Abstract
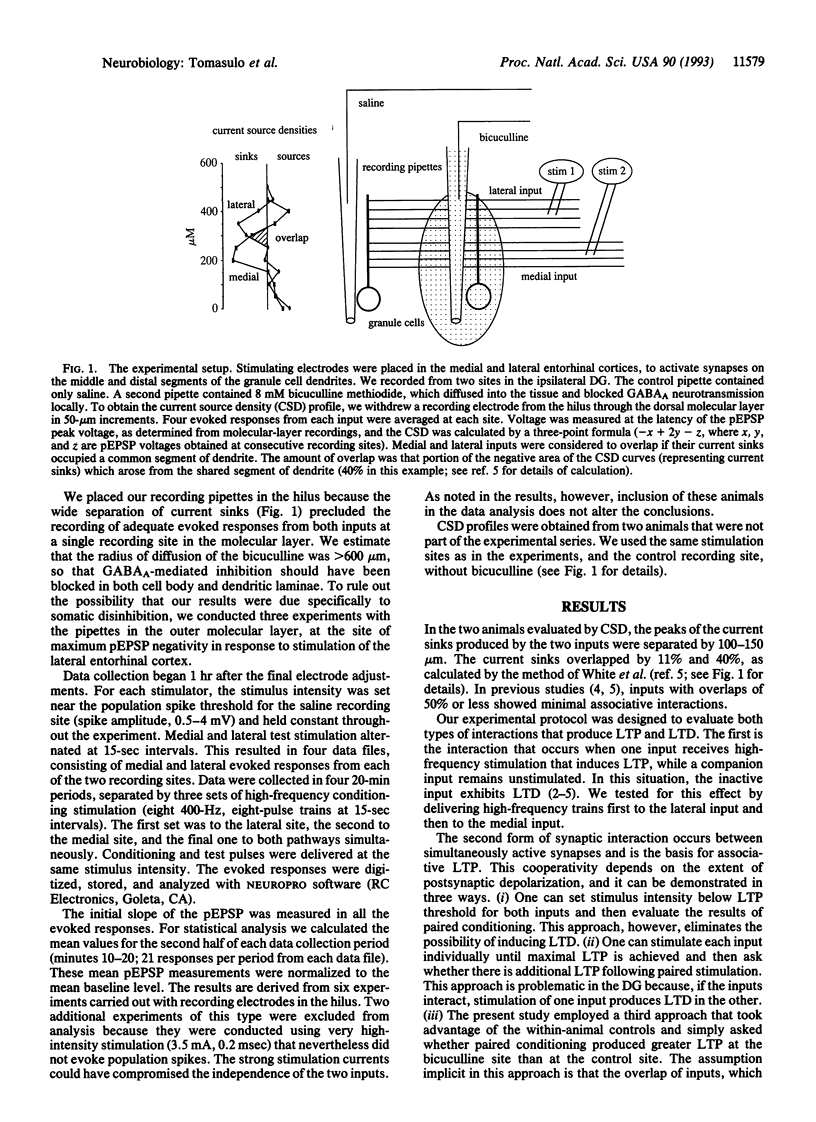
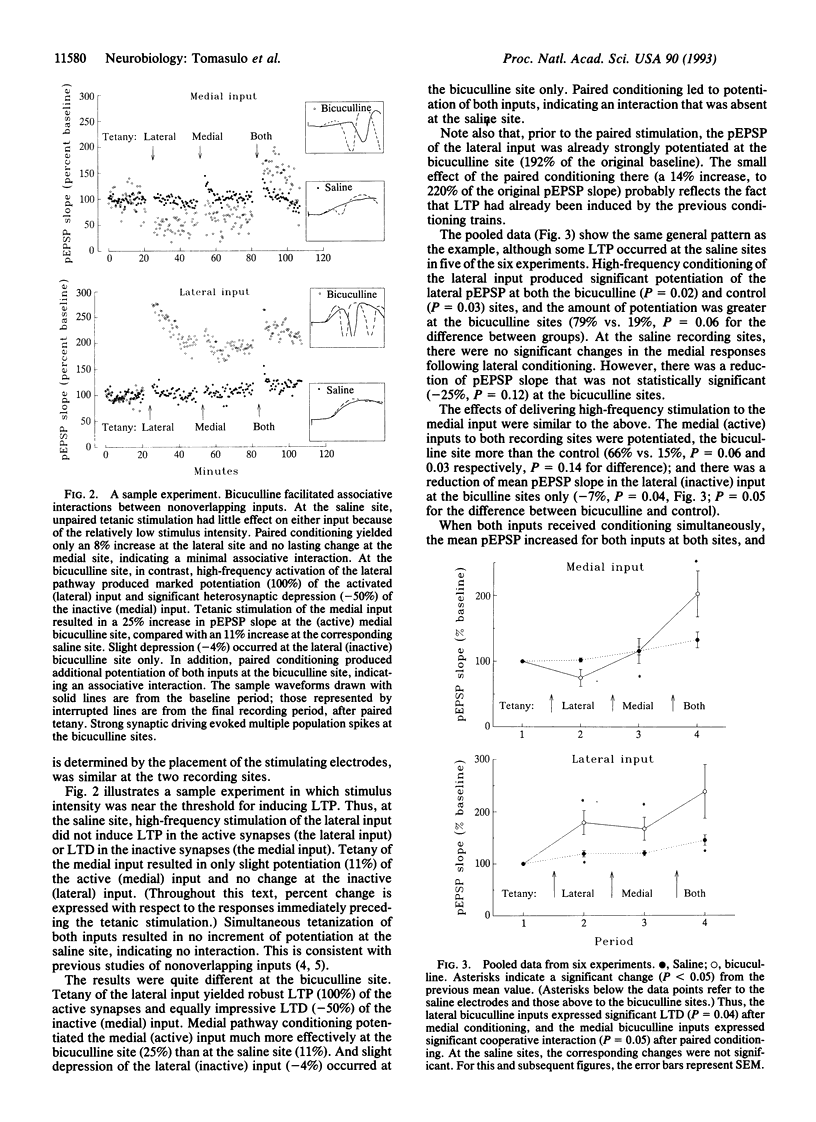
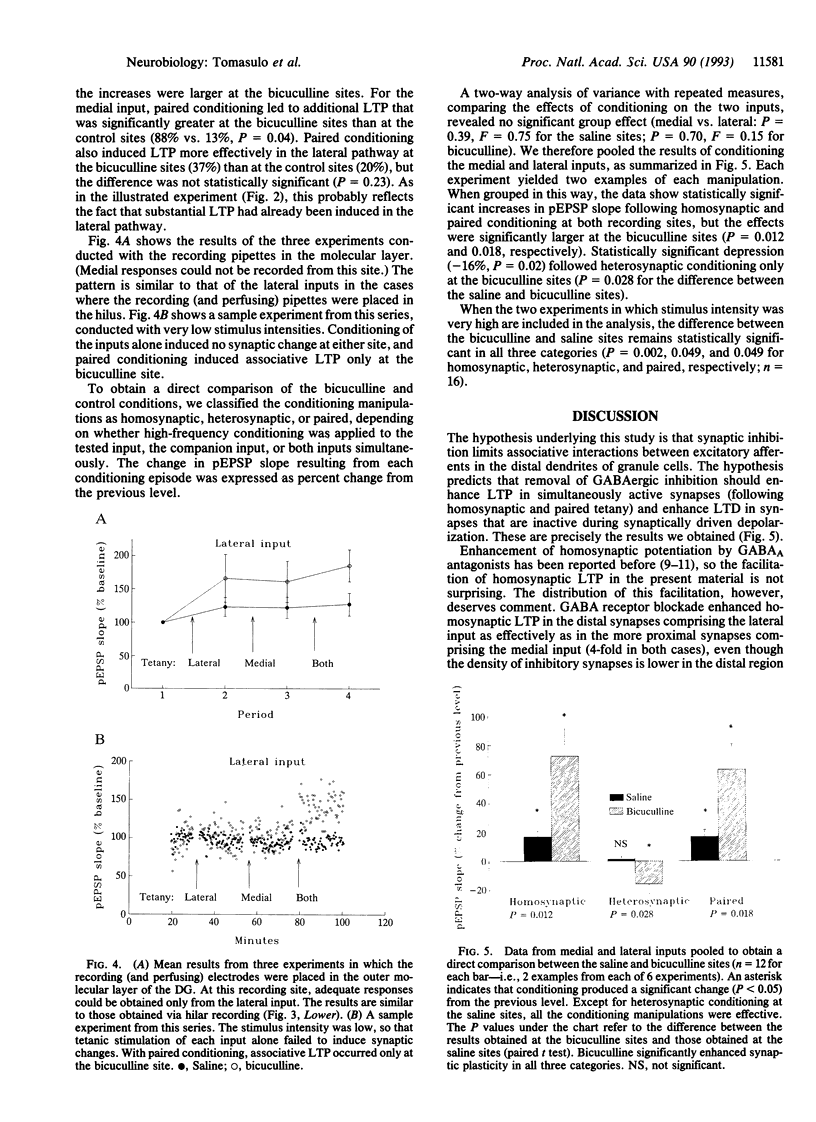
The induction of long-term potentiation and depression depends upon associative interactions between synapses that converge on individual dendrites. The distance over which these associative interactions occur is limited. The present study evaluates whether this limitation is regulated by synaptic inhibition. We evaluated the associative interactions between two inputs that terminate on different proximo-distal locations along the dendrites of dentate granule cells in the presence of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) antagonist bicuculline methiodide. Local blockade of GABAergic inhibition enhanced associative interactions between nonoverlapping inputs, compared to within-animal control sites, where inhibitory transmission was intact. The results suggest that synaptic inhibition limits interactions between excitatory synapses by creating current shunts that limit the spread of depolarization within the dendritic tree.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham W. C., Wickens J. R. Heterosynaptic long-term depression is facilitated by blockade of inhibition in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1991 Apr 19;546(2):336–340. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91498-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie B. R., Abraham W. C. NMDA-dependent heterosynaptic long-term depression in the dentate gyrus of anaesthetized rats. Synapse. 1992 Jan;10(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/syn.890100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert C. M., Levy W. B. Electrophysiological and pharmacological characterization of perforant path synapses in CA1: mediation by glutamate receptors. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;68(1):1–8. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fifková E., Eason H., Schaner P. Inhibitory contacts on dendritic spines of the dentate fascia. Brain Res. 1992 Apr 17;577(2):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90293-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey U., Krug M., Brödemann R., Reymann K., Matthies H. Long-term potentiation induced in dendrites separated from rat's CA1 pyramidal somata does not establish a late phase. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Feb 13;97(1-2):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. R., Woody C. D. Effects of uniform and non-uniform synaptic 'activation-distributions' on the cable properties of modeled cortical pyramidal neurons. Brain Res. 1989 Dec 25;505(1):12–22. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90110-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Hama K., Wu J. Y. GABAergic synaptic boutons in the granule cell layer of rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 1984 Feb 20;293(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel D. D., Lacaille J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A. Ultrastructure of stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons of hippocampal CA1 region. Synapse. 1988;2(4):382–394. doi: 10.1002/syn.890020405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A. Stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons of hippocampal CA1 region. I. Intracellular response characteristics, synaptic responses, and morphology. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1400–1410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01400.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacaille J. C., Schwartzkroin P. A. Stratum lacunosum-moleculare interneurons of hippocampal CA1 region. II. Intrasomatic and intradendritic recordings of local circuit synaptic interactions. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1411–1424. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01411.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W. B., Steward O. Synapses as associative memory elements in the hippocampal formation. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 19;175(2):233–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E., Seress L. Five types of basket cell in the hippocampal dentate gyrus: a combined Golgi and electron microscopic study. J Neurocytol. 1983 Aug;12(4):577–597. doi: 10.1007/BF01181525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley K. J., Mody I. Shunting of excitatory input to dentate gyrus granule cells by a depolarizing GABAA receptor-mediated postsynaptic conductance. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;68(1):197–212. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward O., Tomasulo R., Levy W. B. Blockade of inhibition in a pathway with dual excitatory and inhibitory action unmasks a capability for LTP that is otherwise not expressed. Brain Res. 1990 May 21;516(2):292–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90930-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasulo R. A., Levy W. B., Steward O. LTP-associated EPSP/spike dissociation in the dentate gyrus: GABAergic and non-GABAergic components. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 4;561(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90745-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G., Levy W. B., Steward O. Evidence that associative interactions between synapses during the induction of long-term potentiation occur within local dendritic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2368–2372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G., Levy W. B., Steward O. Spatial overlap between populations of synapses determines the extent of their associative interaction during the induction of long-term potentiation and depression. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Oct;64(4):1186–1198. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.4.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigström H., Gustafsson B. Facilitation of hippocampal long-lasting potentiation by GABA antagonists. Acta Physiol Scand. 1985 Sep;125(1):159–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1985.tb07703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigström H., Gustafsson B., Huang Y. Y., Abraham W. C. Hippocampal long-term potentiation is induced by pairing single afferent volleys with intracellularly injected depolarizing current pulses. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Feb;126(2):317–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. X., Levy W. B. Bicuculline permits the induction of long-term depression by heterosynaptic, translaminar conditioning in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 1993 Jun 11;613(2):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90917-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


