Abstract
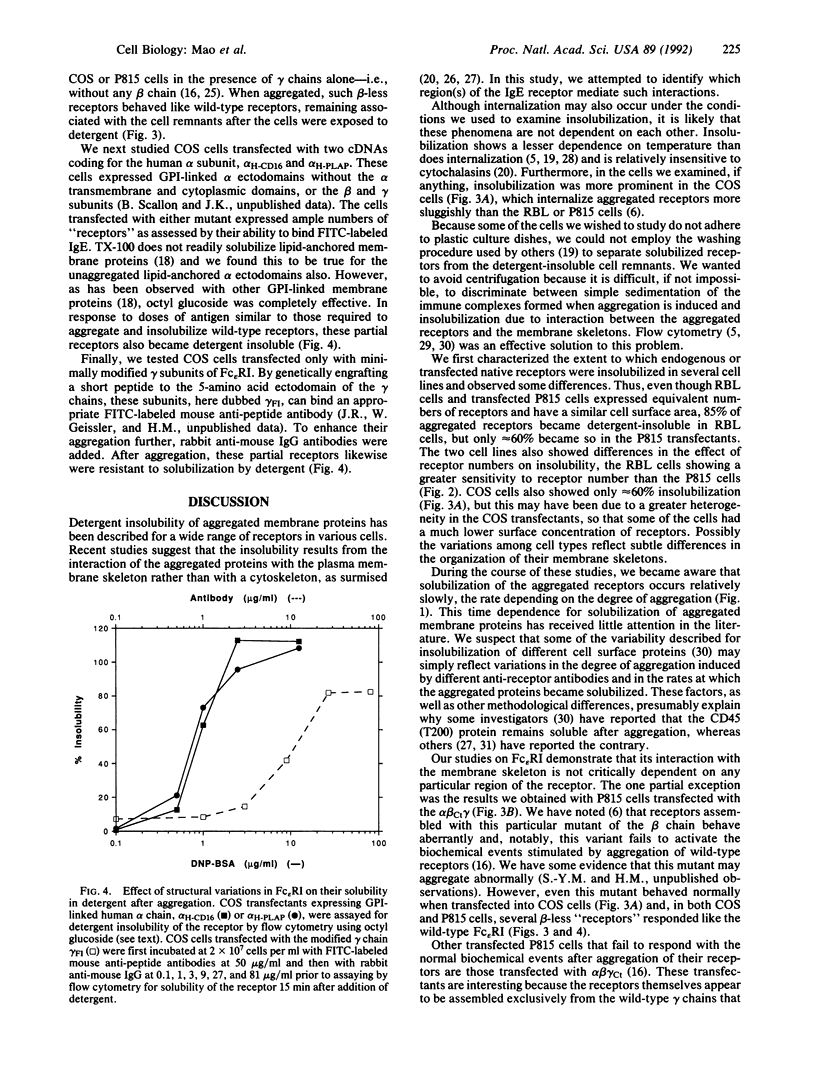
When aggregated, cell surface proteins become resistant to solubilization by detergents, presumably because of aggregation-induced or -stabilized interactions between the membrane protein and the cytoskeleton or plasma membrane skeleton. We genetically engineered variants of the tetrameric high-affinity receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon RI) to identify a site on its alpha, beta, or gamma chains that mediates such putative interactions. Using flow cytofluorometry, we studied rat basophilic leukemia cells, transiently transfected COS cells, and stably transfected P815 cells bearing wild-type and mutated receptors. We observed that (i) solubilization was markedly dependent on the degree of aggregation, the extent varying somewhat with the cell type and, particularly at lower levels of aggregation, with the time after addition of detergent; (ii) truncation of no single cytoplasmic domain of the alpha, beta, or gamma chains ablated the insolubilization effect; and (iii) incomplete receptors were also efficiently insolubilized by aggregation. Thus receptors consisting only of alpha and gamma chains, a "receptor" consisting of only the ectodomain of the alpha chain attached to the plasma membrane by a glycosyl-phosphatidyl inositol anchor, and "receptors" consisting only of minimally modified gamma chains were resistant to solubilization after aggregation. We conclude that no unique subunit or domain of Fc epsilon RI mediates the insolubilization phenomenon. Our results support a model in which the bridging of membrane proteins leads to their becoming nonspecifically enmeshed in a network of membrane skeletal proteins on either the outside and/or the inside of the membrane so that dissolution of the lipid bilayer becomes irrelevant.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht D. L., Noelle R. J. Membrane Ig-cytoskeletal interactions. I. Flow cytofluorometric and biochemical analysis of membrane IgM-cytoskeletal interactions. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3915–3922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apgar J. R. Antigen-induced cross-linking of the IgE receptor leads to an association with the detergent-insoluble membrane skeleton of rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cells. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3814–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apgar J. R. Association of the crosslinked IgE receptor with the membrane skeleton is independent of the known signaling mechanisms in rat basophilic leukemia cells. Cell Regul. 1991 Mar;2(3):181–191. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apgar J. R., Herrmann S. H., Robinson J. M., Mescher M. F. Triton X-100 extraction of P815 tumor cells: evidence for a plasma membrane skeleton structure. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1369–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsumian E. L., Isersky C., Petrino M. G., Siraganian R. P. IgE-induced histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia cell lines: isolation of releasing and nonreleasing clones. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Apr;11(4):317–323. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazin H., Querinjean P., Beckers A., Heremans J. F., Dessy F. Transplantable immunoglobulin-secreting tumours in rats. IV. Sixty-three IgE-secreting immunocytoma tumours. Immunology. 1974 Apr;26(4):713–723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker K. E., Ishizaka T., Metzger H., Ishizaka K., Grimley P. M. Surface IgE on human basophils during histamine release. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):394–409. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank U., Ra C., Miller L., White K., Metzger H., Kinet J. P. Complete structure and expression in transfected cells of high affinity IgE receptor. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):187–189. doi: 10.1038/337187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Suchard S. J., Nagpal M. L., Glenney J. R., Jr A T-lymphoma transmembrane glycoprotein (gp180) is linked to the cytoskeletal protein, fodrin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):477–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert T. D., Lipsky P. E. Association of various T cell-surface molecules with the cytoskeleton. Effect of cross-linking and activation. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3298–3305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holowka D., Metzger H. Further characterization of the beta-component of the receptor for immunoglobulin E. Mol Immunol. 1982 Feb;19(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Differential solubilization by detergents can predict a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):865–869. doi: 10.1042/bj2500865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isersky C., Kulczycki A., Jr, Metzger H. Isolation of IgE from reaginic rat serum. J Immunol. 1974 May;112(5):1909–1919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Bohn J. W., Ferry E. L., Yamamoto H., Molinaro C. A., Sherman L. A., Klinman N. R., Katz D. H. Monoclonal dinitrophenyl-specific murine IgE antibody: preparation, isolation, and characterization. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2728–2737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao S. Y., Varin-Blank N., Edidin M., Metzger H. Immobilization and internalization of mutated IgE receptors in transfected cells. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):958–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza G., Metzger H. Distribution and valency of receptor for IgE on rodent mast cells and related tumour cells. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):548–550. doi: 10.1038/264548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H., Alcaraz G., Hohman R., Kinet J. P., Pribluda V., Quarto R. The receptor with high affinity for immunoglobulin E. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:419–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Alber G., Varin-Blank N., Ludowyke R., Metzger H. Transmembrane signaling in P815 mastocytoma cells by transfected IgE receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12444–12453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Blank U., Metzger H., Kinet J. P. Expression of high-affinity binding of human immunoglobulin E by transfected cells. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):334–337. doi: 10.1126/science.2523561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Seagrave J., Stump R. F., Pfeiffer J. R., Deanin G. G. Signal transduction and cellular response in RBL-2H3 mast cells. Prog Allergy. 1988;42:185–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Holowka D., Baird B. Cross-linking of immunoglobulin E-receptor complexes induces their interaction with the cytoskeleton of rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4565–4572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Webb W. W., Elson E. L., Metzger H. Lateral motion and valence of Fc receptors on rat peritoneal mast cells. Nature. 1976 Dec 9;264(5586):550–552. doi: 10.1038/264550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Haimovich J. Quantitative fluorometric assay for detection and characterization of Fc receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;93:147–155. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)93039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seagrave J., Oliver J. M. Antigen-dependent transition of IgE to a detergent-insoluble form is associated with reduced IgE receptor-dependent secretion from RBL-2H3 mast cells. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Jul;144(1):128–136. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041440117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taffs R. E., Ewald S. J. Concanavalin A induces a cytoskeletal association of T200 molecules in T lymphocytes. Mol Immunol. 1989 Oct;26(10):925–937. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Mendoza G. R., Hook W. A., Siraganian R. P., Metzger H. Noncytotoxic IgE-mediated release of histamine and serotonin from murine mastocytoma cells. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1757–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Ohnishi S. Restriction of the lateral motion of band 3 in the erythrocyte membrane by the cytoskeletal network: dependence on spectrin association state. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6133–6139. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varin-Blank N., Metzger H. Surface expression of mutated subunits of the high affinity mast cell receptor for IgE. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15685–15694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zidovetzki R., Bartholdi M., Arndt-Jovin D., Jovin T. M. Rotational dynamics of the Fc receptor for immunoglobulin E on histamine-releasing rat basophilic leukemia cells. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4397–4401. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belzen N., Spaargaren M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Interaction of epidermal growth factor receptors with the cytoskeleton is related to receptor clustering. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Nov;145(2):365–375. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


