Abstract
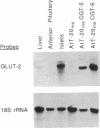
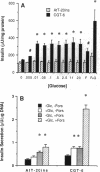
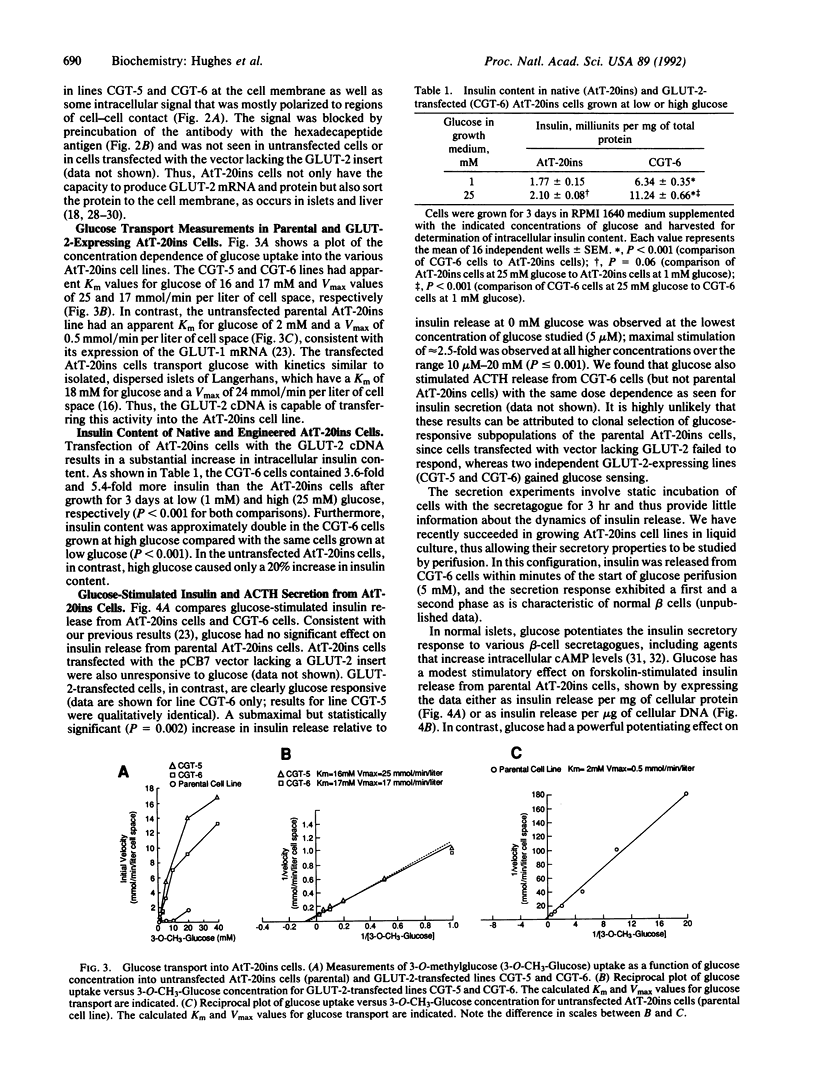
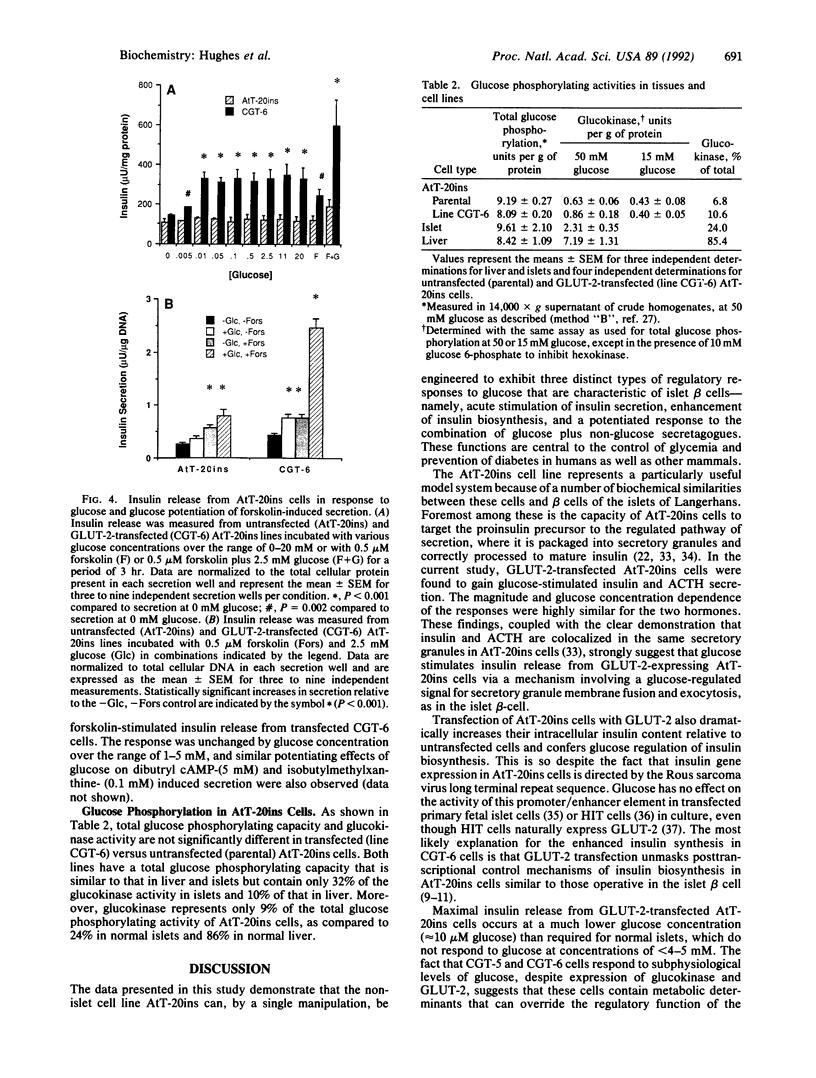
The high-capacity glucose transporter known as GLUT-2 and the glucose phosphorylating enzyme glucokinase are thought to be key components of the "glucose-sensing apparatus" that regulates insulin release from the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in response to changes in external glucose concentration. AtT-20ins cells are derived from anterior pituitary cells and are like beta cells in that they express glucokinase and have been engineered to secrete correctly processed insulin in response to analogs of cAMP, but, unlike beta cells, they fail to respond to glucose and lack GLUT-2 expression. Herein we demonstrate that stable transfection of AtT-20ins cells with the GLUT-2 cDNA confers glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and glucose regulation of insulin biosynthesis and also results in glucose potentiation of the secretory response to non-glucose secretagogues. This work represents a first step toward creation of a genetically engineered "artificial beta cell."
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson S., Davis D. L., Dahlbäck H., Jörnvall H., Russell D. W. Cloning, structure, and expression of the mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 sterol 26-hydroxylase, a bile acid biosynthetic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8222–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J. Glucoreceptor mechanisms and the control of insulin release and biosynthesis. Diabetologia. 1980 Jan;18(1):5–15. doi: 10.1007/BF01228295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Burant C. F., Takeda J., Lin D., Fukumoto H., Seino S. Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):198–208. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Alam T., Johnson J. H., Hughes S., Newgard C. B., Unger R. H. Regulation of beta-cell glucose transporter gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4088–4092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Moss L. G., Rutter W. J. Regulation of insulin gene expression by glucose and calcium in transfected primary islet cultures. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22063–22066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. J., Halban P. A., Kahn C. R., Weir G. C., Villa-Komaroff L. Partial diversion of a mutant proinsulin (B10 aspartic acid) from the regulated to the constitutive secretory pathway in transfected AtT-20 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4107–4111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeskov C. J. Mechanism of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):442–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. D., Quaade C., Milburn J. L., Cassidy L., Newgard C. B. Expression of normal and novel glucokinase mRNAs in anterior pituitary and islet cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4521–4530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Crider B. P., McCorkle K., Alford M., Unger R. H. Inhibition of glucose transport into rat islet cells by immunoglobulins from patients with new-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 8;322(10):653–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003083221003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Newgard C. B., Milburn J. L., Lodish H. F., Thorens B. The high Km glucose transporter of islets of Langerhans is functionally similar to the low affinity transporter of liver and has an identical primary sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6548–6551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. H., Ogawa A., Chen L., Orci L., Newgard C. B., Alam T., Unger R. H. Underexpression of beta cell high Km glucose transporters in noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.2237405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima M., Newgard C. B., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. The glucose-phosphorylating capacity of liver as measured by three independent assays. Implications for the mechanism of hepatic glycogen synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8849–8853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Scharp D. W. Islet transplantation in treating diabetes. Annu Rev Med. 1986;37:33–40. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.37.020186.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Garcia-Morales P., Dufrane S. P., Sener A., Valverde I. Forskolin-induced activation of adenylate cyclase, cyclic adenosine monophosphate production and insulin release in rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):2015–2020. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Rasschaert J., Zähner D., Sener A., Davies D. R., Van Schaftingen E. The fuel concept for insulin release: regulation of glucose phosphorylation in pancreatic islets. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Feb;18(1):107–108. doi: 10.1042/bst0180107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meglasson M. D., Matschinsky F. M. Pancreatic islet glucose metabolism and regulation of insulin secretion. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1986;2(3-4):163–214. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610020301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Walker M. D., Lee F., Kelly R. B. Expressing a human proinsulin cDNA in a mouse ACTH-secreting cell. Intracellular storage, proteolytic processing, and secretion on stimulation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Nakano K., Hwang P. K., Fletterick R. J. Sequence analysis of the cDNA encoding human liver glycogen phosphorylase reveals tissue-specific codon usage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8132–8136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Quaade C., Hughes S. D., Milburn J. L. Glucokinase and glucose transporter expression in liver and islets: implications for control of glucose homoeostasis. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Oct;18(5):851–853. doi: 10.1042/bst0180851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Welsh M., Casadaban M. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. I. Effects of glucose and cyclic AMP on the transcription of insulin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13585–13589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Powell S. K., Quinn D. L., Moore H. P. The trans-most cisternae of the Golgi complex: a compartment for sorting of secretory and plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Baetens D., Inman L., Amherdt M., Peterson R. G., Newgard C. B., Johnson J. H., Unger R. H. Evidence that down-regulation of beta-cell glucose transporters in non-insulin-dependent diabetes may be the cause of diabetic hyperglycemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9953–9957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Thorens B., Ravazzola M., Lodish H. F. Localization of the pancreatic beta cell glucose transporter to specific plasma membrane domains. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.2665080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaade C., Hughes S. D., Coats W. S., Sestak A. L., Iynedjian P. B., Newgard C. B. Analysis of the protein products encoded by variant glucokinase transcripts via expression in bacteria. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 11;280(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80201-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossini A. A., Mordes J. P., Like A. A. Immunology of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:289–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., Schneider D. L., Thorens B., Lodish H. F. Restricted expression of the erythroid/brain glucose transporter isoform to perivenous hepatocytes in rats. Modulation by glucose. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):986–992. doi: 10.1172/JCI114801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F. Molecular physiology of glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):209–218. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Weir G. C., Leahy J. L., Lodish H. F., Bonner-Weir S. Reduced expression of the liver/beta-cell glucose transporter isoform in glucose-insensitive pancreatic beta cells of diabetic rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6492–6496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Wolf B. A., McDaniel M. L. The role of phospholipid-derived mediators including arachidonic acid, its metabolites, and inositoltrisphosphate and of intracellular Ca2+ in glucose-induced insulin secretion by pancreatic islets. Prog Lipid Res. 1987;26(2):125–181. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(87)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich S., Wollheim C. B. Islet cyclic AMP levels are not lowered during alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of insulin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4111–4115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhouse S. Regulation of glucokinase in liver. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;11:1–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Nielsen D. A., MacKrell A. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. II. Regulation of insulin mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13590–13594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Scherberg N., Gilmore R., Steiner D. F. Translational control of insulin biosynthesis. Evidence for regulation of elongation, initiation and signal-recognition-particle-mediated translational arrest by glucose. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):459–467. doi: 10.1042/bj2350459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]