Abstract
Glutamate mediates fast synaptic transmission at the majority of excitatory synapses throughout the central nervous system by interacting with different types of receptor channels. Cloning of glutamate receptors has provided evidence for the existence of several structurally related subunit families, each composed of several members. It has been proposed that KA1 and KA2 and GluR-5, GluR-6, and GluR-7 families represent subunit classes of high-affinity kainate receptors and that in vivo different kainate receptor subtypes might be constructed from these subunits in heteromeric assembly. However, despite some indications from autoradiographic studies and binding data in brain membranes, no functional pure kainate receptors have so far been detected in brain cells. We have found that early after culturing, a high percentage of rat hippocampal neurons express functional, kainate-selective glutamate receptors. These kainate receptors show pronounced desensitization with fast onset and very slow recovery and are also activated by quisqualate and domoate, but not by alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate. Our results provide evidence for the existence of functional glutamate receptors of the kainate type in nerve cells, which are likely to be native homomeric GluR-6 receptors.
Full text
PDF
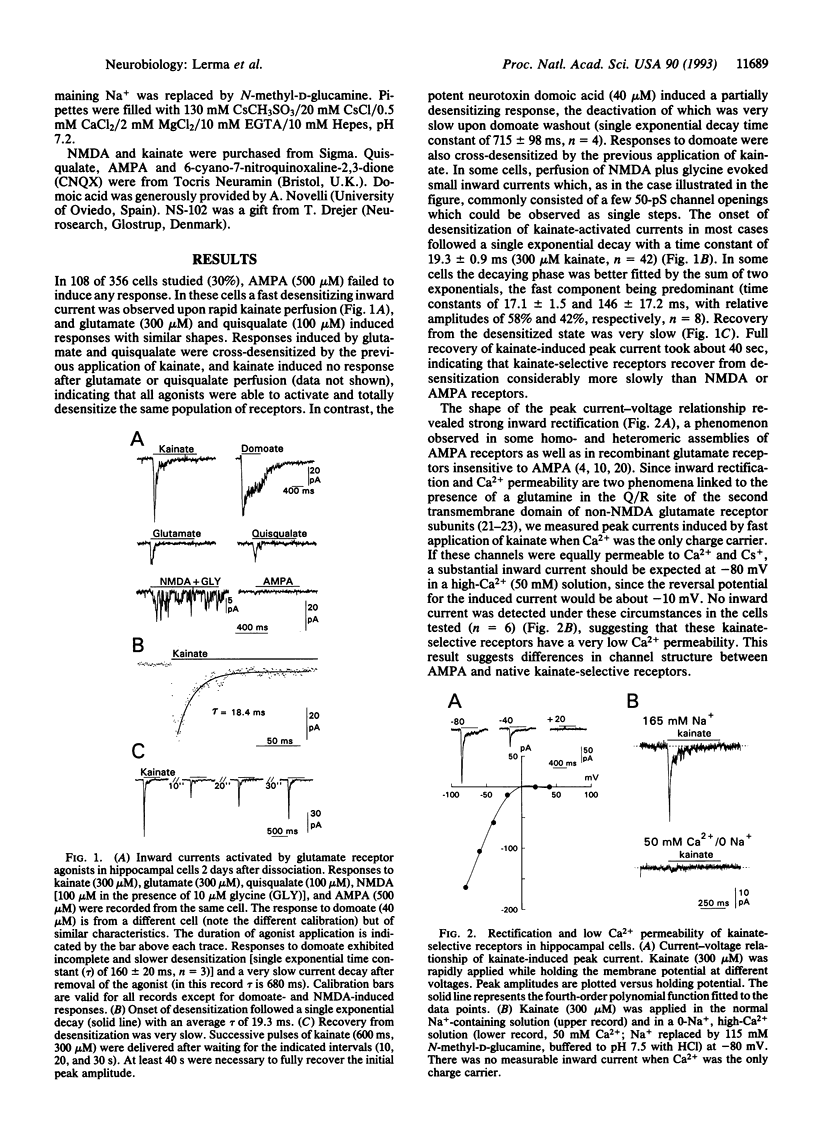
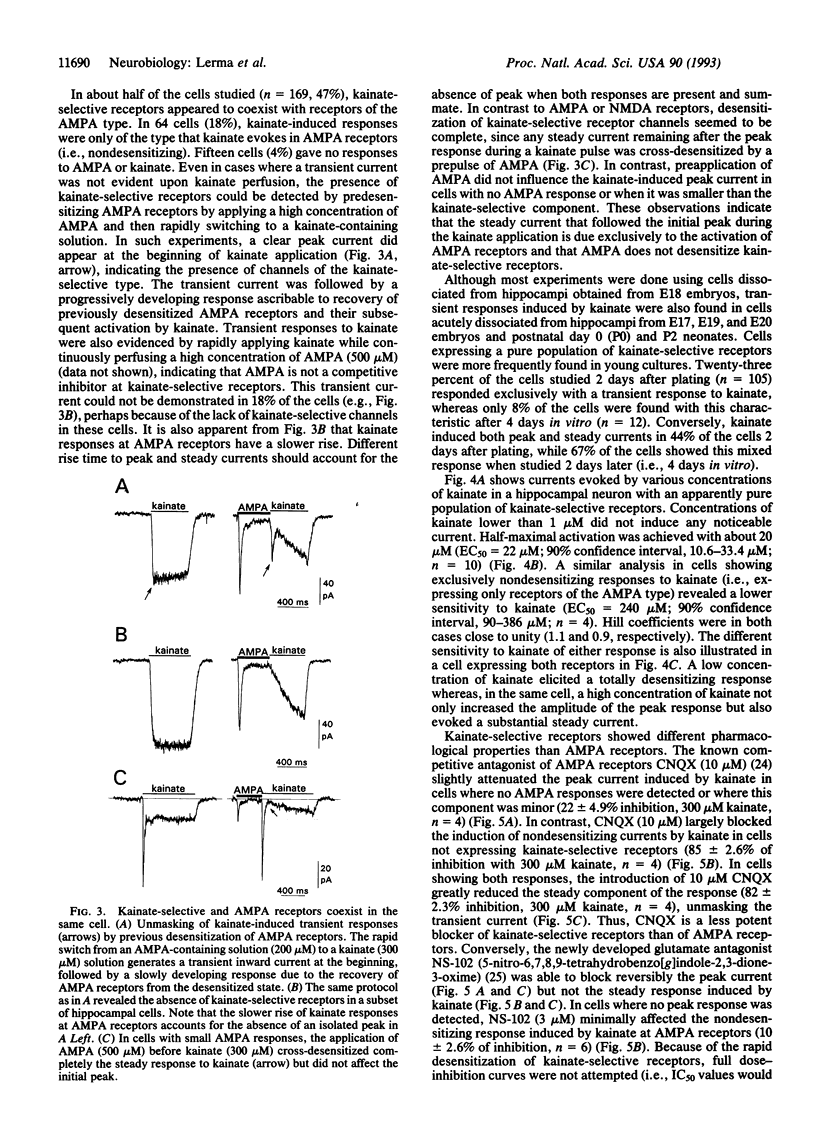
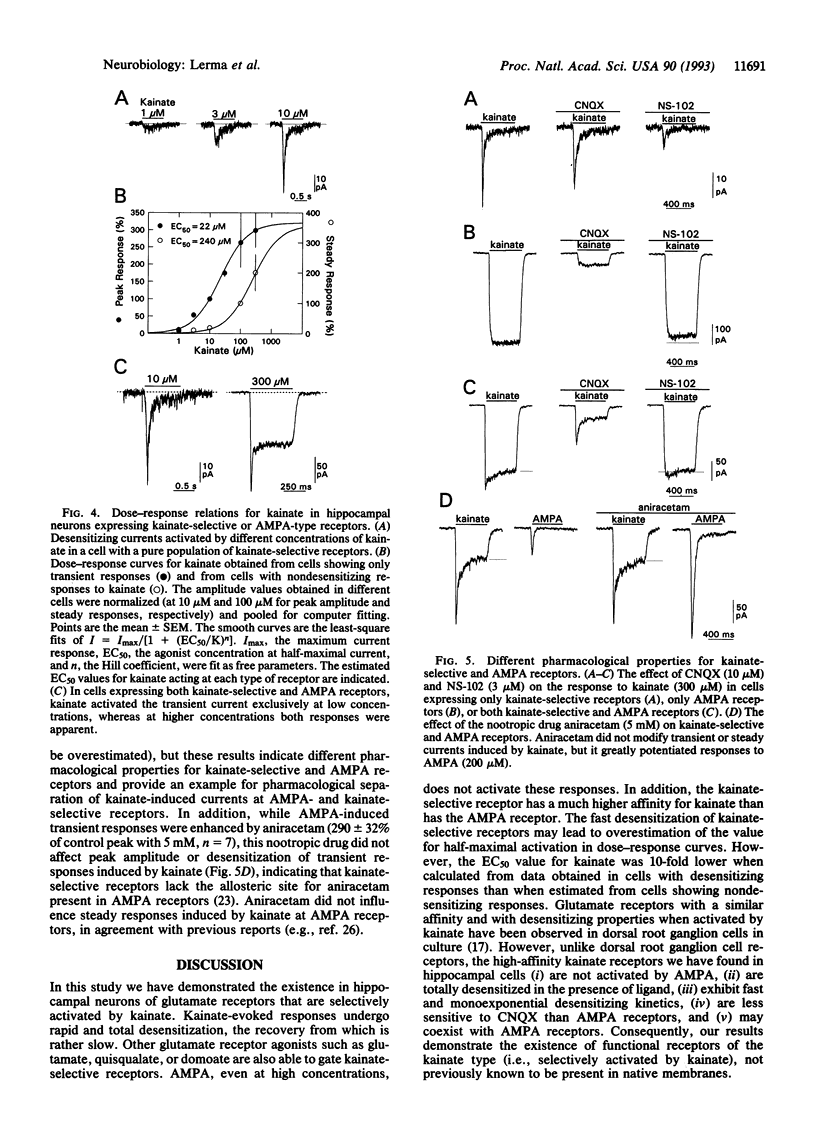

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal S. G., Evans R. H. The primary afferent depolarizing action of kainate in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;87(2):345–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Boulter J., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Deneris E. S., Moll C., Borgmeyer U., Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloning of a novel glutamate receptor subunit, GluR5: expression in the nervous system during development. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90213-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Hartley M., Deneris E., Maron C., Heinemann S. Molecular cloning and functional expression of glutamate receptor subunit genes. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1033–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2168579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Divalent ion permeability of AMPA receptor channels is dominated by the edited form of a single subunit. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Lester R. A. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):143–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Heinemann S. F. Ca2+ permeability of unedited and edited versions of the kainate selective glutamate receptor GluR6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herb A., Burnashev N., Werner P., Sakmann B., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. The KA-2 subunit of excitatory amino acid receptors shows widespread expression in brain and forms ion channels with distantly related subunits. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré T., Davies S. N., Drejer J., Fletcher E. J., Jacobsen P., Lodge D., Nielsen F. E. Quinoxalinediones: potent competitive non-NMDA glutamate receptor antagonists. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):701–703. doi: 10.1126/science.2899909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E. Glutamate receptor channels in rat DRG neurons: activation by kainate and quisqualate and blockade of desensitization by Con A. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):255–266. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90163-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume R. I., Dingledine R., Heinemann S. F. Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1028–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.1653450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito I., Tanabe S., Kohda A., Sugiyama H. Allosteric potentiation of quisqualate receptors by a nootropic drug aniracetam. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:533–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T. H., Drejer J., Wätjen F., Nielsen E. O. A novel non-NMDA receptor antagonist shows selective displacement of low-affinity [3H]kainate binding. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug 15;246(3):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas P., Sakmann B. Glutamate receptor channels in isolated patches from CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cells of rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:143–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):556–560. doi: 10.1126/science.2166337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler M., Burnashev N., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Determinants of Ca2+ permeability in both TM1 and TM2 of high affinity kainate receptor channels: diversity by RNA editing. Neuron. 1993 Mar;10(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90336-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambolez B., Audinat E., Bochet P., Crépel F., Rossier J. AMPA receptor subunits expressed by single Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerma J. Spermine regulates N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor desensitization. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain C. J., Dingledine R. Heterogeneity of synaptic glutamate receptors on CA3 stratum radiatum interneurones of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:373–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Sakimura K., Kushiya E., Yamazaki M., Meguro H., Araki K., Abe T., Mori K. J., Mishina M. Cloning and functional expression of a cDNA encoding the mouse beta 2 subunit of the kainate-selective glutamate receptor channel. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Jun;14(1-2):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi N., Shneider N. A., Axel R. A family of glutamate receptor genes: evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric receptors with distinct channel properties. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):569–581. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90212-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakimura K., Morita T., Kushiya E., Mishina M. Primary structure and expression of the gamma 2 subunit of the glutamate receptor channel selective for kainate. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90293-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Burnashev N., Verdoorn T. A., Keinänen K., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. A glutamate receptor channel with high affinity for domoate and kainate. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1651–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Seeburg P. H. Glutamate receptor channels: novel properties and new clones. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jul;13(7):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90088-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Burnashev N., Monyer H., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Structural determinants of ion flow through recombinant glutamate receptor channels. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1715–1718. doi: 10.1126/science.1710829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Fagg G. E. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the brain: membrane binding and receptor autoradiographic approaches. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Mar;11(3):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90199-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


