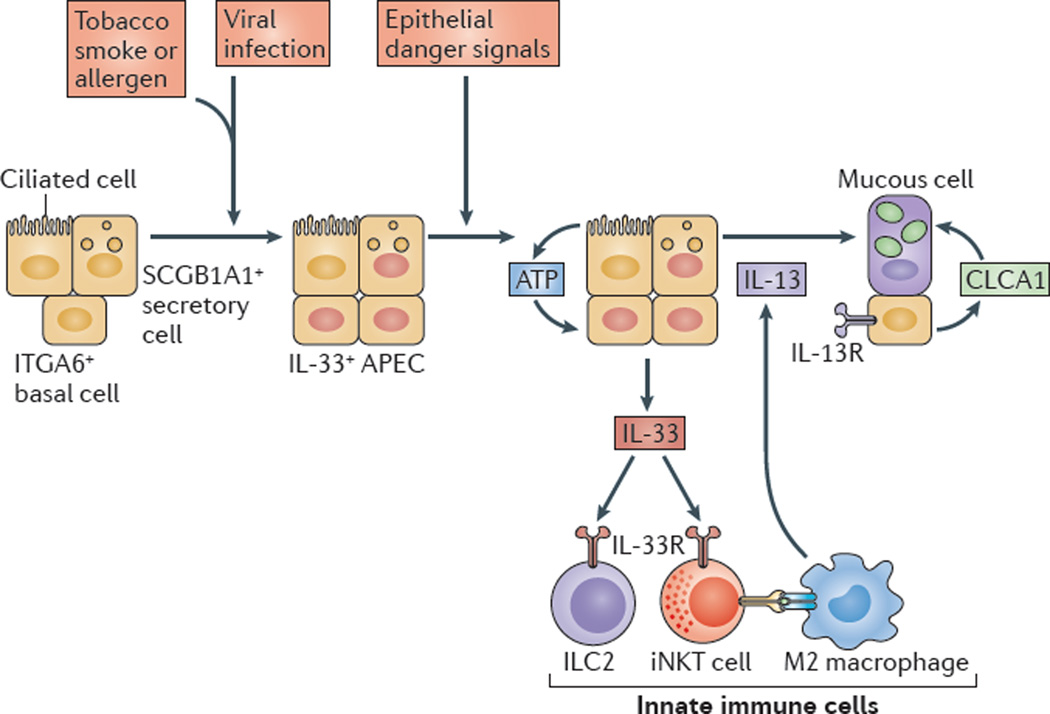
Figure 3. Innate immune responses of AECs drive airway disease.
Respiratory viral infection (which is perhaps enhanced by exposure to allergens or tobacco smoke) leads to an expansion of airway progenitor epithelial cells (APECs), which are a subset of integrin α6 (ITGA6)-expressing basal cells in humans or secretory cells expressing SCGB1A1 (also known as uteroglobin) in mice that are programmed for increased interleukin-33 (IL-33) expression. Subsequent epithelial ‘danger’ signals stimulate ATP-regulated release of IL-33 that acts on innate immune cells in the lungs — for example, type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) and invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells, which can interact with M2-like macrophages to stimulate IL-13 production. IL-13 then induces IL-13 receptor (IL-13R) signalling to stimulate calcium-activated chloride channel regulator 1 (CLCA1) expression and mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 (MAPK13)-dependent signalling, which activate expression of MUC5AC (which encodes mucin 5AC) and, consequently, lead to airway mucous cell activation and mucus formation. Figure modified with permission from the American Society for Clinical Investigation (REF. 16).
This proposal for APECs as key regulators of chronic inflammatory disease may be generalizable to other environmental stimuli. Thus, several groups have identified APEC populations in the mouse and human lungs that expand in response to injury86,95–98. Epithelial repair pathways may remain activated following the initial injury response and may be dysregulated in the subsequent repair phase after these other forms of injury as well. For example, discrete clusters of APECs — identified in the mouse by basal cell markers — were also present for several weeks after influenza A virus infection99, which is another potential stimulus of chronic airway disease100. Together with the work on the post-parainfluenza virus model of chronic airway disease, these studies suggest that viral infection may result in expansion and persistence of reprogrammed APECs that could mediate ongoing susceptibility to airway disease. The specificity required for reprogramming probably depends on the type of respiratory virus, as well as the genetic and epigenetic elements of the host response, and so future studies must address all of these issues. In addition, there is substantial evidence of a role for viral infection in the pathogenesis of both asthma and COPD, but the relative importance of epithelial reprogramming for each of these diseases will need to be defined using carefully characterized patients. Experimental and clinical evidence suggests that the combination of allergen exposure and viral infection might be fundamental to the pathogenesis of asthma, whereas the combination of smoke exposure and viral infection might be fundamental to the pathogenesis of COPD. Additional studies will also need to determine the currently uncertain influence of bacterial infection (primary or secondary to viral infection), as well that of the airway and gut microbiome, on the role of the innate immune system in airway disease.
In addition to initiating the innate immune pathway to airway disease, AECs are also an important target of this pathway. Thus, a chief end product of this pathway is IL-13, which potently stimulates AEC production of inflammatory mucus that can markedly alter the normal mucociliary clearance that is required for mucosal immunity, and that is probably responsible for much of the morbidity and mortality of chronic airway disease101,102. Recent work has directly linked IL-13 to airway mucus production by identifying a signalling pathway involving IL-13R, calcium-activated chloride channel regulator 1 (CLCA1) and mitogen-activated protein kinase 13 (MAPK13) that regulates MUC5AC gene expression in human AECs, and showing that this pathway is activated in COPD87,88 (FIG. 3). The pathway may also be coupled to mucus fluid secretion, as CLCA1 also regulates self-cleavage and consequent calcium-activated chloride channel activity103. New and more potent MAPK13 inhibitors have been designed that can attenuate IL-13-induced mucus production88, and further study of these inhibitors in vivo will also be useful in defining the role of airway mucus in innate immunity for host defence and airway disease.
Innate immune cells
The connection between inhaled stimuli, AECs and downstream innate immune cells is typified by the IL-33–IL-13 immune axis. Accordingly, this section concentrates on the specific types of innate immune cells — namely, NKT cells, macrophages and innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) — that are particularly implicated in this pathway to chronic airway disease. We also provide an update on how granulocytes may be involved in this disease paradigm.
NKT cells
The role of NKT cells in chronic airway disease was initially proposed for allergic asthma when iNKT cells were reported to be necessary for airway hyperreactivity in a mouse model of allergen-induced asthma and were found in increased numbers in patients at baseline104–107. However, subsequent studies indicated that iNKT cells were not necessary for airway inflammation in the mouse model, and that the numbers of iNKT cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid or endobronchial biopsies were not increased at baseline and were increased only upon allergen challenge or in the presence of severe asthma108–111. More recent analysis has continued to search for CD1d–presented microbial and endogenous (self) lipid antigens that might activate iNKT cells, and how T cell receptor (TCR) and cytokine signals might synergize for innate-like activation of iNKT cells112. One report suggests that a fungus-derived glycolipid (asperamide B from Aspergillus fumigatus) — which may be relevant to allergic airway disease — can activate iNKT cells in an IL-33R–dependent fashion113, but the precise mechanism for this effect and whether it is functional in human disease remains uncertain.
NKT cell contributions to chronic airway disease have also been found in the context of viral infection. In the post-parainfluenza virus mouse model of airway disease, long-term airway hyperreactivity and excessive mucus production both depend on the activation of iNKT cells and macrophages to a type 2 pattern of cytokine production and gene expression83. This process seems to depend on contact between the invariant Vα14–Jα18 TCR on lung iNKT cells and the oligomorphic MHC-like protein CD1d on macrophages, as well as amplification through IL-13–IL-13R signalling (FIG. 4). Whether iNKT cells contribute to airway disease in humans is still under study. Initial analysis suggested an increase in the frequency of iNKT cells in patients with very severe COPD that may have been missed in earlier studies of less severe disease83. However, as yet, no studies have assessed the level of iNKT cell activation in patients with asthma or COPD, which is likely to be more informative than counting rare cell populations. Similarly, new approaches for intravital imaging of rare cell populations will allow better definition of NKT cell behaviour in experimental models and human lung samples.
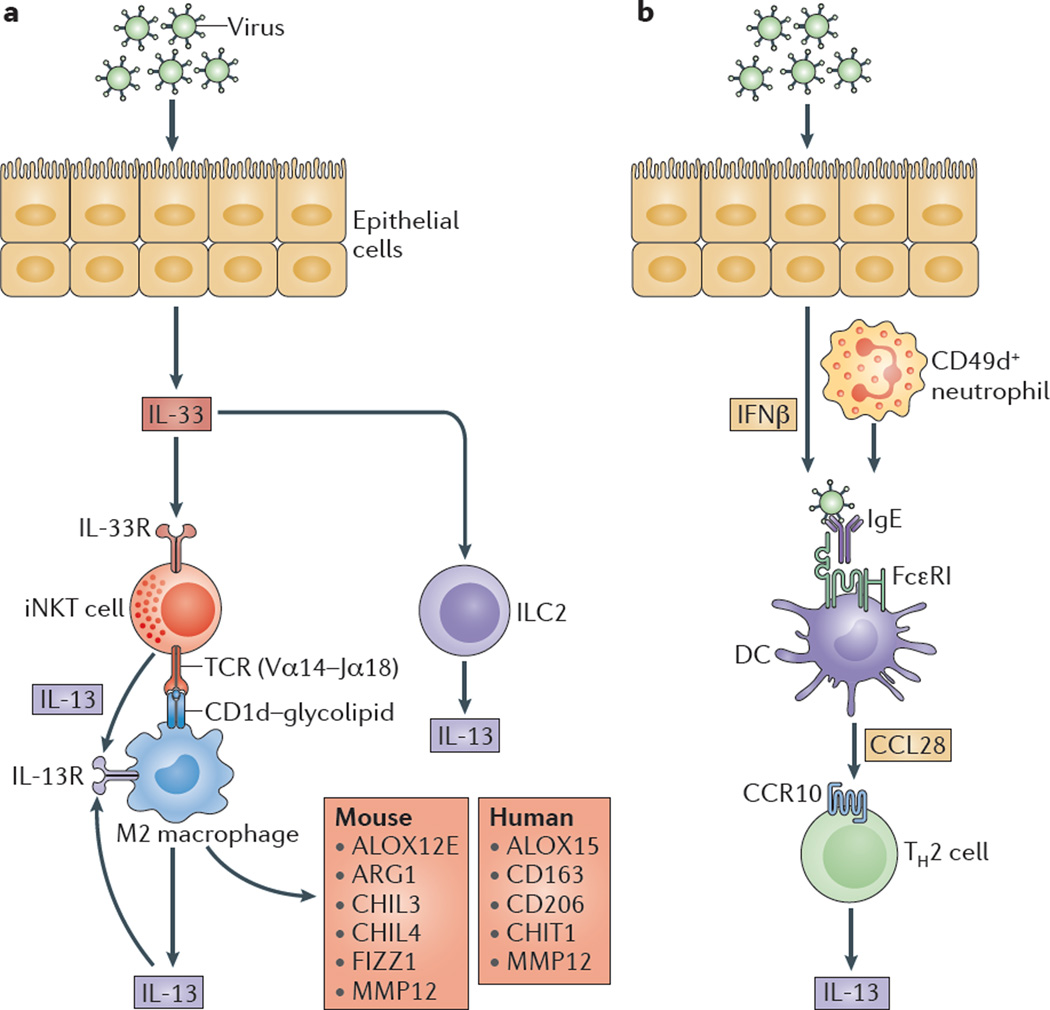
Figure 4. Innate immune cells in post-viral airway disease.
a | Viral infection drives airway epithelial cell (AEC) release of interleukin-33 (IL-33) and the subse quent activation of invariant NKT (iNKT) cells that express an invariant Vα 14-Jα 18 T cell receptor (TCR) that recognizes glycolipids presented on CD1d molecules by lung monocytes and M2 macrophages. These signals lead to increased expression of the IL-13 receptor (IL-13R), and production of IL-13 that facilitates a positive feedback loop to amplify IL-13 production and alternative activation of monocytes and macrophages. Alternatively activated monocytes and macrophages are marked by epidermal arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase (ALOX12E), arginase 1 (ARG1), chitinase-like protein 3 (CHIL3), CHIL4, FIZZ1 (also known as resistin-like molecule-α) and matrix metalloproteinase 12 (MMP12) expression in mice, and by ALOX15, CD163, CD206, chitotriosidase 1 (CHIT1) and MMP12 expression in humans. AEC release of IL-33 may also stimulate type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), as well as effector granulocytes (such as eosinophils, mast cells and basophils; not shown), to produce IL-13. b | Viral infection also stimulates interferon-β (IFNβ)-dependent and CD49d+ neutrophil-dependent upregulation of the high-affinity Fc receptor for IgE (FcεRI) expression on resident lung dendritic cells (DCs). In turn, FcεRI activation by viral antigens and IgE leads to the production of CC-chemokine ligand 28 (CCL28) and the recruitment of CC-chemokine receptor 10 (CCR10)-expressing IL-13-producing T helper 2 (TH2) cells to the lungs.
Macrophages
Similarly to other innate immune cell populations, a role for macrophages in chronic airway disease was initially identified in allergen-challenge models. For example, the house dust mite allergen Der-p2 contains ligands for TLR4 and dectin 2 that can activate macrophages, as well as other cell types, in mouse models of allergy18,114. Allergen-associated proteases may also activate TLR4 in a process that depends on fibrinogen cleavage, with similar consequences for the stimulation of macrophages and other cell types in the airway tissue19. These studies suggest that aero-allergens may rely on molecular mimicry to trigger innate immune responses, but the implications for human airway disease still need to be defined.
As introduced above, analysis of the post-parainfluenza mouse model of airway disease showed that lung macrophages are capable of regulated IL-13 and IL-13R expression, and that they can thereby promote alternative M2-type macrophage activation (in contrast to the classical activation of macrophages that might be expected for a viral stimulus)115. Presumably, this alternative mechanism evolved to mount a long-term innate immune response independently of CD4+ T cells or CD8+ T cells, and thereby enable a response to pathogens that are poorly presented by classical and divergent MHC molecules but that are adequately presented by the more conserved CD1d. However, in at least some genetic backgrounds, this type of innate immune activation can also lead to chronic airway disease. Similarly to the case for NKT cells, the level of M2 macrophage activation that occurs, and its role in asthma and COPD, still needs to be fully defined116. However, analysis of airway tissues from patients with COPD revealed the upregulation of IL-13, the IL-13Rα1 subunit and IL-13-dependent gene products16,88. Other potential markers of M2 macrophage activation — such as chitinase 1, CD163, CD206 (also known as mannose receptor 1) and matrix metalloproteinase 12 (MMP12; also known as macrophage metallo elastase) — also seem to be upregulated in patients with COPD, particularly those in the most severe stages of this disease117–119. Further human studies are required, but it is likely that markers of M2 macrophage differentiation that are more stable and expressed at higher levels than cytokines such as IL-13 will be more reliable to track this type of response.
Innate lymphoid cells
ILCs represent a rare, lineage-negative (LIN−) population of lymphocytes that are classified as ILC1s, ILC2s and ILC3s on the basis of cytokine production patterns that are analogous to those seen for conventional T helper 1 (TH1) cell, TH2 cell and TH17 cell subsets120. ILC development requires the transcription factor PLZF (also known as ZBTB16), which also mediates NKT cell development121, suggesting a link across innate lymphocyte populations. ILC2s also require GATA-binding protein 3 (GATA3), nuclear receptor RORα and IL-7 for their differentiation122–125, and they are most naturally connected to the type 2 immune response that is characteristic of chronic airway disease as they produce high levels of type 2 cytokines in allergen-challenge and post-viral mouse models122–127. ILC2s respond to IL-25 (also known as IL-17E) or IL-33 with high levels of IL-5 and IL-13 production, and LIN− ILCs expressing inducible T cell co-stimulator (ICOS) can be adoptively transferred to reconstitute IL-25- or IL-33-induced airway disease in IL-13-deficient mice128. In addition, adoptive transfer of ILCs into ILC-depleted recombination activating gene 1 (RAG1)-deficient mice129, as well as mice deficient in IL-13, IL-7 or IL-33R130–132, reconstitutes some end points of IL-13-dependent airway disease. However, it is still unclear if ILC2s are sufficient or required for this type of disease. ILC2s represent only a fraction of a percent of the lymphoid population in the lungs, so they require highly selective enrichment before they can be studied. Similarly, better tools to specifically target ILC2s while maintaining an otherwise intact immune system are still needed to further define ILC2 function.
In humans, ILC2s can be identified as LIN− lymphoid cells that express CD127 (also known as IL-7Rα) and CRTH2, and that can produce IL-13 following stimulation with IL-2 in combination with IL-25 and IL-33 in vitro129,133. Human ILCs can be isolated from broncho-alveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood samples but, similarly to in mice, they represent a very small percentage of the total lymphoid cell population and they are not increased in patients with asthma compared with healthy subjects135. In a survey of gut, lung and nasal tissues, ILC2s were most abundant in the polyps from patients with chronic rhinosinusitis, representing 0.1–3.6% of the total CD45+ cells that were recovered from these tissues133. Although ILC2s are rare, they may still occupy a special niche in airway immunity. Lung ILC2s are primarily found along the airways in mice and perhaps in humans134,135, where epithelial cell-activating signals, such as IL-33, could locally drive IL-5 and IL-13 production and a consequent type 2 response. In this case, IL-13 release may be further augmented by the local release of IL-25, IL-33, TSLP, prostaglandin D2 and other factors from neighbouring innate immune cells135. More studies are needed to define the physiological and pathological functions of ILC2s in both the human and mouse airways.
Although ILC2s have been a major focus of ILC research, it is possible that ILC1 and ILC3 populations may also contribute to the pathogenesis of respiratory disease. The ILC1 population can include NK cells, which are probably more abundant in the lungs than ILC2s or ILC3s136. NK cell recruitment and activation is primarily mediated by epithelial cell release of IL-15, which increases in the nasal mucosa within a few days after HRV challenge137. The relevance of this response to post-viral airway disease is uncertain, but NK cell expression of NK group 2 member D (NKG2D; also known as KLRK1) and granzyme B was required for the allergic response to house dust mite extract in mice138. Other work showed that IL-17-producing LIN−THY1.2+ ILC3s were required for airway hyperreactivity in a mouse model of asthma that was associated with obesity139. The ILC3 response was driven by M1 macrophage production of IL-1β, which seems to be distinct from the association of ILC2s and M2 macrophages with preventing obesity in other mouse models140,141. In contrast to the rarity of ILC2 cells, LIN−IL-17A+ ILC3s were detectable in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with asthma but the contribution of ILC3s to airway disease still needs to be defined. A provocative hypothesis is that dietary factors may alter the overall immune response by ILC2s versus ILC3s at mucosal barriers, and therefore influence the type of chronic disease that develops6,142.
Granulocytes
Similarly to other innate immune cell populations, granulocytes are also capable of responding to AEC cytokines to mediate chronic airway disease. For example, eosinophils are typically recruited to the airways during allergic reactions to release cytokines and granular contents with the potential to cause airway dysfunction143. Peripheral blood and sputum eosinophilia is often used as a biomarker of a type 2 immune response, as well as responsiveness to glucocorticoids or type 2 cytokine-blocking treatments in patients with asthma144–146. Similar utility is found in tracking airway eosinophilia in patients with COPD, which probably reflects the overlap between asthma and COPD147,148. Recent studies suggest that eosinophils are activated in response to IL-33 in a manner that depends, at least in part, on a nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-dependent mechanism149, but as yet there is no experimental or clinical evidence of a functional role for eosinophils in post-viral airway disease.
Mast cells are also increased in the airway tissues of patients with asthma and COPD150,151. Signals such as KIT (also known as SCFR) and IL-3 allow mast cells to survive in the tissue for months to contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic airway disease152. In addition to their effector functions in IgE-mediated allergic asthma, mast cells also express surface receptors for IL-33 and TSLP that may be activated leading to the production of type 2 cytokines independent of IgE-mediated responses153. Basophils are phenotypically and functionally related to mast cells, and have also been proposed for a similar effector role in type 2 immune responses in the lungs8. The relative importance of each innate immune effector cell population in responding to upstream epithelial signals after viral infection and allergen challenge still needs to be defined.
Neutrophils have been implicated in the development of asthma and COPD, in addition to their role in pulmonary emphysema154. Indeed, an initial proposal for the sentinel role of epithelial barrier cells was based on observations that AECs could recruit neutrophils to the airways during experimental asthma induced by exposure to ozone, and that neutrophil depletion could attenuate airway inflammation and hyperreactivity under these conditions11,155. Similarly, neutrophils are characteristic of the early response to allergen challenge, as well as viral infection, and seem to be required for a substantial component of the post-viral airway disease that develops shortly after infection is cleared (FIG. 4). In this case, a subset of neutrophils expressing CD49d (also known as integrin α4) is connected to virus-induced type I IFN production and, in turn, to the development of IgE-IgE receptor-dependent activation of resident DCs and a downstream type 2 immune response156,157. These observations may explain the beneficial effect of IgE-specific monoclonal antibody therapy that might occur in viral exacerbations of asthma158.
Neutrophils have also been linked to IL-17-driven pathology in asthma159. For example, overexpression of IL-17 in mouse lung tissue can lead to neutrophil accumulation, and blockade of IL-17 receptor signalling with antibodies or genetic deficiency of IL-17 and IL-17 receptor A (IL-17RA) can decrease airway neutrophil accumulation in mouse models of allergic asthma160,161. However, IL-17 blockade can also cause an increase in eosinophils and type 2 cytokines162. Moreover, the cellular source and target of IL-17 in experimental and clinical asthma seem to be variable163,164. Thus, methods for identifying which patients have IL-17-dependent airway disease remains problematic and may have already led to an ineffective clinical trial in a non-stratified cohort165. Nonetheless, an increase in the frequency of sputum neutrophils may be characteristic of patients with severe asthma and those experiencing exacerbations of COPD166, suggesting that these subgroups might be responsive to this type of treatment if more precision could be used to identify therapeutic strategies.
Therapeutic strategies
Given the role of AECs and innate immune cells in chronic airway disease, it is also of interest to review therapeutic strategies that might influence this immune axis in patients with asthma and COPD. A number of clinical trials have used therapeutics that target type 2 responses driven by the adaptive immune system to treat patients with asthma167–169. However, we now recognize that at least some of these strategies (for example, IL-13 blockade) may also attenuate chronic airway disease through actions on the innate immune system (TABLE 1). Below, we highlight the Phase II and Phase III clinical trials of therapies that modify the innate immune response that leads to chronic airway disease.
Table 1.
Cytokine-directed therapeutics in advanced clinical trials for chronic airway disease*
| Biologic | Mechanism of action | Efficacy in asthma | Efficacy in COPD | Biomarker for treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mepolizumab | IL-5-specific monoclonal antibody | Decreased blood and sputum eosinophilia, and decreased exacerbations |
Trials underway‡ | Blood eosinophilia |
| Reslizumab | IL-5-specific monoclonal antibody | Decreased sputum and blood eosinophilia, and improved airway function |
No trials | Sputum eosinophilia |
| Benralizumab | IL-5Rα-specific monoclonal antibody | Decreased blood, sputum, tissue and bone marrow eosinophilia |
Trials underway‡ | Sputum eosinophilia |
| Lebrikizumab | IL-13-specific monoclonal antibody | Improved airflow | No trials | Serum periostin |
| Tralokinumab | IL-13-specific monoclonal antibody | Improved airflow | No trials | Serum dipeptidyl peptidase 4 and periostin |
| Dupilumab | IL-4Rα-specific monoclonal antibody | Improved airflow, decreased exacerbations and decreased TH2 cell markers |
No trials | Blood and/or sputum eosinophilia |
| AMG-317 | IL-4Rα-specific monoclonal antibody | Decreased exacerbations | No trials | Not reported |
| Pitrakinra | IL-4 mutein targeting IL-4Rα | Reduced early asthma response and decreased exacerbations |
No trials | Atopy, IL4RA polymorphism and blood eosinophilia |
| Brodalumab | IL-17RA-specific monoclonal antibody |
Marginal airflow improvement in patients with asthma who have a highly reversible FEV1 |
No trials | Not reported |
| AMG-157 | TSLP-specific monoclonal antibody | Reduced early and late asthma response, and decreased sputum and blood eosinophilia |
No trials | Atopy |
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; FEV1, forced expiratory volume 1; IL, interleukin; TH2, T helper 2; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
Based on data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials.
Based on information from the ClinicalTrials.gov website and/or the European Union Clinical Trials Register website. Information accurate as of August 2014.
IL-5-targeting approaches
One of the best examples of an approach that was initially designed to target adaptive type 2 responses but is now known to also affect innate type 2 responses has been the development of the IL-5-specific monoclonal antibodies mepolizumab and reslizumab, and the IL-5 receptor-α (IL-5Rα)-specific monoclonal antibody benralizumab. These strategies primarily target eosinophils, which are closely linked to the development of allergic airway disease, as discussed above. Initial studies suggested that mepolizumab may decrease exacerbations in patients with refractory eosinophilic asthma170,171. Subsequently, a multicentre study showed a significant dose-related decrease in the levels of blood and sputum eosinophilia, and a decrease in the number of exacerbations but no significant improvement in symptoms or airflow179. Similarly, a study of reslizumab in patients with severe eosinophilic asthma also showed a decrease in the levels of sputum and blood eosinophils and the number of exacerbations, and a modest improvement in airflow obstruction172. Benralizumab offers the advantage of targeting eosinophils that may already be present in the lung tissues173, and an initial multicentre trial showed that benralizumab decreased the number of eosinophils in the blood, sputum and airway biopsies of patients with eosinophilic asthma without serious adverse events174. It remains difficult to predict whether therapies targeting the IL-5 signalling pathway will be beneficial for patients with asthma, and there are currently no data for a therapeutic effect in COPD. The role of the eosinophil in the innate immune pathway to airway disease is still uncertain experimentally as well, but eosinophils may accumulate in post-viral airway disease and in COPD. Moreover, IL-5 production from innate immune cells (such as NKT cells and ILCs) may also contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic airway disease, and thus serve as additional therapeutic targets and related biomarkers.
IL-17-targeting approaches
Innate immune responses leading to IL-17 production have also been a target for clinical trials in asthma. Brodalumab is a monoclonal antibody that is directed against IL-17RA, which is subunit that is shared among all IL-17 cytokine receptors, including the receptor for IL-25. An initial study of brodalumab in patients with inadequately controlled moderate-to-severe asthma on a stable dose of inhaled corticosteroids showed no significant improvement in airflow obstruction or symptoms165. Subgroup analysis showed only a nominal improvement in asthma control questionnaire scores in patients with high responsiveness to bronchodilator therapy. The relative lack of efficacy may once again highlight the need for patient stratification in these studies and in those of other targeted therapeutics. Ongoing studies of innate immune responses that lead to airway disease independent of a type 2 response will help to identify and monitor patients with IL-17-dependent types of disease.
IL-13-targeting approaches
Both the conventional TH2 cell response in allergic airway disease and the type 2 innate immune response in post-viral airway disease lead to IL-13 production, thereby making IL-13 a therapeutic target for asthma and COPD. Characterization of IL-13-dependent gene expression has also led to the development of biomarkers to guide clinical trials of IL-13-specific monoclonal antibodies, such as lebri-kizumab and tralokinumab145,175. In a trial that was originally designed to examine the efficacy of lebri-kizumab in patients with poorly controlled asthma stratified by type 2 immune status, a post-hoc analysis revealed that this drug was only effective in patients with increased serum levels of periostin145. In a subsequent trial of tralokinumab in patients with severe asthma, subgroup analysis suggested an even greater improvement in airflow measurements in patients with high blood levels of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) compared to those with high blood levels of periostin175,176. Multicentre clinical trials are underway to validate these biomarkers, but the complex nature of the innate immune system and its role in airway disease already strongly suggests that patient stratification will be required for an effective therapeutic approach to chronic airway disease. The initial biomarkers of the patients that respond to IL-13-specific therapy (namely, periostin and DPP4) are associated with activated AECs, suggesting that this cell population is an important therapeutic target, as well as having a role in the pathogenesis of chronic airway disease. Initial studies of a TSLP-specific monoclonal antibody also showed some benefit in patients with allergic asthma94, indicating that further studies of AEC-derived type 2-promoting cytokines (such as IL-33) may also offer a potential therapeutic approach.
Several therapeutics have also been developed to target IL-13 in combination with IL-4 by blocking the IL-4Rα chain (which is encoded by IL4RA) that is common to the IL-4 and IL-13 receptors. For example, dupilumab is an IL-4Rα-specific monoclonal antibody that achieved significant improvements in terms of improved airflow, fewer disease exacerbations and lower expression of several biomarkers of disease — such as CC-chemokine ligand 17 (CCL17), CCL26, fraction of exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) and IgE — particularly in patients with increased eosinophilia180. In addition, pitrakinra is a recombinant IL-4 mutein that blocks ligand binding to IL-4Rα and is capable of decreasing early-phase allergen-provoked bronchoconstriction in patients with allergic asthma177. Pitrakinra may be more effective in patients with polymorphisms in the IL4RA gene178, suggesting that pharmacogenomics may identify subgroups that might benefit from this type of therapy. IL-4 production was not found in the post-viral model of airway disease83, but even if IL-4 is not a feature of the type 2 innate immune response, it may still be advantageous to use combined blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 in patients who are sensitive to both allergen exposure and viral infection as triggers of airway disease.
Conclusion
It has been difficult to understand how an abnormal immune response leads to the development of chronic inflammatory disease in general, and this has also been the case for chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and COPD. However, ongoing progress in in vitro and in vivo models, and in corresponding human studies, suggests that the innate immune response can drive the initiation, exacerbation and progression of this type of disease in response to inhaled allergens, respiratory viruses and, most probably, other environmental stimuli. The innate immune axis seems to begin with the response of sentinel AECs that then transmit activation signals to innate immune cell populations. Recent progress provides two major insights: first, that APECs may be reprogrammed and expanded with specific cytokines (such as IL-33) to provide an ongoing susceptibility to a type 2 immune response; and second, that once activated, AECs may transmit signals to various innate immune cell populations — including NKT cells, macro phages and ILCs — that in turn produce additional cytokines (such as IL-13) to drive airway inflammation, airway hyperreactivity and excessive airway mucus production. These insights have translated into the first encouraging efforts to block these cytokine signalling pathways and treat chronic airway disease.
Future studies of this type of disease need to address ongoing and crucial questions. These include: first, the nature of epithelial PRR activation and signalling, and its relationship to the development of long-term airway disease; second, a more precise definition of the mouse and human APEC niche within the AEC population, and the basis for possible viral reprogramming of these cells; third, the relationship of the pathway from epithelial cell IL-33 to immune cell IL-13 with other environmental risk factors for chronic lung disease, such as tobacco smoking and allergen exposure, as well as underlying genetic risk factors for this type of disease; fourth, the specific nature of the immune cell populations (including NKT cells, macrophages, ILCs and granulocytes) activated in this same pathway; fifth, the molecular basis for translating these epithelial cell and immune cell signals to end-organ dysfunction, including the production and processing of IL-33, as well as the signal transduction pathways and expression of IL-33R and IL-13R; and finally, the role of neutrophils in airway disease and how it relates to the cellular sources and targets for IL-17A and/or IL-17F, and other non-type 2 forms of airway disease.
Nonetheless, ongoing research progress already indicates that environmental stimuli (especially respiratory viral infections in synergy with allergic reactions and smoke exposure) can drive innate immune responses with consequences for acute as well as chronic respiratory disease. A better definition of the role of the AEC and innate immune cell components in chronic airway disease should enable the development of new, effective therapeutics for patients.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank the members of the Holtzman laboratory and their collaborators for generating the research perspective that underlies this review. Research on this topic in the laboratory of M.J.H. was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (U19-AI070489, R01-HL121791, U01-AI095776, P01-HL29594 and P50-HL107183).
Glossary
- Airway epithelial cells (AECs)
The AECs that line the airways include ciliated, mucous, secretory and basal cell types. The AECs also line the alveoli and include type 1 and type 2 epithelial cells.
- Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
These receptors are a key part of the initial activation step for innate immune cells. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns that are associated with microbial pathogens, as well as damage-associated molecular patterns associated with cell damage.
- Airway progenitor epithelial cell (APEC)
These cells are able to proliferate and then differentiate into different airway epithelial cell subsets.
- Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs)
A group of cells that are similar in size and shape to lymphocytes but that do not express typical markers of T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, NKT cells or the granulocyte lineage. A current paradigm divides ILCs into three groups ILC1s that produce interferon-γ; ILC2s that produce interleukin-5 (IL-5) and IL-13; and ILC3s that produce IL-17 and/or IL-22 and are also known as ILC17s and ILC22s.
- M2-type macrophage activation
An immune response that involves the alternative activation of macrophages and monocytes, and is characterized by a gene expression profile that is distinctive of stimulation by interleukin-4 (IL-4) or IL-13. There is still some uncertainty over the best markers for interferon-γ-driven classical activation of M1-type macrophages versus IL-4-and IL-13-driven alternative activation of M2-type macrophages, but the concept remains useful in mouse models of disease and is a starting point for defining macrophage responses in human disease.
- Periostin
A ligand for the αVβ3 and αVβ5 integrins that supports epithelial cell migration and adhesion.
- Mutein
A mutant form of a protein.
Footnotes
Competing interests statement
The authors declare competing interests: see Web version for details.
FURTHER INFORMATION
ClinicalTrials.gov: www.clinicaltrials.gov
European Union Clinical Trials Register: www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu
ALL LINKS ARE ACTIVE IN THE ONLINE PDF
References
- 1.Minino AM, Murphy SL, Xu J, Kochanek KD. National vital statistics reports. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, editors. World Health Organization. Global surveillance, prevention and control of chronic respiratory diseases: a comprehensive approach. WHO; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Holtzman MJ. Asthma as a chronic disease of the innate and adaptive immune systems responding to viruses and allergens. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122:2741–2748. doi: 10.1172/JCI60325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Galli SJ, Tsai M. IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nature Med. 2012;18:693–704. doi: 10.1038/nm.2755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spits H, Cupedo T. Innate lymphoid cells: emerging insights in development, lineage relationships, and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012;30:647–675. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Walker JA, Barlow JL, McKenzie ANJ. Innate lymphoid cells — how did we miss them? Nature Rev. Immunol. 2013;13:75–87. doi: 10.1038/nri3349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Van Dyken SJ, Locksley RM. Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-mediated alternatively activated macrophages: roles in homeostasis and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013;31:317–343. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Siracusa MC, Kim BS, Spergel JM, Artis D. Basophils and allergic inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013;132:789–801. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.07.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Paget C, Trottein F. Role of type 1 natural killer T cells in pulmonary immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 2013;6:1054–1067. doi: 10.1038/mi.2013.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Holt PG, Strickland DH, Hales BJ, Sly PD. Defective respiratory tract immune surveillance in asthma. Chest. 2014;145:370–378. doi: 10.1378/chest.13-1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Holtzman MJ, et al. Importance of airway inflammation for hyperresponsiveness induced by ozone. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1983;127:686–690. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.6.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boushey HA, Holtzman MJ. Experimental airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness: searching for cells and mediators. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985;131:312–313. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Holtzman MJ, et al. Control of epithelial immune-response genes and implications for airway immunity and inflammation. Proc. Assoc. Am. Phys. 1998;110:1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Holgate ST, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in the pathogenesis of asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000;105:193–204. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(00)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lambrecht B, Hammad H. The airway epithelium in asthma. Nature Med. 2012;18:684–692. doi: 10.1038/nm.2737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Byers DE, et al. Long-term IL-33-producing epithelial progenitor cells in chronic obstructive lung disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2013;123:3967–3982. doi: 10.1172/JCI65570. This study identifies the role of an APEC population that releases IL-33 to drive IL-13-dependent airway disease in a post-viral mouse model and in patients with very severe COPD.
- 17.Alexander-Brett J, Holtzman MJ. In: Mucosal Immunology. Cheroutre H, Kelsall B, Lambrecht B, Russell M, editors. Academic Press; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 18. Trompette A, Karp C. Allergenicity resulting from functional mimicry of a Toll-like receptor complex protein. Nature. 2009;457:585–588. doi: 10.1038/nature07548. This study was the first to demonstrate that allergens might use molecular mimicry of TLR ligands to trigger an allergic reaction.
- 19.Millien VO, et al. Cleavage of fibrinogen by proteinases elicits allergic responses through Toll-like receptor 4. Science. 2013;341:792–796. doi: 10.1126/science.1240342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gitlin L, et al. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) is involved in the innate immune response to Paramyxoviridae infection in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e10000734. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barton GM, Kagan JC. A cell biological view of Toll-like receptor function: regulation through compartmentalization. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2009;9:535–542. doi: 10.1038/nri2587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ioannidis I, Ye F, McNally B, Willette M, Flano E. Toll-like receptor expression and induction of type I and type III interferons in primary airway epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2013;87:3261–3270. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01956-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Groskreutz DJ, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus induces TLR3 protein and protein kinase R, leading to increased double-stranded RNA responsiveness in airway epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2006;176:1733–1740. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.3.1733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hewson CA, Jardine A, Edwards MR, Laza-Stanca V, Johnston SL. Toll-like receptor 3 is induced by and mediates antiviral activity against rhinovirus infection of human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2005;79:12273–12279. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.19.12273-12279.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kato A, Favoreto S, Avila PC, Schleimer RP. TLR3- and Th2 cytokine-dependent production of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in human airway epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 2007;179:1080–1087. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.2.1080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Guillot L, et al. Involvement of Toll-like receptor 3 in the immune response of lung epithelial cells to double-stranded RNA and influenza A virus. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:5571–5580. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410592200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Diebold SS, Kaisho T, Hemmi H, Akira S, Reis e Sousa C. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science. 2004;303:1529–1531. doi: 10.1126/science.1093616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Heil F, et al. Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via Toll-like receptor 7 and 8. Science. 2004;303:1526–1529. doi: 10.1126/science.1093620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hemmi H, et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000;408:740–745. doi: 10.1038/35047123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Triantafilou K, et al. Human rhinovirus recognition in non-immune cells is mediated by Toll-like receptors and MDA-5, which trigger a synergetic pro-inflammatory immune response. Virulence. 2011;2:22–29. doi: 10.4161/viru.2.1.13807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang T, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 mediates West Nile virus entry into the brain causing lethal encephalitis. Nature Med. 2004;10:1366–1373. doi: 10.1038/nm1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Le Goffic R, et al. Detrimental contribution of the Toll-like receptor (TLR)3 to influenza A virus-induced acute pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2006;2:e53. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gowen BB, et al. TLR3 deletion limits mortality and disease severity due to Phlebovirus infection. J. Immunol. 2006;177:6301–6307. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.9.6301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hutchens M, et al. TLR3 increases disease morbidity and mortality from vaccinia infection. J. Immunol. 2008;180:483–491. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.1.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rudd BD, et al. Deletion of TLR3 alters the pulmonary immune environment and mucus production during respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Immunol. 2006;176:1937–1942. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.3.1937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wang Q, et al. MDA5 and TLR3 initiate pro-inflammatory signaling pathways leading to rhinovirus-induced airways inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002070. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lukacs NW, et al. Respiratory virus-induced TLR7 activation controls IL-17-associated increased mucus via IL-23 regulation. J. Immunol. 2010;185:2231–2239. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bezemer GFG, et al. Dual role of Toll-like receptors in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012;64:337–358. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yoneyama M, et al. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nature Immunol. 2004;5:730–737. doi: 10.1038/ni1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Gitlin L, et al. Essential role of mda-5 in type I IFN responses to polyriboinosinic:polyribocytidylic acid and encephalomyocarditis picornavirus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:8459–8464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603082103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kato H, et al. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature. 2006;441:101–105. doi: 10.1038/nature04734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Meylan E, et al. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature. 2005;437:1167–1172. doi: 10.1038/nature04193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Chen ZJ. Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-κB and IRF 3. Cell. 2005;122:669–682. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xu LG, et al. VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-β signaling. Mol. Cell. 2005;19:727–740. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ichinohe T, Lee HK, Ogura Y, Flavell RA, Iwasaki A. Inflammasome recognition of influenza virus is essential for adaptive immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 2009;206:79–87. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Thomas PG, et al. The intracellular sensor NLRP3 mediates key innate and healing responses to influenza A virus via the regulation of caspase-1. Immunity. 2009;30:566–575. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM. Inflammasomes and their roles in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012;28:137–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101011-155745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Muruve DA, et al. The inflammasome recognizes cytosolic microbial and host DNA and triggers an innnate immune response. Nature. 2008;452:103–107. doi: 10.1038/nature06664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Allen IC, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome mediates in vivo innate immunity to influenza A virus through recognition of viral RNA. Immunity. 2009;30:556–565. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Allen IC, et al. Analysis of NLRP3 in the development of allergic airway disease in mice. J. Immunol. 2012;188:2884–2893. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schoggins JW, et al. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature. 2011;472:481–485. doi: 10.1038/nature09907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Iversen MB, Paludan SR. Mechanisms of type III interferon expression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010;30:573–578. doi: 10.1089/jir.2010.0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Osterlund PI, Pietila TE, Veckman V, Kotenko SV, Julkunen I. IFN regulatory factor family members differentially regulate the expression of type III IFN (IFN-λ) genes. J. Immunol. 2007;179:3434–3442. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.6.3434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sommereyns C, Paul S, Staeheli P, Michiels T. IFN-lambda (IFN-λ) is expressed in a tissue-dependent fashion and primarily acts on epithelial cells in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000017. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ioannidis I, et al. Plasticity and virus specificity of the airway epithelial cell immune response during respiratory virus infection. J. Virol. 2012;86:5422–5436. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06757-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Okabayashi T, et al. Type-III interferon, not type-I, is the predominant interferon induced by respiratory viruses in nasal epithelial cells. Virus Res. 2011;160:360–366. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shornick LP, et al. Airway epithelial versus immune cell Stat1 function for innate defense against respiratory viral infection. J. Immunol. 2008;180:3319–3328. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.3319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wark PA, et al. Asthmatic bronchial epithelial cells have a deficient innate immune response to infection with rhinovirus. J. Exp. Med. 2005;201:937–947. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Contoli M, et al. Role of deficient type III interferon-λ production in asthma exacerbations. Nature Med. 2006;12:1023–1026. doi: 10.1038/nm1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Edwards MR, et al. Impaired innate interferon induction in severe therapy resistant atopic asthmatic children. Mucosal Immunol. 2013;6:797–806. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Djukanovic R, et al. The effect of inhaled interferon-β on worsening of asthma symptoms caused by viral infections: a randomized trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014;190:145–154. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201312-2235OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cakebread JA, et al. Exogenous IFN-β has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties in primary bronchial epithelial cells from asthmatic subjects exposed to rhinovirus. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011;127:1148–1154. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Harada M, et al. Functional polymorphism in the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene associated with adult asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2007;36:491–496. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0090OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Torgerson DG, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of asthma in ethnically diverse North American populations. Nature Genet. 2011;43:887–893. doi: 10.1038/ng.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zheng S, et al. Impaired innate host defense causes susceptibility to respiratory virus infections in cystic fibrosis. Immunity. 2003;18:619–630. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Schneider D, et al. Increased cytokine resonse of rhinovirus-infected airway epithelial cells in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010;182:332–340. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200911-1673OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Mallia P, et al. Experimental rhinovirus infection as a human model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011;183:734–742. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201006-0833OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bochkov YA, et al. Rhinovirus-induced modulation of gene expression in bronchial epithelial cells from subjects with asthma. Mucosal Immunol. 2010;3:69–80. doi: 10.1038/mi.2009.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Lopez-Souza N, et al. In vitro susceptibility to rhinovirus infection is greater for bronchial than for nasal airway epithelial cells in human subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009;123:1384–1390. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.DeMore JP, et al. Similar colds in subjects with allergic asthma and nonatopic subjects after inoculation with rhinovirus-16. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009;124:245–252. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Message SD, et al. Rhinovirus-induced lower respiratory illness is increased in asthma and related to virus load and Th1/2 cytokine and IL-10 production. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:13562–13567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804181105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Sampath D, Castro M, Look DC, Holtzman MJ. Constitutive activation of an epithelial signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat1) pathway in asthma. J. Clin. Invest. 1999;103:1353–1361. doi: 10.1172/JCI6130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bullens DM, et al. Type III IFN-λ mRNA expression in sputum of adult and school-aged asthmatics. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2008;38:1459–1467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Jakiela B, et al. Th2-type cytokine induced mucous metaplasia decreases susceptibility of human bronchial epithelium to rhinovirus infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2014;51:229–241. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0395OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Patel DA, et al. Interferon response and respiratory virus control are preserved in bronchial epithelial cells in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014 doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Zhang Y, et al. Modification of the Stat1 SH2 domain broadly improves interferon efficacy in proportion to p300/CREB-binding protein coactivator recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:34306–34315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503263200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Patel DA, Patel AC, Nolan WC, Zhang Y, Holtzman MJ. High throughput screening for small molecule enhancers of the interferon signaling pathway to drive next-generation antiviral drug discovery. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e36594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Patel DA, et al. High-throughput screening normalized to biological response: application to antiviral drug discovery. J. Biomol. Screen. 2014;19:119–130. doi: 10.1177/1087057113496848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ibricevic A, et al. Influenza virus receptor specificity and cell tropism in mouse and human airway epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2006;80:7469–7480. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02677-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lachowicz-Scroggins ME, Boushey HA, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH. Interleukin-13 induced mucous metaplasia increases susceptibility of human airway epithelium to rhinovirus infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2010;43:652–661. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0244OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Gu B, et al. Volatile sensing functions for pulmonary neuroendocrine cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2014;50:637–646. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2013-0199OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Walter MJ, Morton JD, Kajiwara N, Agapov E, Holtzman MJ. Viral induction of a chronic asthma phenotype and genetic segregation from the acute response. J. Clin. Invest. 2002;110:165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI14345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Kim EY, et al. Persistent activation of an innate immune response translates respiratory viral infection into chronic inflammatory lung disease. Nature Med. 2008;14:633–640. doi: 10.1038/nm1770. This study identifies the iNKT cell–macrophage axis that drives chronic lung disease and is characterized by IL-13 production, alternative M2 macrophage activation, airway hyperreactivity and excessive mucus production.
- 84.Rawlins EL, et al. The role of Scgb1a1+ Clara cells in the long-term maintenance and repair of lung airway, but not alveolar, epithelium. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4:525–534. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2009.04.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Evans CM, et al. Mucin is produced by Clara cells in the proximal airway of antigen-challenged mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004;31:382–394. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2004-0060OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Rock JR, et al. Basal cells as stem cells of the mouse trachea and human airway epithelium. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:12771–12775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906850106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Patel AC, et al. Genetic segregation of airway disease traits despite redundancy of chloride channel calcium-activated family members. Physiol. Genom. 2006;25:502–513. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00321.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Alevy Y, et al. IL-13-induced airway mucus production is attenuated by MAPK13 inhibition. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122:4555–4568. doi: 10.1172/JCI64896. This study identifies the IL-13–CLCA1–MAPK13 signalling pathway to excessive mucus production in AECs and provides structure-based drug design for MAPK13 inhibitors that attenuate inflammatory mucus production.
- 89.Lefrancais E, et al. IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109:1673–1678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1115884109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Moffat MF, et al. A large-scale, consortium-based genomewide association study of asthma. N. Eng. J. Med. 2010;363:1211–1221. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0906312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Kouzaki H, Iijima K, Kobayashi T, O’Grady SM, Kita H. The danger signal, extracellular ATP, is a sensor for an airborne allergen and triggers IL-33 release and innate Th2-type responses. J. Immunol. 2011;186:4375–4387. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Willart MA, et al. Interleukin-1α controls allergic sensitization to inhaled house dust mite via the epithelial release of GM-CSF and IL-33. J. Exp. Med. 2012;209:1505–1517. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lommatzsch M, et al. Extracellular adenosine triphosphate and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010;181:928–934. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200910-1506OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Gauvreau GM, et al. Effects of an anti-TSLP antibody on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;370:2102–2110. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Teisanu RM, et al. Functional analysis of two distinct bronchiolar progenitors during lung injury and repair. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2011;44:794–803. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0098OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Chapman HA, et al. Integrin α6β4 identifies an adult distal lung epithelial population with regenerative potential in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2011;121:2855–2862. doi: 10.1172/JCI57673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.McQualter JL, Yuen K, Williams B, Bertoncello I. Evidence of an epithelial stem/ progenitor cell hierarchy in the adult mouse lung. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:1414–1419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909207107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kajstura J, et al. Evidence for human lung stem cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;364:1795–1806. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1101324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 99. Kumar PA, et al. Distal airway stem cells yield alveoli in vitro and during lung regeneration following H1N1 influenza infection. Cell. 2011;147:525–538. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.001. This study demonstrates that a lung progenitor cell population expands in the setting of influenza virus infection and might participate in alveolar repair.
- 100.Papadopoulos NG, et al. Viruses and bacteria in acute asthma exacerbations-a GA2LEN-DARE systematic review. Allergy. 2011;66:458–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kuyper LM, et al. Characterization of airway plugging in fatal asthma. Am. J. Med. 2003;115:6–11. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(03)00241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Hogg JC, et al. The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Eng. J. Med. 2004;350:2645–2653. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Yurtsever Z, et al. Self-cleavage of human CLCA1 by a novel internal metalloprotease domain controls calcium-activated chloride channel activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012;287:42138–42149. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Lisbonne M, et al. Cutting edge: invariant Vα14 NKT cells are required for allergen-induced airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in an experimental asthma model. J. Immunol. 2003;171:1637–1641. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.4.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Akbari O, et al. Essential role of NKT cells producing IL-4 and IL-13 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyper-reactivity. Nature Med. 2003;9:582–588. doi: 10.1038/nm851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Sen Y, et al. Vα24-invariant NKT cells from patients with allergic asthma express CCR9 at high frequency and induce Th2 bias of CD3+ T cells upon CD226 engagement. J. Immunol. 2005;175:4914–4926. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.8.4914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Akbari O, et al. CD4+ invariant T-cell-receptor+ natural killer T cells in bronchial asthma. New. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:1117–1129. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa053614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Das J, et al. Natural killer T cells and CD8+ T cells are dispensable for T cell-dependent allergic airway inflammation. Nature Med. 2006;12:1345–1346. doi: 10.1038/nm1206-1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Vijayanand P, et al. Invariant natural killer T cells in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. New. Engl. J. Med. 2007;356:1410–1422. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa064691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Reynolds C, et al. Natural killer T cells in bronchial biopsies from human allergen challenge model of allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009;124:860–862. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Matangkasombut P, et al. Natural killer T cells in the lungs of patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009;123:1181–1185. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Brennan PJ, Brigl M, Brenner MB. Invariant natural killer T cells: an innate activation scheme linked to diverse effector functions. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2013;13:101–117. doi: 10.1038/nri3369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Albacker LA, et al. Invariant natural killer T cells recognize a fungal glycophingolipid that can induce airway hyperreactivity. Nature Med. 2013;19:1297–1304. doi: 10.1038/nm.3321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Parsons MW, et al. Dectin-2 regulates the effector phase of house dust mite-elicited pulmonary inflammation independently from its role in sensitization. J. Immunol. 2014;192:1361–1371. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Gordon S, Martinez FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32:593–604. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Byers DE, Holtzman MJ. Alternatively activated macrophages as cause or effect in asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2010;43:1–4. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0407ED. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Agapov E, et al. Macrophage chitinase 1 stratifies chronic obstructive lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2009;41:379–384. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0122RC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Kaku Y, et al. Overexpression of CD163, CD204, and CD206 on alveolar macrophages in the lungs of patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e87400. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Chaudhuri R, et al. Sputum matrix metallo-proteinase-12 in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma: relationship to disease severity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;129:655–663. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.12.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Spits H, et al. Innate lymphoid cells — a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2013;13:145–149. doi: 10.1038/nri3365. This consensus statement provides an approach to categorize ILC1s, ILC2s and ILC3s on the basis of their patterns of receptor expression, cytokine production and pathways for development from a common progenitor cell.
- 121.Constantinides MG, McDonald BD, Verhoef PA, Bendelac A. A committed precursor to innate lymphoid cells. Nature. 2014;508:397–401. doi: 10.1038/nature13047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Neill DR, et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature. 2010;464:1367–1370. doi: 10.1038/nature08900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Saenz SA, et al. IL-25 elicits a multi-potent progenitor cell population that promotes Th2 cytokine responses. Nature. 2010;464:1362–1366. doi: 10.1038/nature08901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Moro K, et al. Innate production of TH2 cytokines by adipose tissue-associated c-Kit+ Sca-1+ lymphoid cells. Nature. 2010;463:540–544. doi: 10.1038/nature08636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Price AE, et al. Systemically dispersed innate IL-13-expressing cells in type 2 immunity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:11489–11494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003988107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Fallon PG, et al. Identification of an interleukin (IL)-25-dependent cell population that provides IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 at the onset of helminth explusion. J. Exp. Med. 2006;203:1105–1116. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Byers DE, et al. A distinct population of non-B, non-T (NBNT) cells express high levels of IL-13 during acute and chronic airway disease after viral infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009;179:A4293. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Barlow JL, et al. IL-33 is more potent than IL-25 in provoking IL-13-producing nuocytes (type 2 innate lymphoid cells) and airway contraction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013;132:933–941. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Monticelli LA, et al. Innate lymphoid cells promote lung-tissue homeostasis after infection with influenza virus. Nature Immunol. 2011;12:1045–1054. doi: 10.1031/ni.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Barlow JL, et al. Innate IL-13-producing nuocytes arise during allergic lung inflammation and contribute to airways hyperreactivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;129:191–198. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.09.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Bartemes KR, et al. IL-33-responsive lineage CD25+ CD44hi lymphoid cells mediate innate type 2 immunity and allergic inflammation in the lungs. J. Immunol. 2012;188:1503–1513. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Chang Y, et al. Innate lymphoid cells mediate influenza-induced airway hyper-reactivity independently of adaptive immunity. Nature Immunol. 2011;12:631–638. doi: 10.1038/ni.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Mjosberg JM, et al. Human IL-25- and IL-33-responsive type 2 innate lymphoid cells are defined by expression of CRTH2 and CD161. Nature Immunol. 2011;12:1055–1162. doi: 10.1038/ni.2104. This study represents one of the initial efforts to examine ILC2s across several mucosal barriers in humans.
- 134.Nussbaum JC, et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells control eosinophil homeostasis. Nature. 2013;502:245–248. doi: 10.1038/nature12526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Barnig C, et al. Lipoxin A4 regulates natural killer cell and type 2 innate lymphoid cell activation in asthma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013;5:174ra26. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Gregoire C, et al. The trafficking of natural killer cells. Immunol. Rev. 2007;220:169–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Jayaraman A, et al. IL-15 complexes induce NK- and T-cell responses independent of type I IFN signaling during rhinovirus infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2014;7:1151–1164. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Fahradi N, et al. Natural killer cell NKG2D and granzyme B are critical for allergic pulmonary inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013;133:827–835. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.09.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Kim HY, et al. Interleukin-17-producing innate lymphoid cells and the NLRP3 inflammasome facilitate obesity-associated airway hyperreactivity. Nature Med. 2014;20:54–61. doi: 10.1038/nm.3423. This study suggests that IL-17-producing ILC3s may contribute to the pathogenesis of obesity-related asthma.
- 140.Molofsky AB, et al. Innate lymphoid type 2 cells sustain visceral adipose tissue eosinophils and alternatively activated macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2013;210:535–549. doi: 10.1084/jem.20121964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Hams E, Locksley RM, McKenzie AN, Fallon PG. IL-25 elicits innate lymphoid type 2 and type II NKT cells that regulate obesity in mice. J. Immunol. 2013;191:5349–5353. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Spencer SP, et al. Adaptation of innate lymphoid cells to a micronutrient deficiency promotes type 2 barrier immunity. Science. 2014;343:432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1247606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Neves JS, Weller PF. Functional extracellular eosinophil granules: novel implications in eosinophil immunobiology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009;21:694–699. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2009.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Woodruff PG, et al. Genome-wide profiling identifies epithelial cell genes associated with asthma and with treatment response to corticosteroids. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:15858–15863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707413104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Corren J, et al. Lebrikizumab treatment in adults with asthma. New. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:1088–1098. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1106469. This study identifies serum periostin as a useful biomarker for patients who might respond to treatment with the IL-13-specific monoclonal antibody lebrikizumab.
- 146.Corren J. Anti-interleukin-5 antibody therapy in asthma and allergies. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011;11:565–570. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32834c3d30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Kitaguchi Y, Komatsu Y, Fujimoto K, Hanaoka M, Kubo K. Sputum eosinophilia can predict responsiveness to inhaled corticosteroid treatment in patients with overlap syndrome of COPD and asthma. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2012;7:283–289. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S30651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Bafadhel M, et al. Blood eosinophils to direct corticosteroid treatment of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012;186:48–55. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201108-1553OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Bouffi C, et al. IL-33 markedly activates murine eosinophils by an NF-KB-dependent mechanism differentially dependent upon an IL-4-driven autoinflammatory loop. J. Immunol. 2013;191:4317–4325. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Balzar S, et al. Mast cell phenotype, location, and activation in severe asthma. Data from the Severe Asthma Research Program. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011;183:299–309. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201002-0295OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Ballarin A, et al. Mast cell infiltration discriminates between histopathological phenotypes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012;186:233–239. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201112-2142OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Kawakami T, Galli SJ. Regulation of mast-cell and basophil function and survival by IgE. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2002;2:773–786. doi: 10.1038/nri914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Ho LH, et al. IL-33 induces IL-13 production by mouse mast cells independently of IgE-FceRI signals. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007;82:1481–1490. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0407200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Hoenderdos K, Condliffe A. The neutrophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir Cell. Mol. Biol. 2013;48:531–539. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0492TR. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.O’Byrne PM, et al. Neutrophil depletion inhibits airway hyperresponsiveness induced by ozone exposure. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1984;130:214–219. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Grayson MH, et al. Induction of high-affinity IgE receptor on lung dendritic cells during viral infection leads to mucous cell metaplasia. J. Exp. Med. 2007;204:2759–2769. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Cheung DS, et al. Cutting Edge: CD49d+ neutrophils induce FceRI expression on lung dendritic cells in a mouse model of postviral asthma. J. Immunol. 2010;185:4983–4987. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Busse WW, et al. Randomized trial of omalizumab (anti-IgE) for asthma in inner-city children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;364:1005–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1009705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Manni ML, Robinson KR, Alcorn JF. A tale of two cytokines: IL-17 and IL-22 in asthma and infection. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2014;8:25–42. doi: 10.1586/17476348.2014.854167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Nakae S, Suto H, Berry GJ, Galli SJ. Mast cell-derived TNF can promote Th17 cell-dependent neutrophil recruitment in ovalbumin-challenged OTII mice. Blood. 2007;109:3640–3648. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-09-046128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Hellings PW, et al. Interleukin-17 orchestrates the granulocyte influx into airways after allergen inhalation in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2003;28:42–50. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.4832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Alcorn JF, Crowe CR, Kolls JK. TH17 cells in asthma and COPD. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010;72:495–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Lajole S, et al. Complement-mediated regulation of the IL-17A axis is a central genetic determinant of the severity of experimental allergic asthma. Nature Immunol. 2010;11:928–935. doi: 10.1038/ni.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Kudo M, et al. IL-17A produced by αβ T cells drives airway hyper-responsiveness in mice and enhances mouse and human airway smooth muscle contraction. Nature Med. 2013;18:547–554. doi: 10.1038/nm.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Busse WW, et al. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab, a human anti-IL-17 receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013;188:1294–1302. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201212-2318OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Moore WC, et al. Sputum neutrophil counts are associated with more severe asthma phenotypes using cluster analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014;133:1557–1563. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Pelaia G, Vatrella A, Maselli R. The potential of biologics for the treatment of asthma. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 2012;11:958–972. doi: 10.1038/nrd3792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Holgate ST. Trials and tribulations in identifying new biologic treatments for asthma. Trends Immunol. 2012;33:238–246. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Busse WW, Ring J, Huss-Marp J, Kahn JE. A review of treatment with mepolizumab, an anti-IL-5 mAb, in hypereosinophilic syndromes and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;125:803–813. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Nair P, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;360:985–993. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Haldar P, et al. Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;360:973–984. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Castro M, et al. Relizumab for poorly controlled, eosinophilic asthma: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011;184:1125–1132. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201103-0396OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Kolbeck R, et al. MEDI-563, a humanized anti-IL-5 receptor α mAb with enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity function. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;125:1344–1353. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Laviolette M, et al. Effect of benralizumab on airway eosinophils in asthmatic patients with sputum eosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013;132:1086–1096. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.05.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Brightling CE, She D, Ranade K, Piper E. Efficacy and safety of tralokinumab, an anti-IL-13 monoclonal antibody, in a Phase 2b study of uncontrolled severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014;189:A6770. [Google Scholar]
- 176.Piper E, et al. A phase II placebo-controlled study of tralokinumab in moderate-to-severe asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2013;41:330–338. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00223411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Wenzel S, Wilbraham D, Fuller R, Getz EB, Longphre M. Effect of an interleukin-4 variant on late phase asthmatic response to allergen challenge in asthmatic patients: results of two phase 2a studies. Lancet. 2007;370:1396–1398. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61600-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Slager RE, et al. IL-4-receptor polymorphisms predict reduction in asthma exacerbations during response to an anti-IL-4 receptor a antagonist. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;130:516–522. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.03.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Pavord ID, et al. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): a multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380:651–659. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60988-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Wenzel S, et al. Dupilumab in persistent asthma with elevated eosinophil levels. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;368:2455–2466. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1304048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]