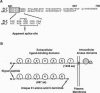
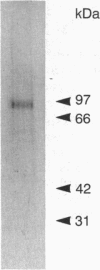
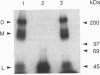
Abstract
Vascular endothelial cell growth factor, a mitogen selective for vascular endothelial cells in vitro that promotes angiogenesis in vivo, functions through distinct membrane-spanning tyrosine kinase receptors. The cDNA encoding a soluble truncated form of one such receptor, fms-like tyrosine kinase receptor, has been cloned from a human vascular endothelial cell library. The mRNA coding region distinctive to this cDNA has been confirmed to be present in vascular endothelial cells. Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase receptor mRNA, generated by alternative splicing of the same pre-mRNA used to produce the full-length membrane-spanning receptor, encodes the six N-terminal immunoglobulin-like extracellular ligand-binding domains but does not encode the last such domain, transmembrane-spanning region, and intracellular tyrosine kinase domains. The recombinant soluble human receptor binds vascular endothelial cell growth factor with high affinity and inhibits its mitogenic activity for vascular endothelial cells; thus this soluble receptor could act as an efficient specific antagonist of vascular endothelial cell growth factor in vivo.
Full text
PDF

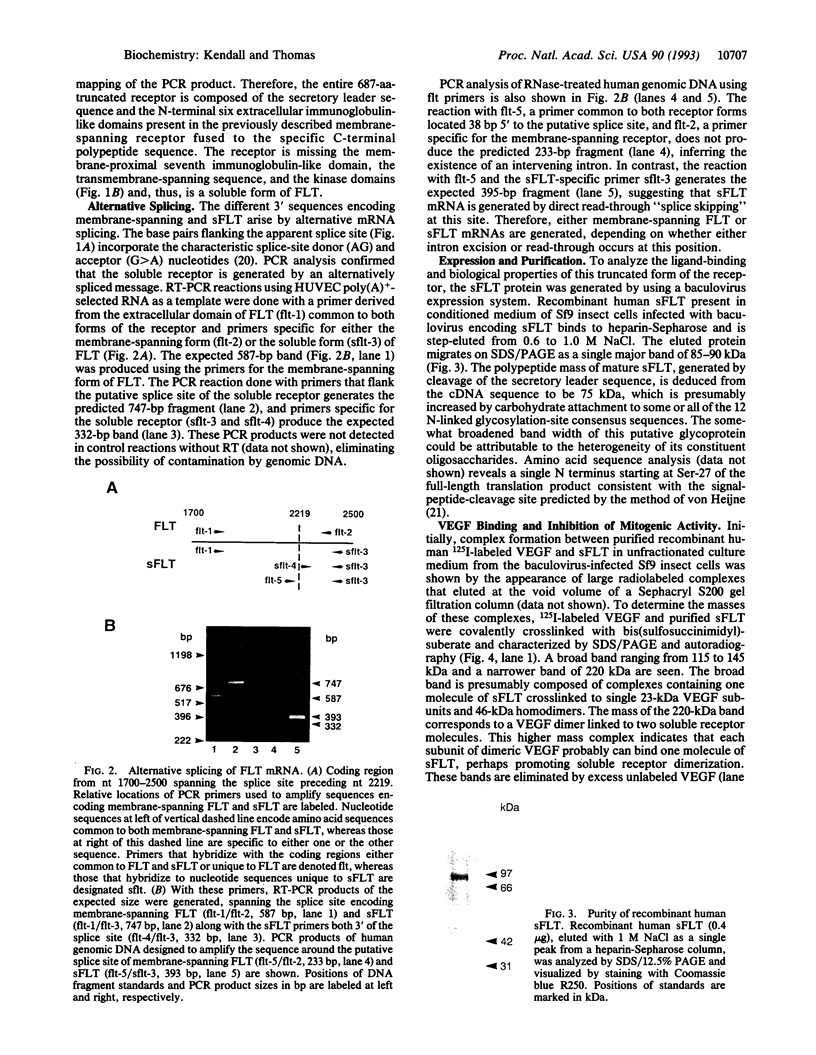


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conn G., Bayne M. L., Soderman D. D., Kwok P. W., Sullivan K. A., Palisi T. M., Hope D. A., Thomas K. A. Amino acid and cDNA sequences of a vascular endothelial cell mitogen that is homologous to platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2628–2632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T. Vascular permeability factor: a unique regulator of blood vessel function. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Nov;47(3):219–223. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan D. S., Pazin M. J., Fretto L. J., Williams L. T. A functional soluble extracellular region of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) beta-receptor antagonizes PDGF-stimulated responses. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):413–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara N., Houck K., Jakeman L., Leung D. W. Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):18–32. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-1-18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Friend D., Ziegler S. F., Jerzy R., Falk B. A., Gimpel S., Cosman D., Dower S. K., March C. J., Namen A. E. Cloning of the human and murine interleukin-7 receptors: demonstration of a soluble form and homology to a new receptor superfamily. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90342-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak E. R., Leek R., Klenk N., LeJeune S., Smith K., Stuart N., Greenall M., Stepniewska K., Harris A. L. Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet. 1992 Nov 7;340(8828):1120–1124. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93150-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lu J., Chen H., Werner S., Williams L. T. The human fibroblast growth factor receptor genes: a common structural arrangement underlies the mechanisms for generating receptor forms that differ in their third immunoglobulin domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4627–4634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck P. J., Hauser S. D., Krivi G., Sanzo K., Warren T., Feder J., Connolly D. T. Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1309–1312. doi: 10.1126/science.2479987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. D., Haldeman B. A., Grant F. J., Murray M. J., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Cooper J. A., Kazlauskas A. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates PDGF receptor subunit dimerization and intersubunit trans-phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8987–8992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Li B., Winer J., Armanini M., Gillett N., Phillips H. S., Ferrara N. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):841–844. doi: 10.1038/362841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassman C. R., Milcarek C. Regulated expression of the mouse gamma 2b Ig H chain gene is influenced by polyA site order and strength. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2578–2585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maglione D., Guerriero V., Viglietto G., Delli-Bovi P., Persico M. G. Isolation of a human placenta cDNA coding for a protein related to the vascular permeability factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9267–9271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley B., Beckmann M. P., March C. J., Idzerda R. L., Gimpel S. D., VandenBos T., Friend D., Alpert A., Anderson D., Jackson J. The murine interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):335–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myoken Y., Kayada Y., Okamoto T., Kan M., Sato G. H., Sato J. D. Vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) produced by A-431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells and identification of VEGF membrane binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5819–5823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petch L. A., Harris J., Raymond V. W., Blasband A., Lee D. C., Earp H. S. A truncated, secreted form of the epidermal growth factor receptor is encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript in normal rat tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2973–2982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate K. H., Breier G., Weich H. A., Risau W. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):845–848. doi: 10.1038/359845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Liu L., Quan S. G., Joe V., DiPersio J. F., Golde D. W. Identification and molecular cloning of a soluble human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8203–8207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. A., Megyesi J. F., Henzel W. J., Ferrara N., Folkman J. Conditioned medium from mouse sarcoma 180 cells contains vascular endothelial growth factor. Growth Factors. 1990;4(1):53–59. doi: 10.3109/08977199009011010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R. A., Hart C. E., Phillips P. E., Forstrom J. W., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two different subunits associate to create isoform-specific platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8771–8778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Yamaguchi S., Yamane A., Ikeda T., Tojo A., Matsushime H., Sato M. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a novel human receptor-type tyrosine kinase gene (flt) closely related to the fms family. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shweiki D., Itin A., Soffer D., Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):843–845. doi: 10.1038/359843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Wignall J. M., Din W. S., Farrah T., Upton C., McFadden G., Goodwin R. G. T2 open reading frame from the Shope fibroma virus encodes a soluble form of the TNF receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90929-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Hruby D. E., Maliszewski C. R., Pickup D. J., Sims J. E., Buller R. M., VanSlyke J. Vaccinia and cowpox viruses encode a novel secreted interleukin-1-binding protein. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90273-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Tuypens T., Plaetinck G., Verhee A., Fiers W., Devos R. Molecular basis of the membrane-anchored and two soluble isoforms of the human interleukin 5 receptor alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teicher B. A., Sotomayor E. A., Huang Z. D. Antiangiogenic agents potentiate cytotoxic cancer therapies against primary and metastatic disease. Cancer Res. 1992 Dec 1;52(23):6702–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terman B. I., Carrion M. E., Kovacs E., Rasmussen B. A., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B. Identification of a new endothelial cell growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1677–1683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terman B. I., Dougher-Vermazen M., Carrion M. E., Dimitrov D., Armellino D. C., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P. Identification of the KDR tyrosine kinase as a receptor for vascular endothelial cell growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Sep 30;187(3):1579–1586. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischer E., Gospodarowicz D., Mitchell R., Silva M., Schilling J., Lau K., Crisp T., Fiddes J. C., Abraham J. A. Vascular endothelial growth factor: a new member of the platelet-derived growth factor gene family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1198–1206. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92729-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton C., Mossman K., McFadden G. Encoding of a homolog of the IFN-gamma receptor by myxoma virus. Science. 1992 Nov 20;258(5086):1369–1372. doi: 10.1126/science.1455233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries C., Escobedo J. A., Ueno H., Houck K., Ferrara N., Williams L. T. The fms-like tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):989–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1312256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]