Abstract
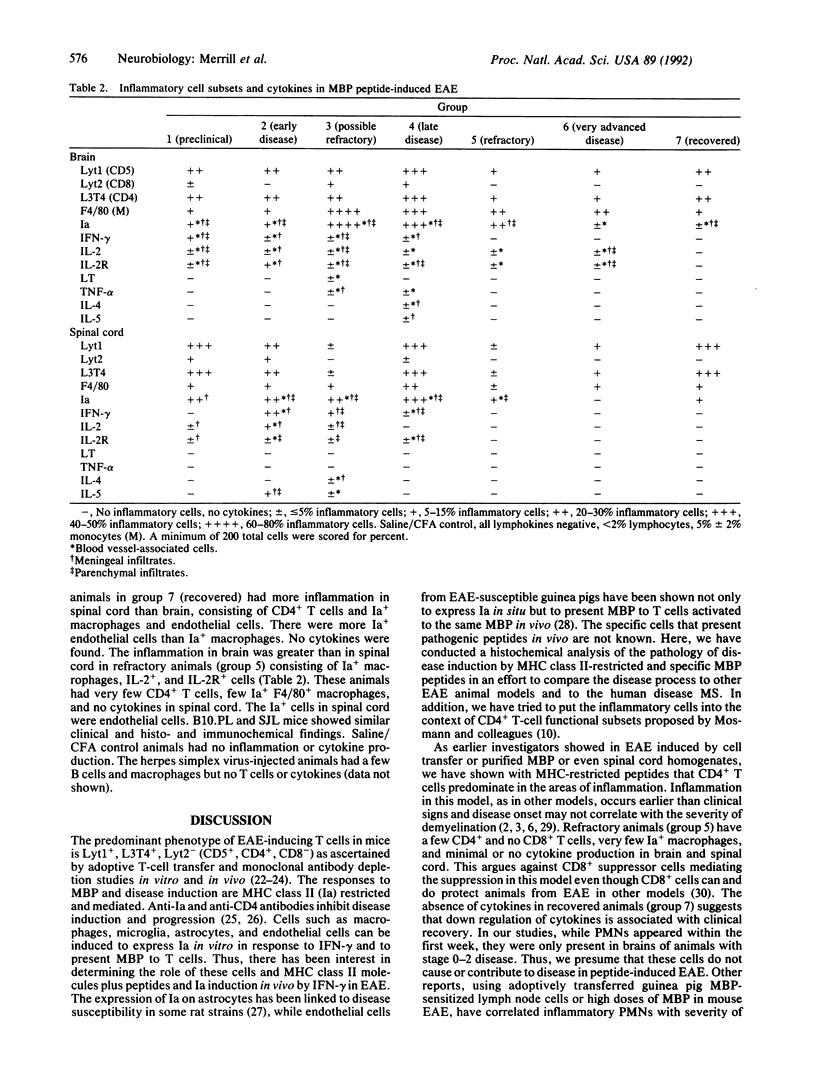
Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) was generated in SJL and B10.PL mice by using the synthetic myelin basic protein peptides. Inflammation in brain and spinal cord preceded clinical signs of disease. Infiltrating lymphocytes were predominantly Lyt1+ (CD5+), L3T4+ (CD4+) T cells, until day 18. After that, F4/80+ monocyte/macrophages outnumbered T cells. Ia+ cells were microglia, macrophages, and endothelial cells, but Ia was not detectable on astrocytes in this EAE model. Ia+ endothelial cells appeared later in the disease than Ia+ microglia and macrophages, suggesting that antigen presentation at the blood-brain barrier is not initially responsible for inflammation. Cells staining for interferon gamma, interleukin 2 (IL-2), and IL-2 receptors were more prominent than IL-4, IL-5, lymphotoxin (LT), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), which occurred transiently in the second week and were associated with fewer cells. TNF-alpha and LT were never seen in spinal cord, suggesting that these cytokines are not responsible for initiation of clinical disease. Few or no cells stained for IL-6, IL-1, or transforming growth factor beta. Control animals injected with complete Freund's adjuvant in saline or control antigen demonstrated no inflammatory cell infiltration or cytokine production. Thus, our findings suggest a peptide-induced EAE model in which Th1 T-cell-macrophage interactions result in the disease process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando D. G., Clayton J., Kono D., Urban J. L., Sercarz E. E. Encephalitogenic T cells in the B10.PL model of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) are of the Th-1 lymphokine subtype. Cell Immunol. 1989 Nov;124(1):132–143. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Nun A., Wekerle H., Cohen I. R. The rapid isolation of clonable antigen-specific T lymphocyte lines capable of mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):195–199. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherwinski H. M., Schumacher J. H., Brown K. D., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse helper T cell clone. III. Further differences in lymphokine synthesis between Th1 and Th2 clones revealed by RNA hybridization, functionally monospecific bioassays, and monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1229–1244. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton J. P., Gammon G. M., Ando D. G., Kono D. H., Hood L., Sercarz E. E. Peptide-specific prevention of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neonatal tolerance induced to the dominant T cell determinant of myelin basic protein. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1681–1691. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Restricted replication of herpes simplex virus in spinal ganglia of resistant mice is accompanied by an early infiltration of immunoglobulin G-bearing cells. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):752–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.752-758.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Rabinowitz S. G. Experimental models of virus-induced demyelination of the central nervous system. Ann Neurol. 1982 Feb;11(2):109–127. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2081–2095. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Malipiero U. V., Leist T. P., Zinkernagel R. M., Schwab M. E., Fontana A. On the cellular source and function of interleukin 6 produced in the central nervous system in viral diseases. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):689–694. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gijbels K., Van Damme J., Proost P., Put W., Carton H., Billiau A. Interleukin 6 production in the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):233–235. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Baemayr J., Weil M., Merrill J. E. Lymphokines and immunoregulatory molecules in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Mar;58(3):331–342. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(91)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., Hinton D. R., Johnson K., Merrill J. E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman F. M., von Hanwehr R. I., Dinarello C. A., Mizel S. B., Hinton D., Merrill J. E. Immunoregulatory molecules and IL 2 receptors identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3239–3245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono D. H., Urban J. L., Horvath S. J., Ando D. G., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. Two minor determinants of myelin basic protein induce experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL/J mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):213–227. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Weigle W. O. Passive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by myelin basic protein-specific L3T4+ T cell clones possessing several functions. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3169–3174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Robb R. J., Shevach E. M. Identification and initial characterization of a rat monoclonal antibody reactive with the murine interleukin 2 receptor-ligand complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5694–5698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa P. T., ter Meulen V., Fontana A. Hyperinducibility of Ia antigen on astrocytes correlates with strain-specific susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4219–4223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Kagan J. M., Schmid I., Strom S. R., Quan S. G., Chen I. S. T cell lines established from multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid T cells using human retroviruses. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Feb;21(2-3):213–226. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Moore K. W. The role of IL-10 in crossregulation of TH1 and TH2 responses. Immunol Today. 1991 Mar;12(3):A49–A53. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara J., Paul W. E. Production of a monoclonal antibody to and molecular characterization of B-cell stimulatory factor-1. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):333–336. doi: 10.1038/315333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., Hirsch R. L., Schindler J., Johnson K. P. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with gamma interferon: exacerbations associated with activation of the immune system. Neurology. 1987 Jul;37(7):1097–1102. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.7.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinelli C. B., McFarlin D. E. Adoptive transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in SJL/J mice after in vitro activation of lymph node cells by myelin basic protein: requirement for Lyt 1+ 2- T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1420–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell M. B., Mitchell D., Lederman J., Buckmeier J., Zamvil S. S., Graham M., Ruddle N. H., Steinman L. Lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by myelin basic protein-specific T cell clones correlates with encephalitogenicity. Int Immunol. 1990;2(6):539–544. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.6.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Mokhtarian F., McFarlin D. E. Adoptively transferred chronic relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Neuropathologic analysis. Lab Invest. 1984 Nov;51(5):534–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H., Bergman C. M., McGrath K. M., Lingenheld E. G., Grunnet M. L., Padula S. J., Clark R. B. An antibody to lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor prevents transfer of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1193–1200. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Tabira T., Endoh M., Steinman L. Ia expression in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis induced by long-term cultured T cell lines in mice. Lab Invest. 1986 Mar;54(3):345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher J. H., O'Garra A., Shrader B., van Kimmenade A., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R., Coffman R. L. The characterization of four monoclonal antibodies specific for mouse IL-5 and development of mouse and human IL-5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1576–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sriram S., Steinman L. Anti I-A antibody suppresses active encephalomyelitis: treatment model for diseases linked to IR genes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1362–1367. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Qin Y., Chluba J., Epplen J. T., Wekerle H. Suppression of experimentally induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis by cytolytic T-T cell interactions. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):843–845. doi: 10.1038/332843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E. Acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse: immunopathology of the developing lesion. Cell Immunol. 1985 Mar;91(1):240–254. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J., Steinman L. Homing of Lyt-2+ and Lyt-2- T cell subsets and B lymphocytes to the central nervous system of mice with acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2919–2923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldor M. K., Sriram S., Hardy R., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A., Lanier L., Lim M., Steinman L. Reversal of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis with monoclonal antibody to a T-cell subset marker. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):415–417. doi: 10.1126/science.3155574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K., Stevens J. G., Cook M. L., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Latency competence of thirteen HSV-1 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jul;49(1):149–159. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-49-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. E., Baker D., Butter C., Willoughby D. A., Turk J. L. Differential expression of guinea pig class II major histocompatibility complex antigens on vascular endothelial cells in vitro and in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):82–91. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Moore A. C., Kitamura K., Steinman L., Rothbard J. B. T-cell epitope of the autoantigen myelin basic protein that induces encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):258–260. doi: 10.1038/324258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]