Abstract
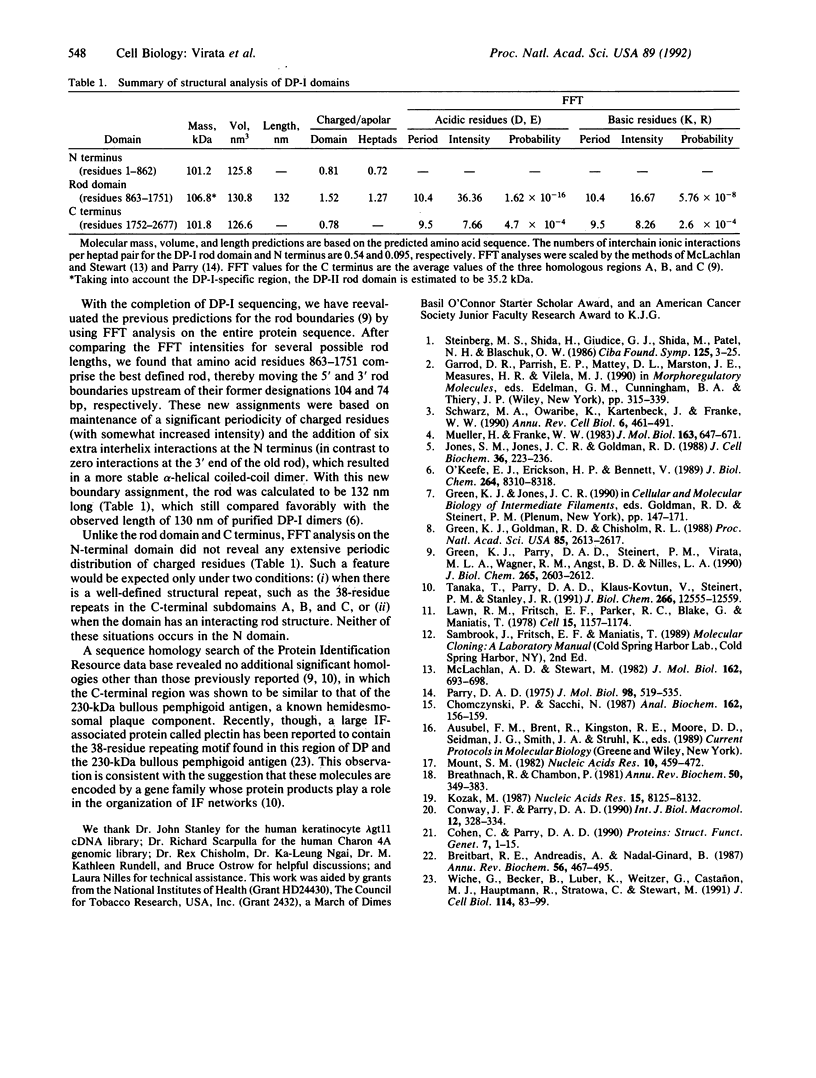
Desmoplakins (DPs) I and II are closely related proteins found in the innermost region of the desmosomal plaque, which serves as a cell surface attachment site for cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. Overlapping cDNA clones comprising 9.2 kilobases of DP-I, predicted to encode a full-length 310-kDa polypeptide (2677 amino acid residues), have now been identified. Here we report the predicted protein sequence and structural analysis of the N terminus of DP, extending our previous study of the rod and carboxyl domains. The N terminus contains groups of heptad repeats that are predicted to form at least two major alpha-helical-rich bundles. Unlike the rod and carboxyl domains, the N terminus did not display a periodic distribution of charged residues. Northern blot mapping and genomic sequence analysis were also undertaken to examine the organization of the DP mRNAs. A 1-kilobase intron was located at the 3' boundary of a DP-I-specific region; however, instead of an intron at the 5' junction, a possible splice donor site was observed within a potential coding sequence, suggesting alternative RNA splicing from an internal donor site.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Andreadis A., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing: a ubiquitous mechanism for the generation of multiple protein isoforms from single genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:467–495. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Parry D. A. Alpha-helical coiled coils and bundles: how to design an alpha-helical protein. Proteins. 1990;7(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway J. F., Parry D. A. Structural features in the heptad substructure and longer range repeats of two-stranded alpha-fibrous proteins. Int J Biol Macromol. 1990 Oct;12(5):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0141-8130(90)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Goldman R. D., Chisholm R. L. Isolation of cDNAs encoding desmosomal plaque proteins: evidence that bovine desmoplakins I and II are derived from two mRNAs and a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2613–2617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Parry D. A., Steinert P. M., Virata M. L., Wagner R. M., Angst B. D., Nilles L. A. Structure of the human desmoplakins. Implications for function in the desmosomal plaque. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2603–2612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Jones J. C., Goldman R. D. Fractionation of desmosomes and comparison of the polypeptide composition of desmosomes prepared from two bovine epithelial tissues. J Cell Biochem. 1988 Mar;36(3):223–236. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240360304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M. Periodic charge distribution in the intermediate filament proteins desmin and vimentin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):693–698. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90396-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller H., Franke W. W. Biochemical and immunological characterization of desmoplakins I and II, the major polypeptides of the desmosomal plaque. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):647–671. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe E. J., Erickson H. P., Bennett V. Desmoplakin I and desmoplakin II. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8310–8318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A. Analysis of the primary sequence of alpha-tropomyosin from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):519–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz M. A., Owaribe K., Kartenbeck J., Franke W. W. Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes: constitutive molecular components. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:461–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg M. S., Shida H., Giudice G. J., Shida M., Patel N. H., Blaschuk O. W. On the molecular organization, diversity and functions of desmosomal proteins. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;125:3–25. doi: 10.1002/9780470513408.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Parry D. A., Klaus-Kovtun V., Steinert P. M., Stanley J. R. Comparison of molecularly cloned bullous pemphigoid antigen to desmoplakin I confirms that they define a new family of cell adhesion junction plaque proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12555–12559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Becker B., Luber K., Weitzer G., Castañon M. J., Hauptmann R., Stratowa C., Stewart M. Cloning and sequencing of rat plectin indicates a 466-kD polypeptide chain with a three-domain structure based on a central alpha-helical coiled coil. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):83–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]