Abstract
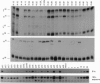
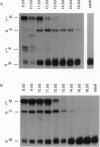
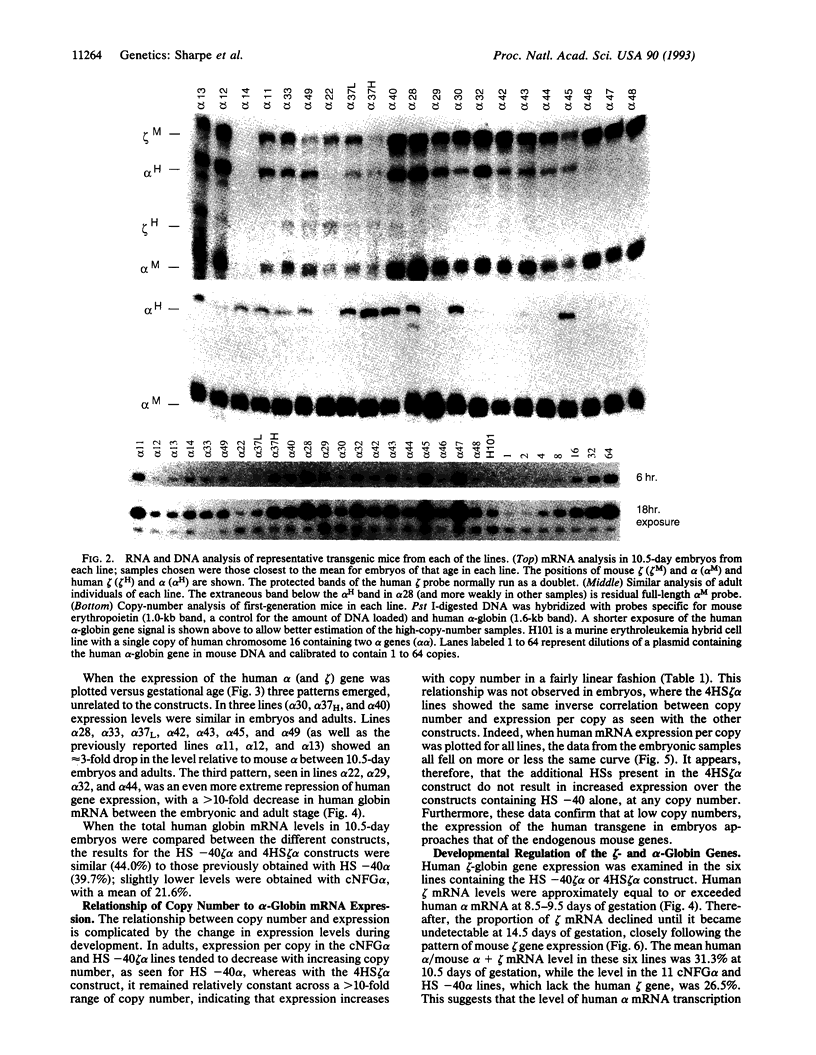
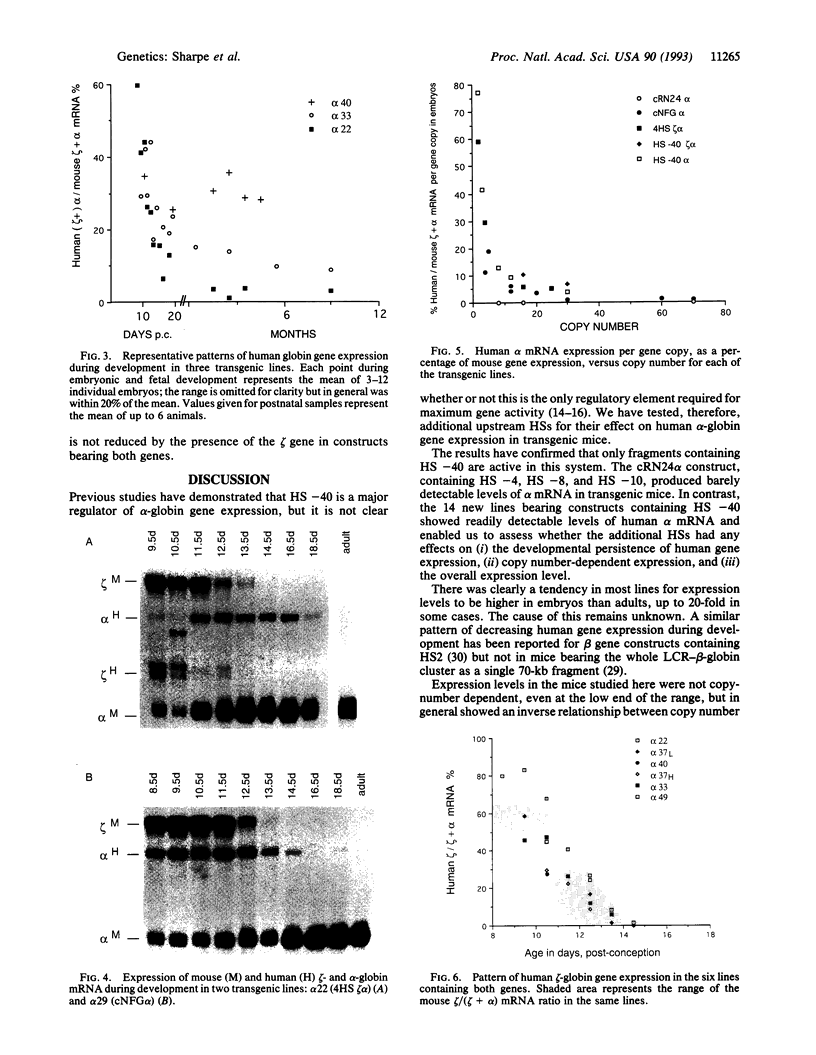
A 350-bp segment of DNA associated with an erythroid-specific DNase I-hypersensitive site (HS-40), upstream of the alpha-globin gene cluster, has been identified as the major tissue-specific regulator of the alpha-globin genes. However, this element does not direct copy number-dependent or developmentally stable expression of the human genes in transgenic mice. To determine whether additional upstream hypersensitive sites could provide more complete regulation of alpha gene expression we have studied 17 lines of transgenic mice bearing various DNA fragments containing HSs -33, -10, -8, and -4, in addition to HS -40. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human zeta- and alpha-globin genes was consistently observed in embryonic erythroid cells. However, the additional HSs did not confer copy-number dependence, alter the level of expression, or prevent the variable down-regulation of expression in adults. These results suggest that the region upstream of the human alpha-globin genes is not equivalent to that upstream of the beta locus and that although the two clusters are coordinately expressed, there may be differences in their regulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albitar M., Katsumata M., Liebhaber S. A. Human alpha-globin genes demonstrate autonomous developmental regulation in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3786–3794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Maniatis T. Rapid reprogramming of globin gene expression in transient heterokaryons. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90885-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M., Grosveld F., Dillon N. A single point mutation is the cause of the Greek form of hereditary persistence of fetal haemoglobin. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):499–502. doi: 10.1038/358499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollekens J. A., Forget B. G. Delta beta thalassemia and hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991 Jun;5(3):399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll M. C., Dobkin C. S., Alter B. P. Gamma delta beta-thalassemia due to a de novo mutation deleting the 5' beta-globin gene activation-region hypersensitive sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7470–7474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Novak U., Gelinas R., Groudine M. Molecular analysis of the human beta-globin locus activation region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Takegawa S., Papayannopoulou T., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Groudine M. Evidence for a locus activation region: the formation of developmentally stable hypersensitive sites in globin-expressing hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10159–10177. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser P., Hurst J., Collis P., Grosveld F. DNaseI hypersensitive sites 1, 2 and 3 of the human beta-globin dominant control region direct position-independent expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3503–3508. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton C. S., Wilkie A. O., Drysdale H. C., Wood W. G., Vickers M. A., Sharpe J., Ayyub H., Pretorius I. M., Buckle V. J., Higgs D. R. Alpha-thalassemia caused by a large (62 kb) deletion upstream of the human alpha globin gene cluster. Blood. 1990 Jul 1;76(1):221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Vickers M. A., Wilkie A. O., Pretorius I. M., Jarman A. P., Weatherall D. J. A review of the molecular genetics of the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Blood. 1989 Apr;73(5):1081–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Wood W. G., Jarman A. P., Sharpe J., Lida J., Pretorius I. M., Ayyub H. A major positive regulatory region located far upstream of the human alpha-globin gene locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1588–1601. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Wood W. G., Sharpe J. A., Gourdon G., Ayyub H., Higgs D. R. Characterization of the major regulatory element upstream of the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4679–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Vanin E., deLange T., Flavell R. A., Grosveld F. G. Beta-globin gene inactivation by DNA translocation in gamma beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):662–666. doi: 10.1038/306662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauer J., Shen C. K., Maniatis T. The chromosomal arrangement of human alpha-like globin genes: sequence homology and alpha-globin gene deletions. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Kuo A., Shen M. M., Leder P. In situ hybridization reveals co-expression of embryonic and adult alpha globin genes in the earliest murine erythrocyte progenitors. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):1041–1049. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Griese E. U., Weiss I., Cash F. E., Ayyub H., Higgs D. R., Horst J. Inactivation of human alpha-globin gene expression by a de novo deletion located upstream of the alpha-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9431–9435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley B. J., Abbott C. A., Sharpe J. A., Lida J., Chan-Thomas P. S., Wood W. G. A single beta-globin locus control region element (5' hypersensitive site 2) is sufficient for developmental regulation of human globin genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2057–2066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Higgs D. R. Recombination at the human alpha-globin gene cluster: sequence features and topological constraints. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottolenghi S., Mantovani R., Nicolis S., Ronchi A., Giglioni B. DNA sequences regulating human globin gene transcription in nondeletional hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin. Hemoglobin. 1989;13(6):523–541. doi: 10.3109/03630268908993104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pondel M. D., Proudfoot N. J., Whitelaw C., Whitelaw E. The developmental regulation of the human zeta-globin gene in transgenic mice employing beta-galactosidase as a reporter gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5655–5660. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romao L., Osorio-Almeida L., Higgs D. R., Lavinha J., Liebhaber S. A. Alpha-thalassemia resulting from deletion of regulatory sequences far upstream of the alpha-globin structural genes. Blood. 1991 Sep 15;78(6):1589–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe J. A., Chan-Thomas P. S., Lida J., Ayyub H., Wood W. G., Higgs D. R. Analysis of the human alpha globin upstream regulatory element (HS-40) in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4565–4572. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe J. A., Summerhill R. J., Vyas P., Gourdon G., Higgs D. R., Wood W. G. Role of upstream DNase I hypersensitive sites in the regulation of human alpha globin gene expression. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1666–1671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler E. A., Andrews K. A., Rubin E. M. Developmental regulation of the human zeta globin gene in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7093–7097. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. C., Andrews N. C., Higgs D. R., Orkin S. H. In vivo footprinting of the human alpha-globin locus upstream regulatory element by guanine and adenine ligation-mediated polymerase chain reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2135–2142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strouboulis J., Dillon N., Grosveld F. Developmental regulation of a complete 70-kb human beta-globin locus in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1857–1864. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Grosveld F. The 5'HS2 of the globin locus control region enhances transcription through the interaction of a multimeric complex binding at two functionally distinct NF-E2 binding sites. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1391–1398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Philipsen S., Fraser P., Grosveld F. Detailed analysis of the site 3 region of the human beta-globin dominant control region. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2169–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D. Y., Solomon W. B., London I. M., Lee D. P. An erythroid-specific, developmental-stage-independent enhancer far upstream of the human "beta-like globin" genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas P., Sharpe J. A., Watt P., Higgs D. R., Wood W. G. Regulation of human embryonic globin genes zeta 2 and epsilon in stably transformed mouse erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1992 Oct 1;80(7):1832–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Lamb J., Harris P. C., Finney R. D., Higgs D. R. A truncated human chromosome 16 associated with alpha thalassaemia is stabilized by addition of telomeric repeat (TTAGGG)n. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):868–871. doi: 10.1038/346868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]