Abstract
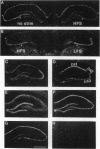
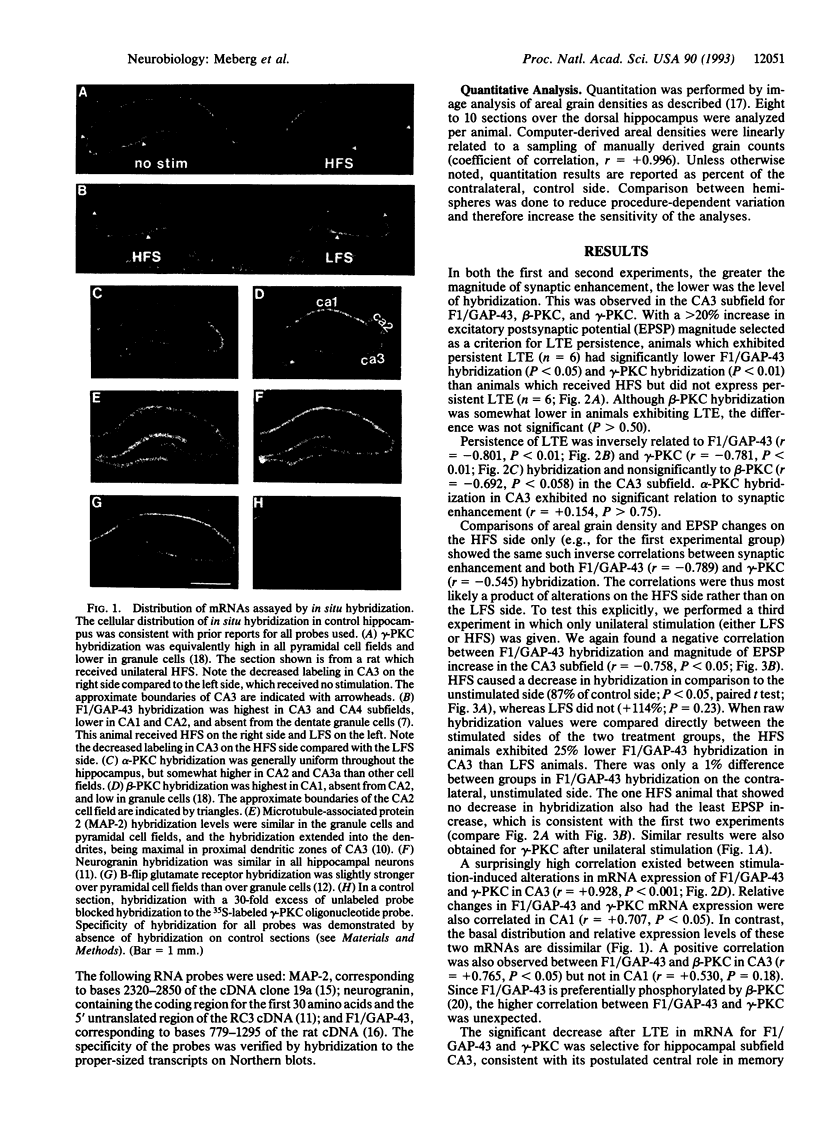
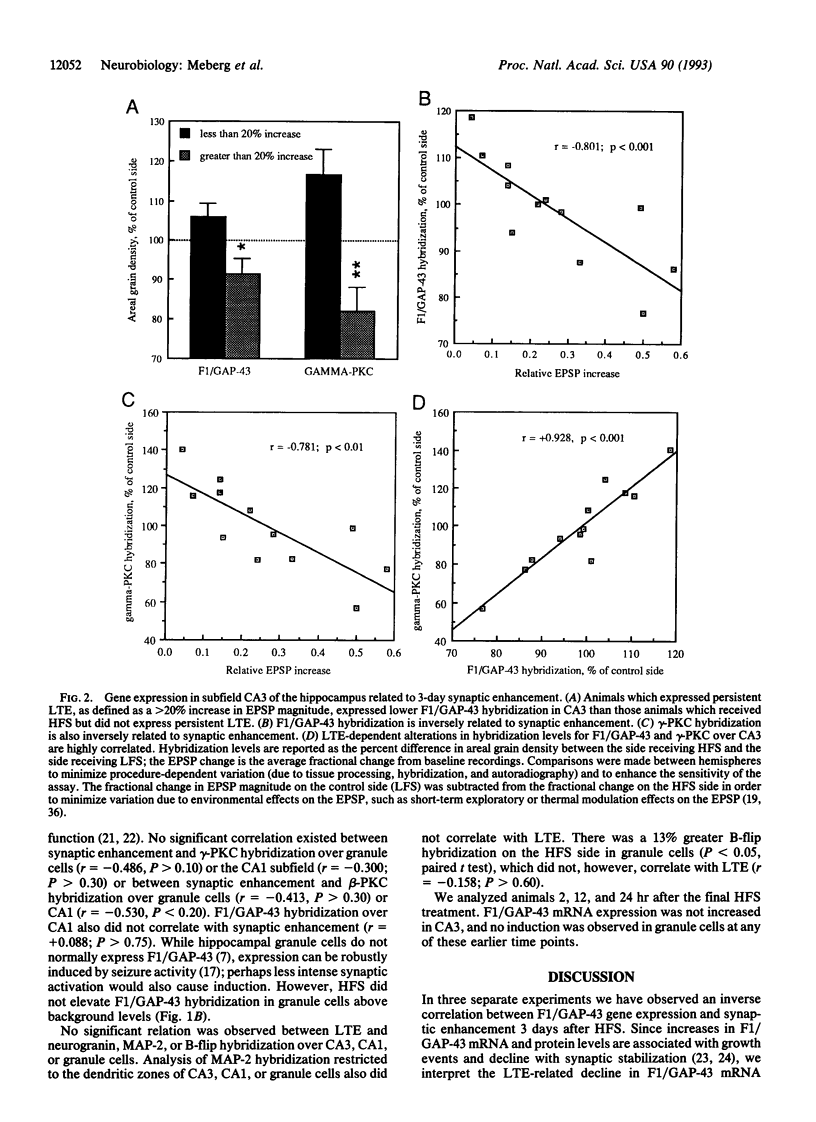
The mRNA levels of protein F1 (also known as GAP-43), and protein kinase C (PKC) subtypes were measured 3 days after the induction of long-term enhancement (also known as long-term potentiation) in the hippocampus of chronically prepared conscious rats by quantitative in situ hybridization. Altered mRNA levels correlated significantly with alternations in synaptic efficacy; such correlations have not been reported previously. Rats with greater synaptic enhancement had lower gene expression in the CA3 subfield of F1/GAP-43 and both beta-PKC and gamma-PKC, but not alpha-PKC. For microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2), neurogranin, and the glutamate receptor subtype B-flip, no correlation was observed in any cell field between synaptic enhancement and hybridization to the mRNA. To our surprise, alterations in mRNA levels of F1/GAP-43 and gamma-PKC were highly correlated (r = +0.928, P < 0.001), suggesting coordinate regulation. Since F1/GAP-43 is associated with neurite growth, its lowered expression at 3 days would reduce potential growth, leading to synaptic stabilization. We propose that long-term synaptic change is mediated by gene expression of the very same proteins initially modified posttranslationally.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akers R. F., Lovinger D. M., Colley P. A., Linden D. J., Routtenberg A. Translocation of protein kinase C activity may mediate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):587–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3003904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki C., Siekevitz P. Ontogenetic changes in the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-stimulatable phosphorylation of cat visual cortex proteins, particularly of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP 2): effects of normal and dark rearing and of the exposure to light. J Neurosci. 1985 Sep;5(9):2465–2483. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-09-02465.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G. S., Jacobson R. D., Virág I., Schilling J., Skene J. H. Primary structure and transcriptional regulation of GAP-43, a protein associated with nerve growth. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):785–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudier J., Deloulme J. C., Van Dorsselaer A., Black D., Matthes H. W. Purification and characterization of a brain-specific protein kinase C substrate, neurogranin (p17). Identification of a consensus amino acid sequence between neurogranin and neuromodulin (GAP43) that corresponds to the protein kinase C phosphorylation site and the calmodulin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):229–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt S. J., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M., Young W. S., 3rd Distinct patterns of expression of different protein kinase C mRNAs in rat tissues. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90755-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. J., Saffen D. W., Baraban J. M., Worley P. F. Rapid increase of an immediate early gene messenger RNA in hippocampal neurons by synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):474–476. doi: 10.1038/340474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner C. C., Tucker R. P., Matus A. Selective localization of messenger RNA for cytoskeletal protein MAP2 in dendrites. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):674–677. doi: 10.1038/336674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianotti C., Nunzi M. G., Gispen W. H., Corradetti R. Phosphorylation of the presynaptic protein B-50 (GAP-43) is increased during electrically induced long-term potentiation. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):843–848. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90198-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapiloff M. S., Farkash Y., Wegner M., Rosenfeld M. G. Variable effects of phosphorylation of Pit-1 dictated by the DNA response elements. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):786–789. doi: 10.1126/science.1652153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler S., Schwanke B., Schulz B., Garner C. C. Complete cDNA sequence encoding rat high and low molecular weight MAP2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 11;18(9):2822–2822. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.9.2822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Lee M. H., Sultzman L. A., Kriz R. W., Loomis C. R., Hewick R. M., Bell R. M. Cloning and expression of multiple protein kinase C cDNAs. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M., Akers R. F., Nelson R. B., Barnes C. A., McNaughton B. L., Routtenberg A. A selective increase in phosporylation of protein F1, a protein kinase C substrate, directly related to three day growth of long term synaptic enhancement. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 16;343(1):137–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Riederer B. Microtubule-associated proteins in the developing brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:167–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meberg P. J., Gall C. M., Routtenberg A. Induction of F1/GAP-43 gene expression in hippocampal granule cells after seizures [corrected]. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Mar;17(3-4):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90014-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meberg P. J., Routtenberg A. Selective expression of protein F1/(GAP-43) mRNA in pyramidal but not granule cells of the hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1991;45(3):721–733. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90284-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser E., Mathiesen I., Andersen P. Association between brain temperature and dentate field potentials in exploring and swimming rats. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1324–1326. doi: 10.1126/science.8446900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Igarashi K., Kikkawa U., Ogita K., Nishizuka Y. Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs for alpha and gamma subspecies of rat brain protein kinase C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5199–5200. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S. L., Grover L. M., Schwartzkroin P. A., Bothwell M. Neurotrophin expression in rat hippocampal slices: a stimulus paradigm inducing LTP in CA1 evokes increases in BDNF and NT-3 mRNAs. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1081–1088. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90067-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone-Bizzozero N. I., Cansino V. V., Kohn D. T. Posttranscriptional regulation of GAP-43 gene expression in PC12 cells through protein kinase C-dependent stabilization of the mRNA. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1263–1270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Z., Gilbert M. E., Colicos M. A., Kandel E. R., Kuhl D. Tissue-plasminogen activator is induced as an immediate-early gene during seizure, kindling and long-term potentiation. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):453–457. doi: 10.1038/361453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Represa A., Deloulme J. C., Sensenbrenner M., Ben-Ari Y., Baudier J. Neurogranin: immunocytochemical localization of a brain-specific protein kinase C substrate. J Neurosci. 1990 Dec;10(12):3782–3792. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-12-03782.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Chan S. Y., Henzel W., Haskell C., Kuang W. J., Chen E., Wilcox J. N., Ullrich A., Goeddel D. V., Routtenberg A. Primary structure and mRNA localization of protein F1, a growth-related protein kinase C substrate associated with synaptic plasticity. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3641–3646. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. S., Maren S., Tocco G., Shors T. J., Thompson R. F. A negative correlation between the induction of long-term potentiation and activation of immediate early genes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Aug;11(1):89–91. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90025-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Flow of conditioned responses in limbic telencephalic system of the rat. J Neurophysiol. 1973 Sep;36(5):840–854. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.5.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu F. S., Marais R. M., Parker P. J., Bazan N. G., Routtenberg A. Neuron-specific protein F1/GAP-43 shows substrate specificity for the beta subtype of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1236–1243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90818-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Keinänen K., Verdoorn T. A., Wisden W., Burnashev N., Herb A., Köhler M., Takagi T., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Flip and flop: a cell-specific functional switch in glutamate-operated channels of the CNS. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1580–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1699275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward O. Topographic organization of the projections from the entorhinal area to the hippocampal formation of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1976 Jun 1;167(3):285–314. doi: 10.1002/cne.901670303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. B., Battenberg E. F., Wong K. K., Bloom F. E., Sutcliffe J. G. Subtractive cDNA cloning of RC3, a rodent cortex-enriched mRNA encoding a novel 78 residue protein. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Aug;26(4):397–408. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Errington M. L., Williams S., Dunnett S. B., Waters C., Hitchcock D., Evan G., Bliss T. V., Hunt S. P. Differential expression of immediate early genes in the hippocampus and spinal cord. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90118-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Morris B. J., Darlison M. G., Hunt S. P., Barnard E. A. Distinct GABAA receptor alpha subunit mRNAs show differential patterns of expression in bovine brain. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):937–947. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]