Abstract
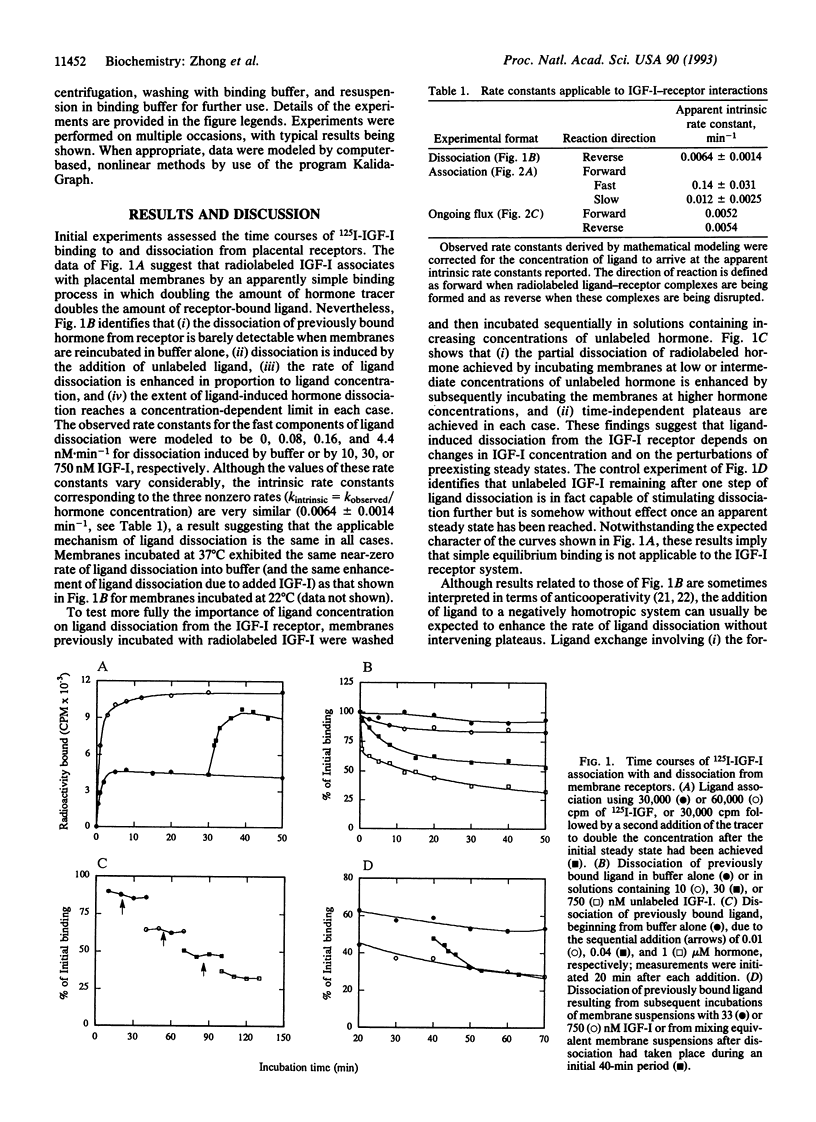
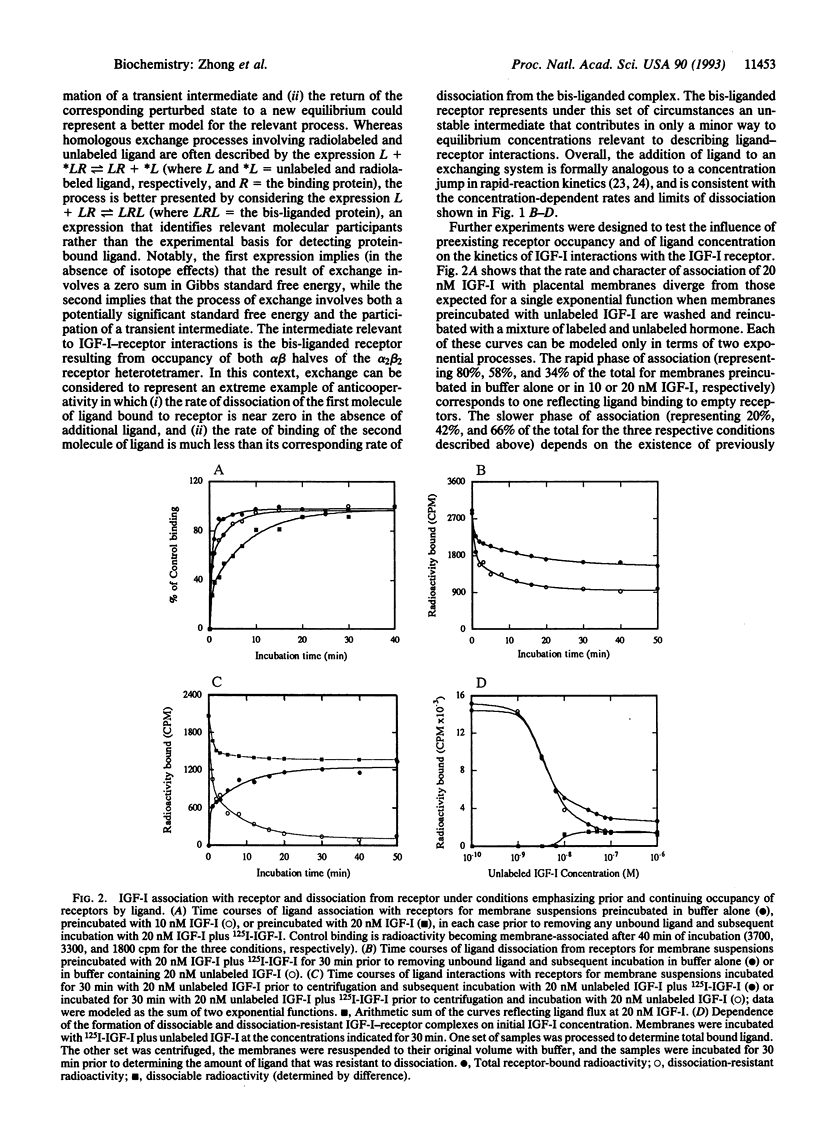
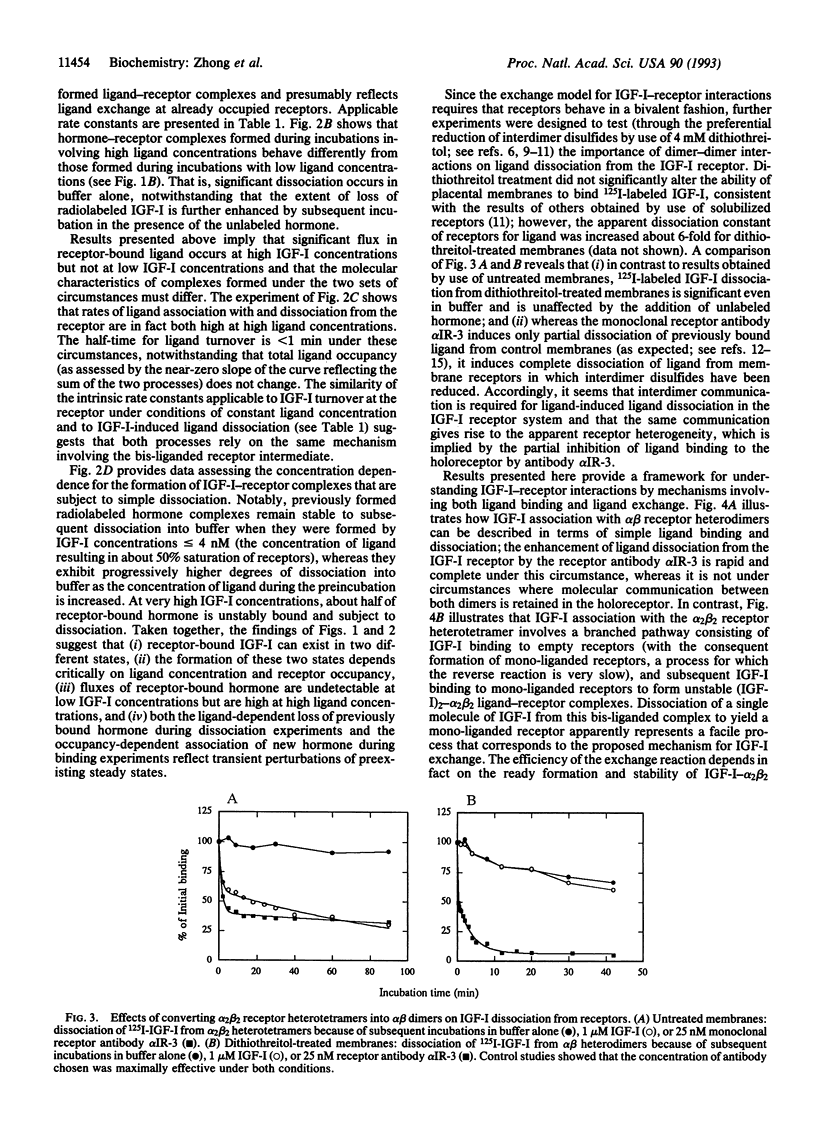
We have investigated by use of placental membranes the mechanisms through which insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) comes to be associated with its alpha 2 beta 2 receptor heterotetramer. Our results suggest that (i) at low ligand concentrations, the formation and disruption of IGF-I--receptor complexes are consistent with ligand binding de novo to empty receptors but not with equilibria involving ligand dissociation; (ii) at higher ligand concentrations, rapid exchange arising from the formation and collapse of bis-liganded receptors leads to a transiently perturbed receptor state; (iii) these nonclassical IGF-I receptor interactions depend on close communication between the alpha beta halves of the alpha 2 beta 2 holo-IGF-I receptor; and (iv) related processes based on ligand exchange have the potential for serving as biological sensors of changes in ligand concentration, while ordinary binding processes serve as sensors of ligand concentrations themselves. A model is presented in which one or two molecules of ligand can be bound to an alpha 2 beta 2 IGF-I receptor heterotetramer, new ligand becomes associated with receptor by exchanging for a previously bound molecule of IGF-I, and fluctuating changes in free-ligand concentration might lead to enhanced IGF-I function.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandrides T. K., Smith R. J. A novel fetal insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I receptor. Mechanism for increased IGF I- and insulin-stimulated tyrosine kinase activity in fetal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12922–12930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., O'Neill K., Riggs M., Wigler M. Characterization of ROS1 cDNA from a human glioblastoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4799–4803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess S. K., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Characterization of a neuronal subtype of insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1618–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cara J. F., Mirmira R. G., Nakagawa S. H., Tager H. S. An insulin-like growth factor I/insulin hybrid exhibiting high potency for interaction with the type I insulin-like growth factor and insulin receptors of placental plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17820–17825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casella S. J., Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Insulin-like growth factor II binding to the type I somatomedin receptor. Evidence for two high affinity binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9268–9273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P., Van Obberghen E., Roth J. Mapping of the residues responsible for the negative cooperativity of the receptor-binding region of insulin. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):504–509. doi: 10.1038/273504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeyts P., Bainco A. R., Roth J. Site-site interactions among insulin receptors. Characterization of the negative cooperativity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1877–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltz S. M., Swanson M. L., Wemmie J. A., Pessin J. E. Functional properties of an isolated alpha beta heterodimeric human placenta insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor complex. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3234–3242. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo R. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin and insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptors during central nervous system development: expression of two immunologically distinct IGF-1 receptor beta subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2806–2817. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Harrison L. C. The human placenta contains two distinct binding and immunoreactive species of insulin-like growth factor-I receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2288–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. N., Underwood L. E., Voina S. J., Foushee D. B., Van Wyk J. J. Characterization of the insulin and somatomedin-C receptors in human placental cell membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Aug;39(2):283–292. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Usher P., Ikari N., King P. P., Tramontano D., Flier J. S. Multiple factors influence insulin-like growth factor-I binding to human skin fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):867–875. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Duronio V., Jacobs S. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor beta-subunit heterogeneity. Evidence for hybrid tetramers composed of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin receptor heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13238–13244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld R. G., Lamson G., Pham H., Oh Y., Conover C., De Leon D. D., Donovan S. M., Ocrant I., Giudice L. Insulinlike growth factor-binding proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1990;46:99–163. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571146-3.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier P., Watt V. M. Primary structure of a putative receptor for a ligand of the insulin family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14605–14608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Field C. E., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Zhang B., Roth R. A., Andersen A. S., Kjeldsen T., Siddle K. A panel of monoclonal antibodies for the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Epitope mapping, effects on ligand binding, and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12955–12963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K. Immunological relationships between receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Evidence for structural heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor I receptors involving hybrids with insulin receptors. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):553–563. doi: 10.1042/bj2630553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Whittaker J., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Siddle K. Receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I can form hybrid dimers. Characterisation of hybrid receptors in transfected cells. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):383–390. doi: 10.1042/bj2700383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Thompson K., Petersen D. J. Separation of the high affinity insulin-like growth factor I receptor from low affinity binding sites by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16461–16469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Thompson K. The structural basis for insulin-like growth factor I receptor high affinity binding. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16267–16273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong L., Kasuya J., Li S. L., Kato J., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Growth-stimulatory monoclonal antibodies against human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5356–5360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee D., Lebovic G. S., Marcus R. R., Rosen N. Identification of an alternate type I insulin-like growth factor receptor beta subunit mRNA transcript. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21439–21441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


