Abstract
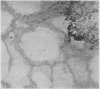
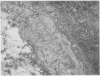
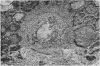
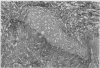
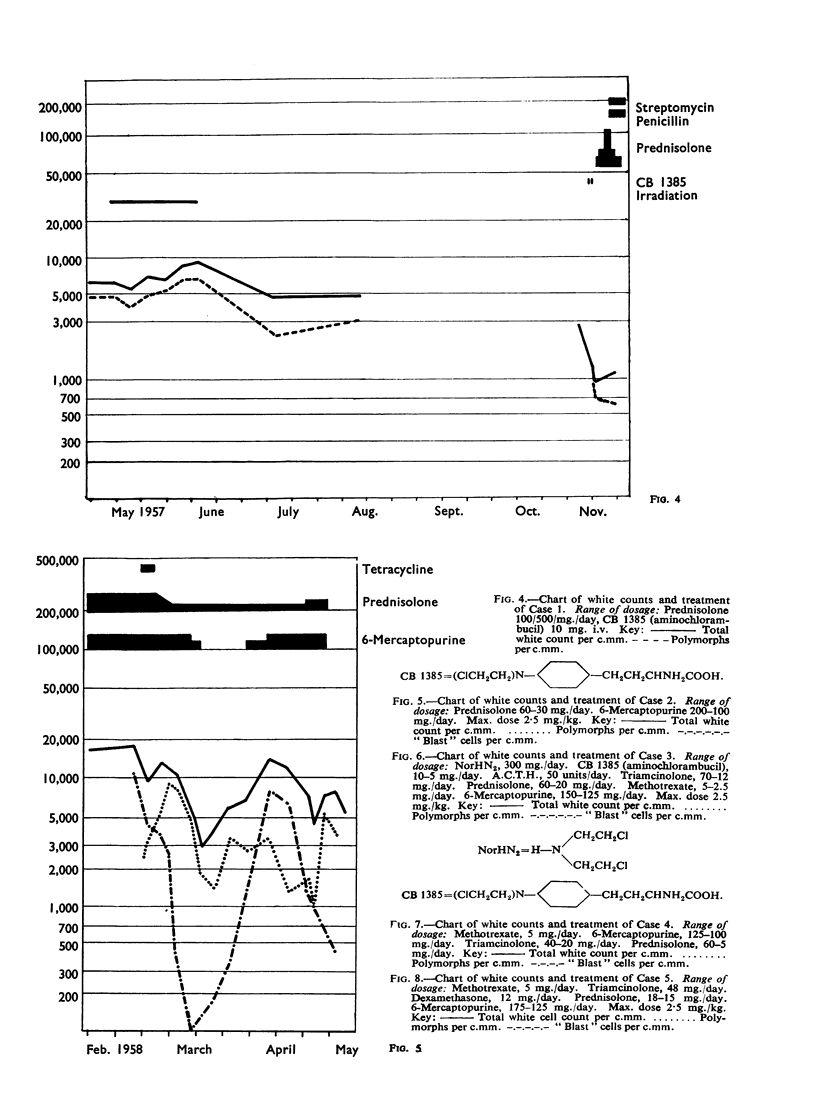
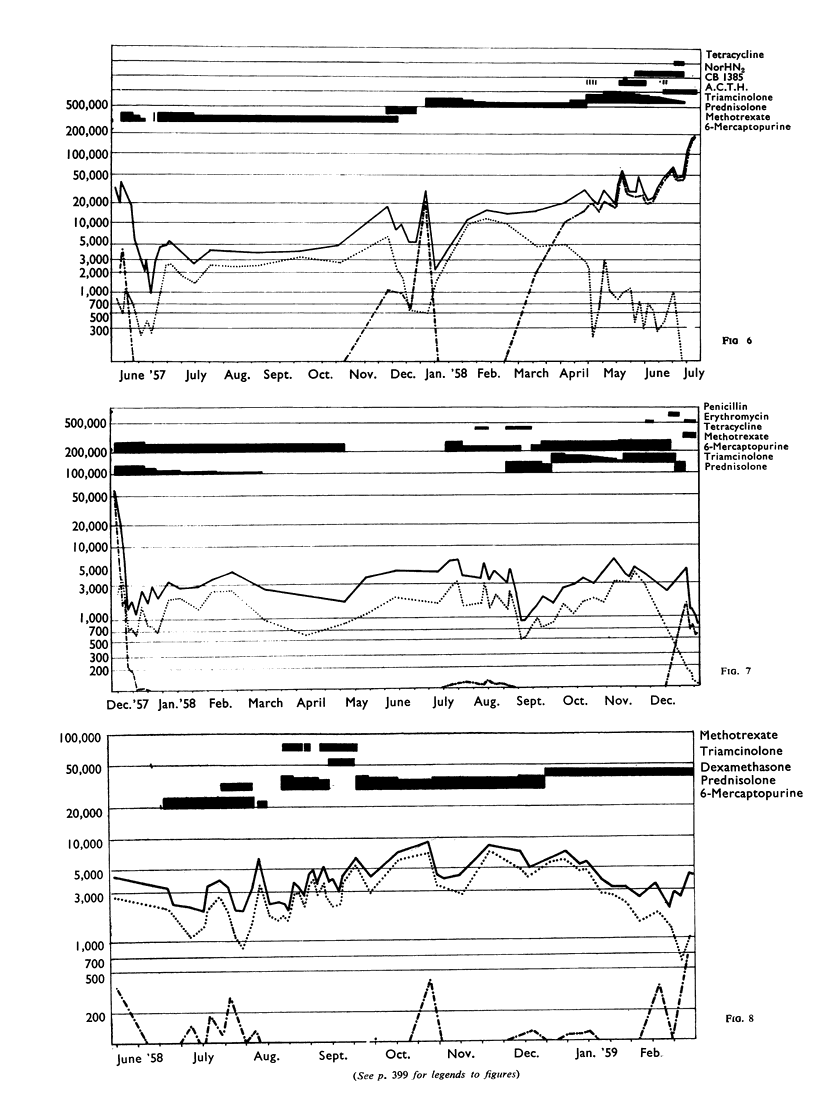
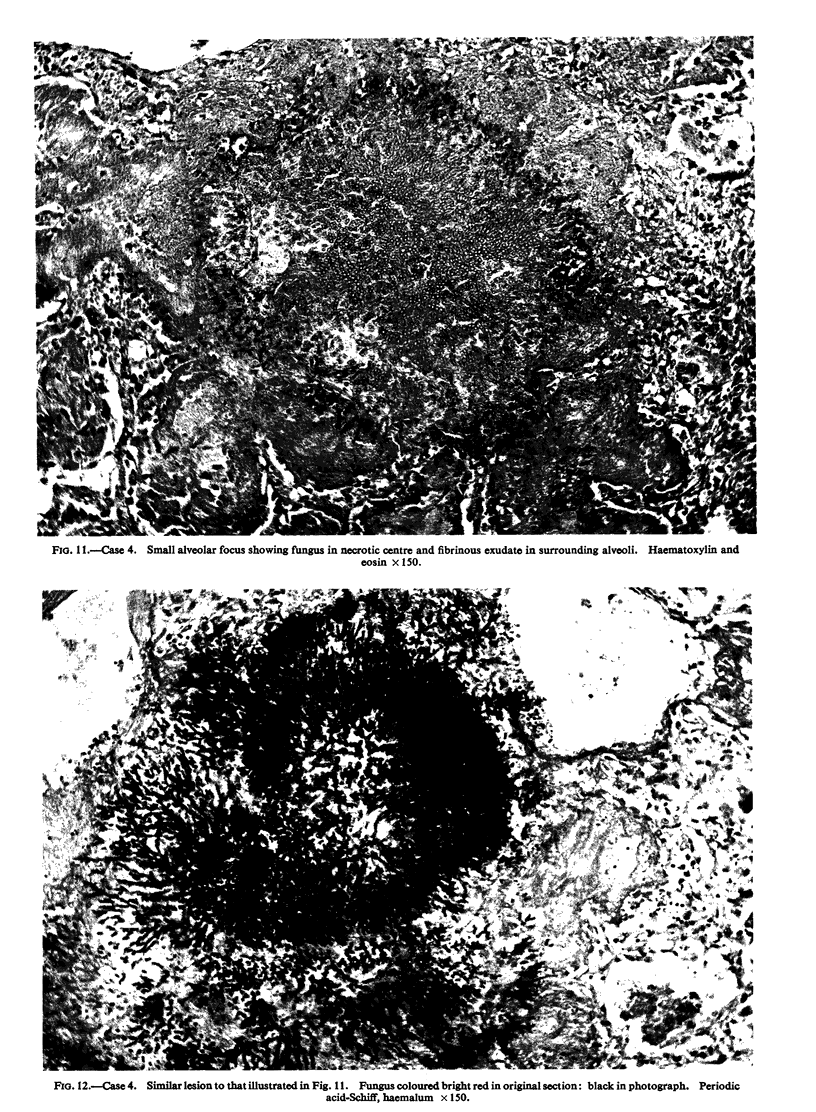
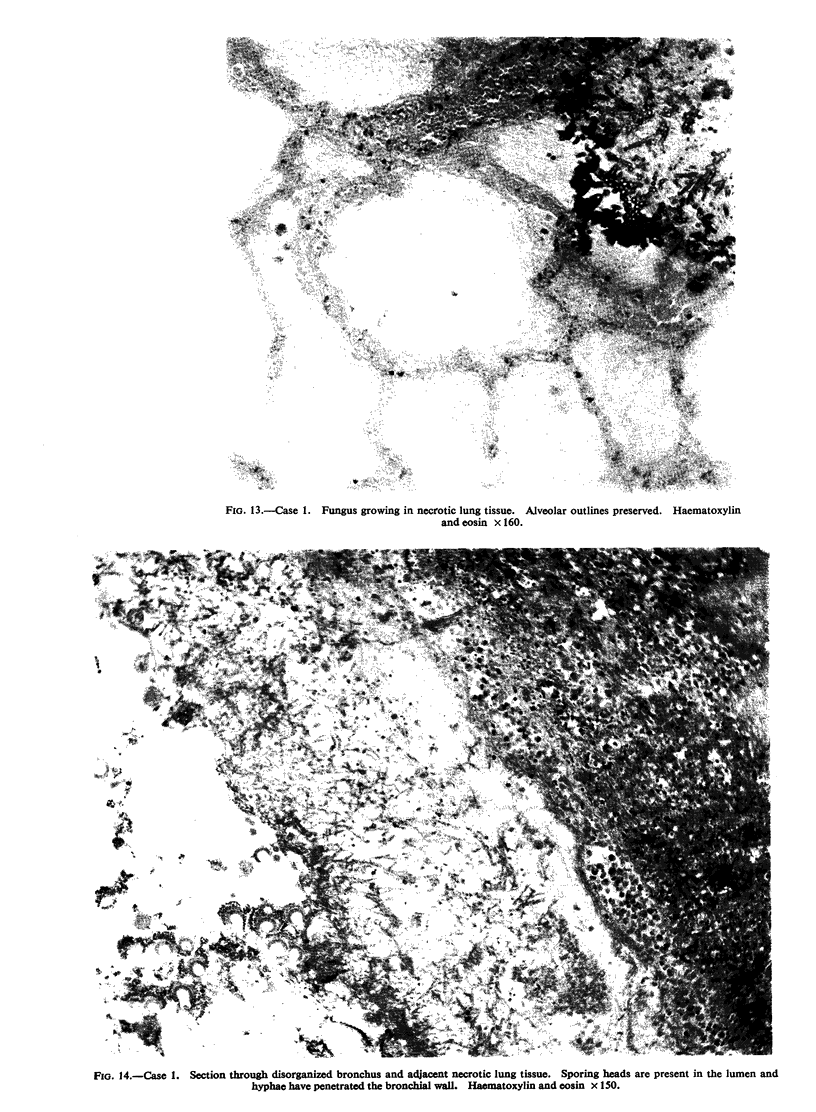
Five cases of aspergillosis complicating Hodgkin's disease and leukaemia are reported. The organs involved were: lungs (all five cases), stomach (Case 3); brain and meninges (Case 4); heart, kidneys, spleen, thyroid, and liver (Case 2). Cultures of Aspergillus fumigatus were obtained from the post-mortem tissues of three patients.
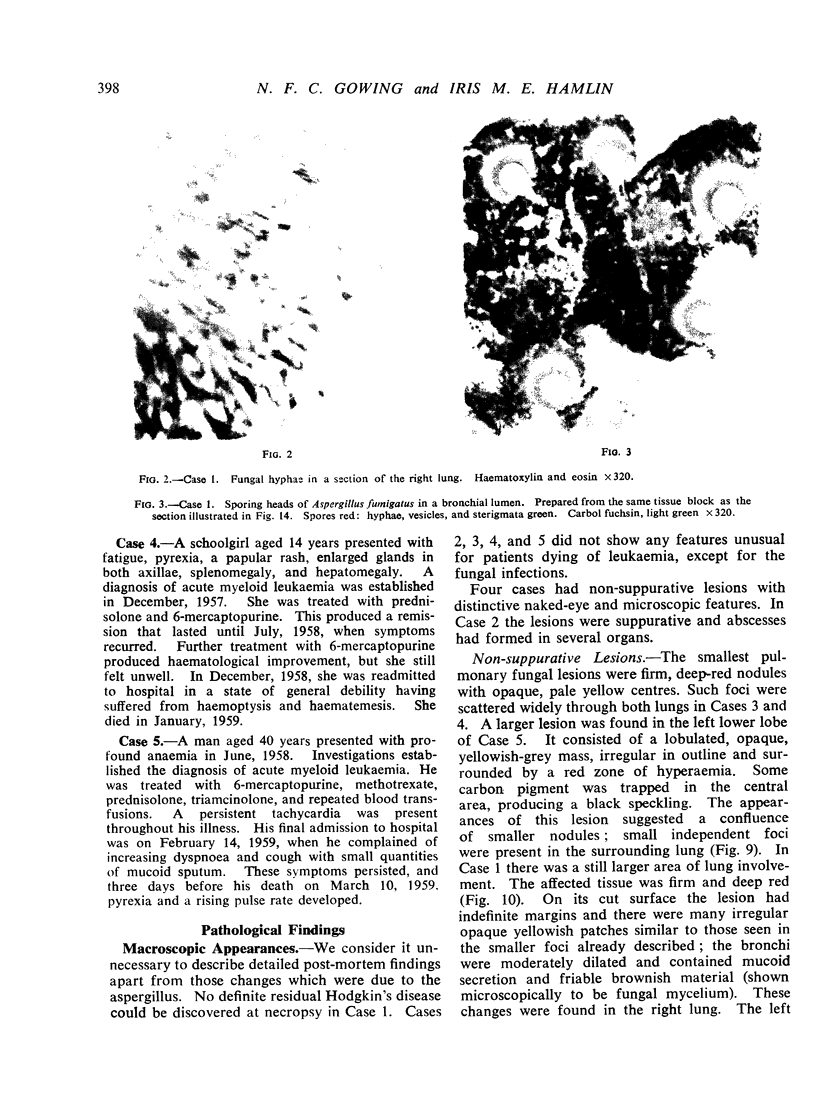
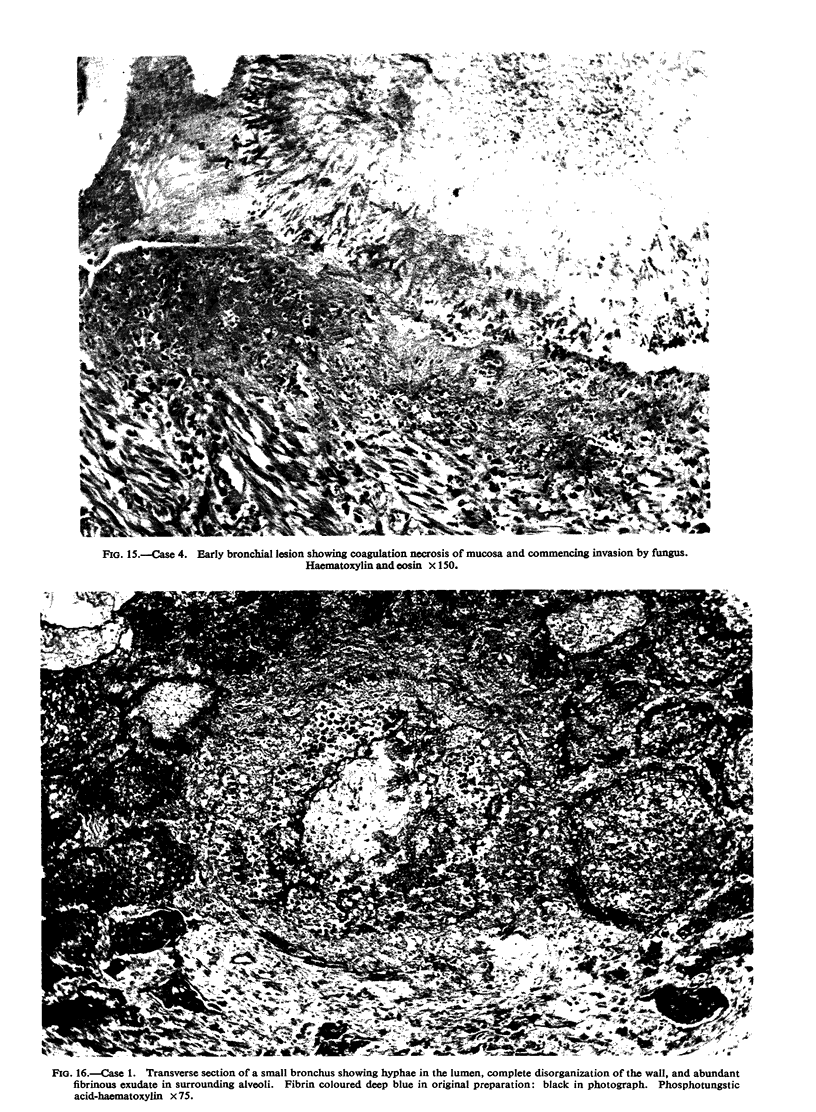
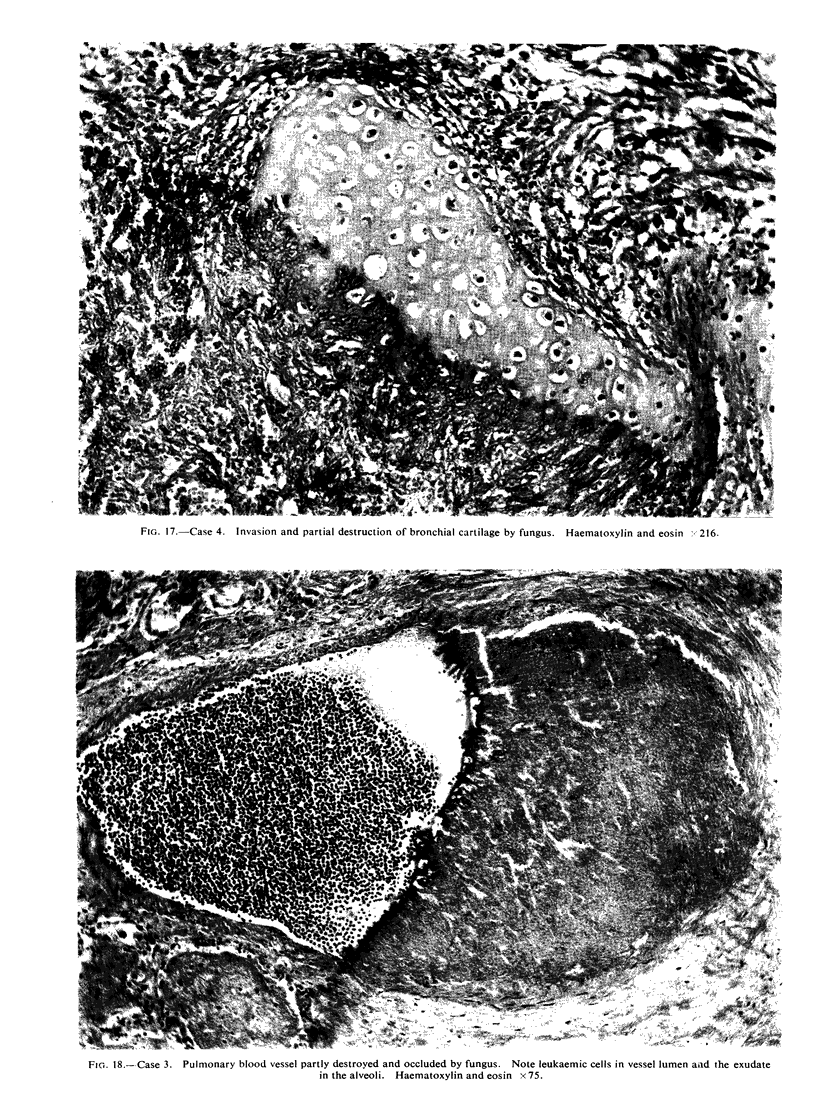
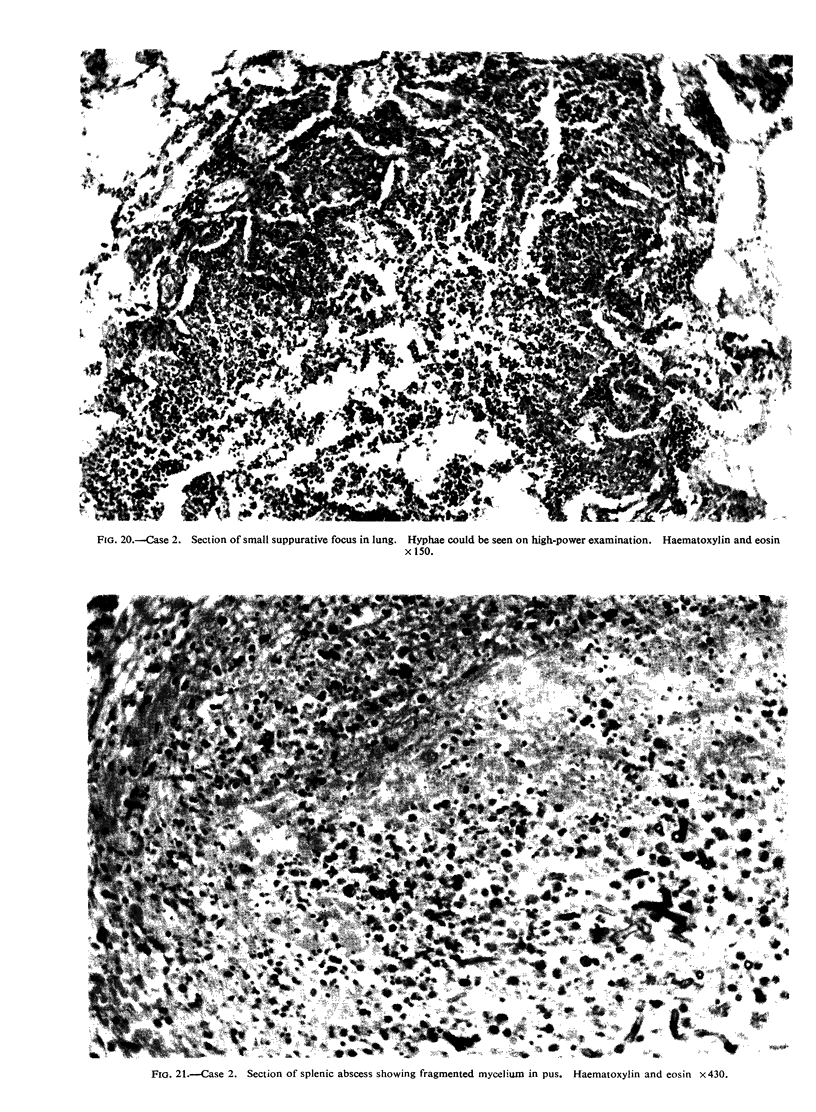
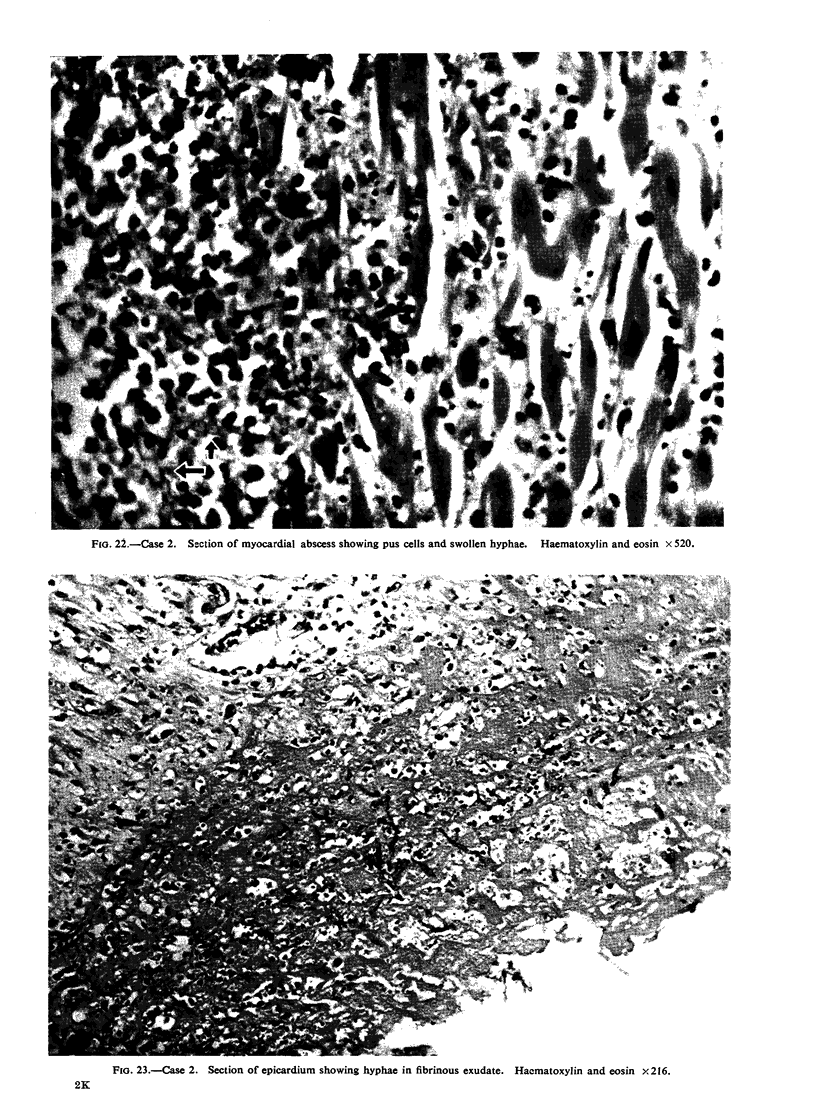
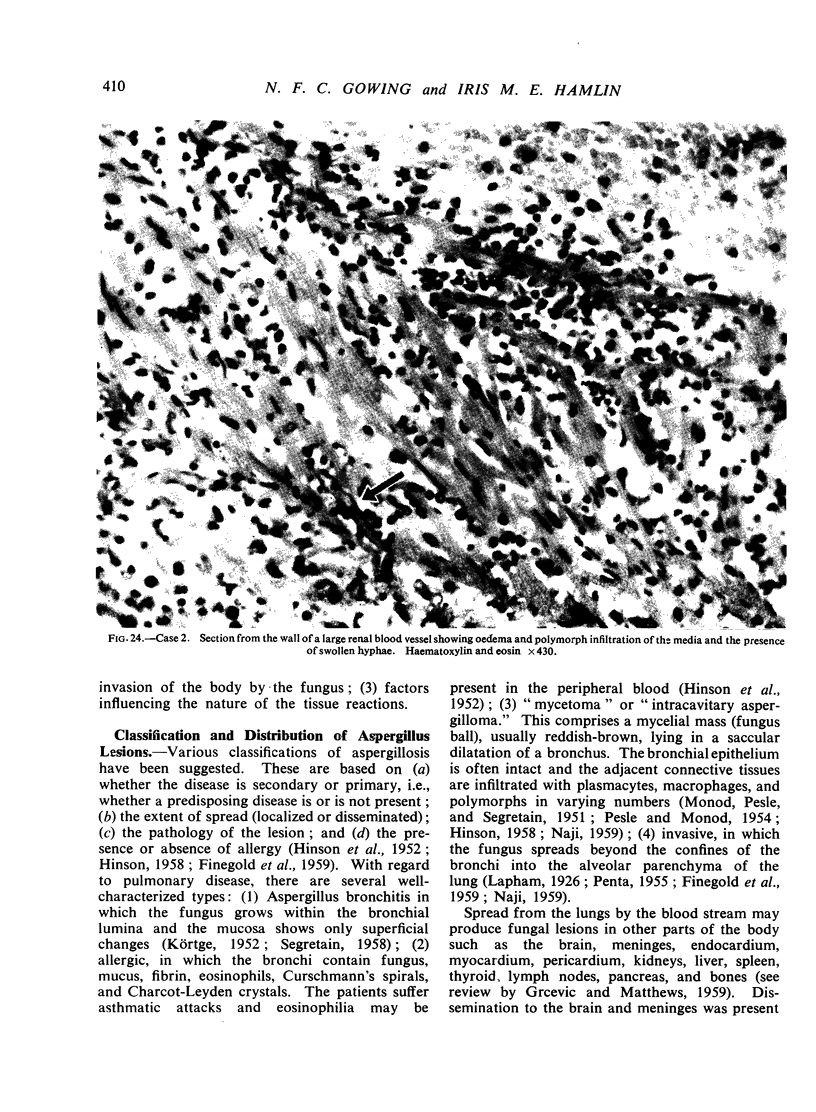
All the lesions in Case 2 were suppurative. The other four cases had non-suppurative lesions characterized by spreading coagulation necrosis with peripheral hyperaemia, exudation, and haemorrhage. Invasion and occlusion of blood vessels occurred frequently.
The various factors that may be responsible for the initiation and progression of the fungal infection are discussed. The available evidence suggests that Aspergillus fumigatus can produce toxic metabolites which are able to cause tissue necrosis and vascular damage. In patients suffering from neoplastic conditions of the lympho-reticular system, especially if steroid hormones or radiomimetic drugs are given, spreading, necrotizing lesions can develop unchecked by antibody or cellular defences.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asheshov I. N., Strelitz F. AN ANTIBIOTIC SUBSTANCE ACTIVE AGAINST MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. Science. 1945 Feb 2;101(2614):119–120. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2614.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHORTIS P. Pulmonary aspergillosis in Greece. Dis Chest. 1952 Aug;22(2):206–212. doi: 10.1378/chest.22.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLEBIOWSKI A. K. Pleural aspergillosis following resection for pulmonary tuberculosis. Tubercle. 1958 Apr;39(2):111–112. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(58)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRCEVIC N., MATTHEWS W. F. Pathologic changes in acute disseminated aspergillosis, particularly involvement of the central nervous system. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Dec;32:536–551. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/32.5.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINSON K. F. W., MOON A. J., PLUMMER N. S. Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis; a review and a report of eight new cases. Thorax. 1952 Dec;7(4):317–333. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUPPERT M., MACPHERSON D. A., CAZIN J. Pathogenesis of Candida albicans infection following antibiotic therapy. I. The effect of antibiotics on the growth of Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1953 Feb;65(2):171–176. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.2.171-176.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IYER S., DODGE P. R., ADAMS R. D. Two cases of Aspergillus infection of the central nervous system. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1952 Aug;15(3):152–163. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.15.3.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYE J. D., Jr, MAGEE W. E. Fungal diseases in a general hospital; a study of 88 patients. Am J Clin Pathol. 1956 Nov;26(11):1235–1253. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/26.11.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORTGE P. Aspergillose der Säuglinglunge. Dtsch Med J. 1952 May 15;3(9-10):202–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON D. L., TOMLINSON L. J. Quantitative antibody studies in man. III. Antibody response in leukemia and other malignant lymphomata. J Clin Invest. 1953 Apr;32(4):317–321. doi: 10.1172/JCI102741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD O., PESLE G., SEGRETAIN G. Sur une forme nouvelle d'aspergillose pulmonaire: l'aspergillome bronchectasiant. Bull Acad Natl Med. 1951 Oct 16;135(29-30):508–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKEE E. E. Mycotic infection of brain with arteritis and subarachnoid hemorrhage; report of case. Am J Clin Pathol. 1950 Apr;20(4):381–384. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/20.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAJI A. F. Bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: report of two new cases, review of literature, and suggestion for classification. Arch Pathol. 1959 Sep;68:282–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENTA A. Q. The mycotic infections of the bronchial-pulmonary tract. Am J Surg. 1955 Jul;90(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(55)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESLE G. D., MONOD O. Bronchiectasis due to asperigilloma. Dis Chest. 1954 Feb;25(2):172–183. doi: 10.1378/chest.25.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERMANN M. L., HAMILTON M. G., REILLY H. C. The basic proteins of Aspergillus fumigatus with tumor-inhibiting properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 May;37(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANKIN N. E. Disseminated aspergillosis and moniliasis associated with agranulocytosis and antibiotic therapy. Br Med J. 1953 Apr 25;1(4816):918–919. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4816.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIDDELL R. W. The role of fungi as human pathogens. Proc R Soc Med. 1958 Jul;51(7):491–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGMANN E. Virulence enhancement of Candida albicans by antibiotics and cortisone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Aug-Sep;83(4):778–781. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEFANINI M., ADAMIS D. M., SOARDI F., HORACE J. F., MARIN H. M., MELE R. Purification of aspergillin O. Lancet. 1959 Sep 26;2(7100):443–444. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90425-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASZEWSKI T. Side-effects of chloramphenicol and aureomycin, with special reference to oral lesions. Br Med J. 1951 Feb 24;1(4703):388–392. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4703.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORACK R. M. Fungus infections associated with antibiotic and steroid therapy. Am J Med. 1957 Jun;22(6):872–882. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRE C. M., LEIKIN S. L. Tissue inflammatory cytology in clinical states. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Oct;32:335–345. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/32.4.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSH R. A., McCLINTON L. T. Aspergillosis of lungs and duodenum with fatal intestinal hemorrhage. AMA Arch Pathol. 1954 May;57(5):379–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYBEL R. E. Mycosis of cervical spinal cord following intrathecal penicillin therapy; report of a case simulating cord tumor. AMA Arch Pathol. 1952 Feb;53(2):167–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN L. E. Fatal fungus infections complicating other diseases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1955 Jan;25(1):46–65. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/25.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]