Abstract
A post-mortem examination, in the case of a 34-year-old man dying suddenly from head injuries sustained in a road accident, showed early cirrhosis of the liver and associated splenomegaly 17 years after an attack of infective hepatitis. The histology of the thymus showed abnormal changes in the medulla, consisting of epithelial hyperplasia and the presence of lymph follicles with germinal centres. It is suggested that an auto-immune mechanism underlay the pathogenesis of the cirrhosis and that the thymic changes were concerned with this.
Full text
PDF
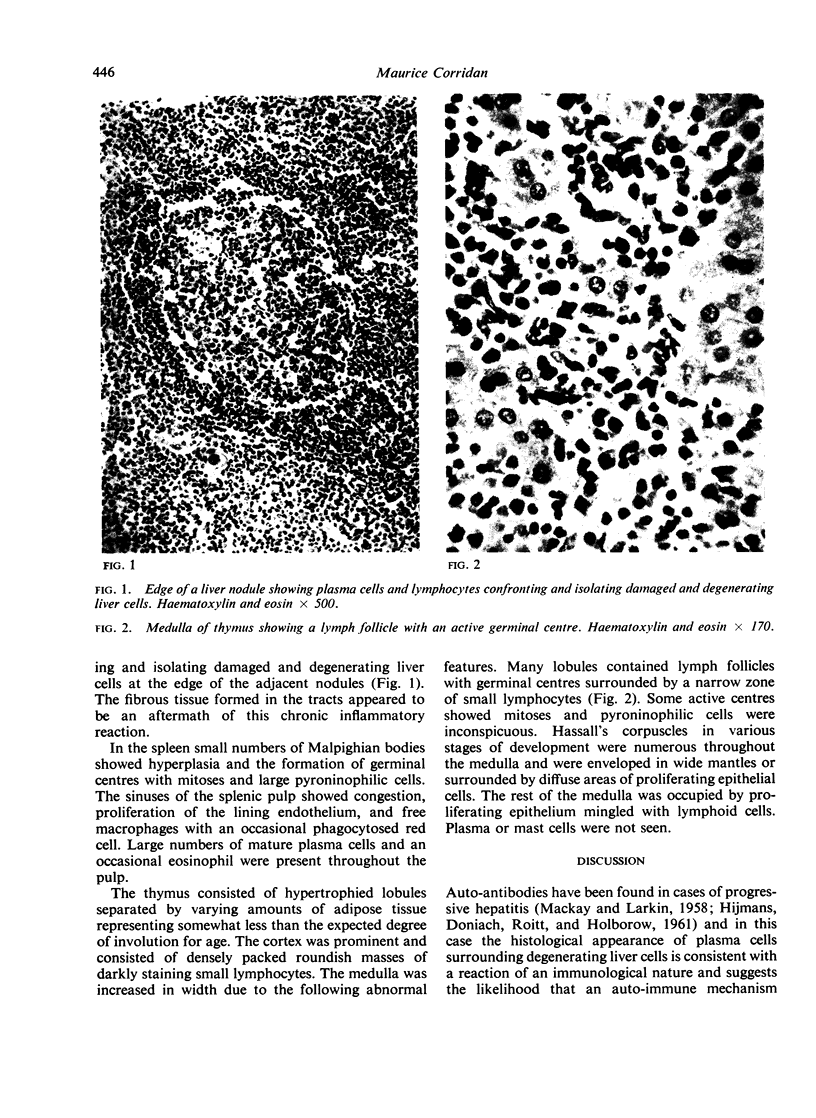

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNET F. M., MACKAY I. R. Lymphoepithelial structures and autoimmune disease. Lancet. 1962 Nov 17;2(7264):1030–1033. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)92710-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREUTZFELDT W., SCHMITT H., RICHERT J., KAISER K., MATTHES M. [Hepatitis transmissions over a period of 10 years by a blood donor with posthepatitis liver cirrhosis]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1962 Sep 7;87:1801–1804. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1114022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIJMANS W., DONIACH D., ROITT I. M., HOLBOROW E. J. Serological overlap between lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid auto-immune disease. Br Med J. 1961 Oct 7;2(5257):909–914. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5257.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAY I. R., LARKIN L. The significance of the presence in human serum of complement-fixing antibodies to human tissue antigens. Australas Ann Med. 1958 Aug;7(3):251–258. doi: 10.1111/imj.1958.7.3.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




