Abstract
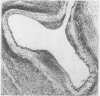
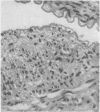
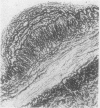
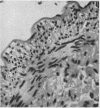
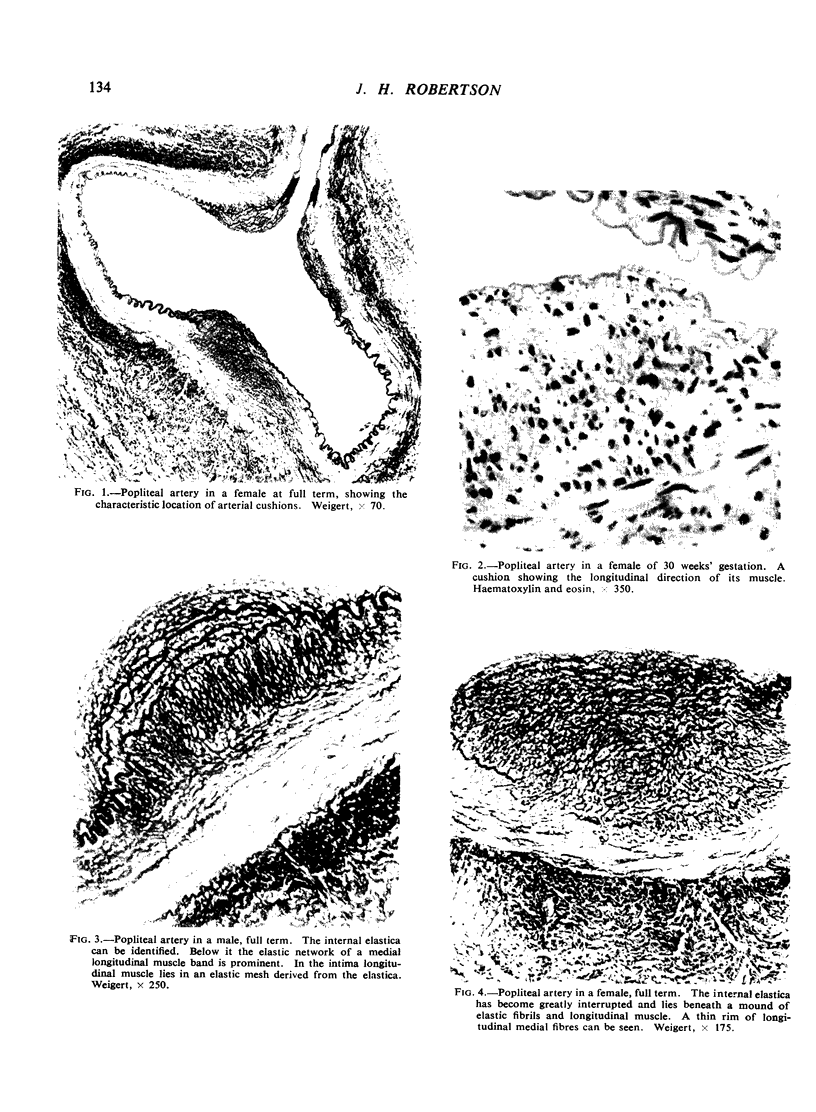
In a study of the peripheral arteries of foetuses it was found that focal areas of intimal thickening and of splitting of the internal elastica had developed, the thickening being similar to that found in the coronary arteries. Characteristically the thickenings were found in the mouths of branches and in those vessels subject to pulsation. It is believed that they are physiological in nature and a response of the vascular wall to the stresses produced by focal areas of impaired pulsation and not degenerative as formerly thought.
The evolution of these arterial cushions is traced from early foetal life; their most important constituent is bundles of medial longitudinal muscle. Both thickening and splitting of the internal elastica are brought about by a radial reorientation and migration of the muscle cells of the media.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON D., HALL D. A., KEECH M. K., REED R., SAXL H., TUNBRIDGE R. E., WOOD M. J. Apparent transformation of collagen fibrils into elastin. Nature. 1955 Nov 19;176(4490):966–969. doi: 10.1038/176966a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross L., Epstein E. Z., Kugel M. A. Histology of the Coronary Arteries and their Branches in the Human Heart. Am J Pathol. 1934 Mar;10(2):253–274.7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENE C. I. The early lesions of atheroma in the coronary arteries. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):79–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOON H. D. Coronary arteries in fetuses, infants, and juveniles. Circulation. 1957 Aug;16(2):263–267. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.16.2.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]