Abstract
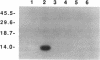
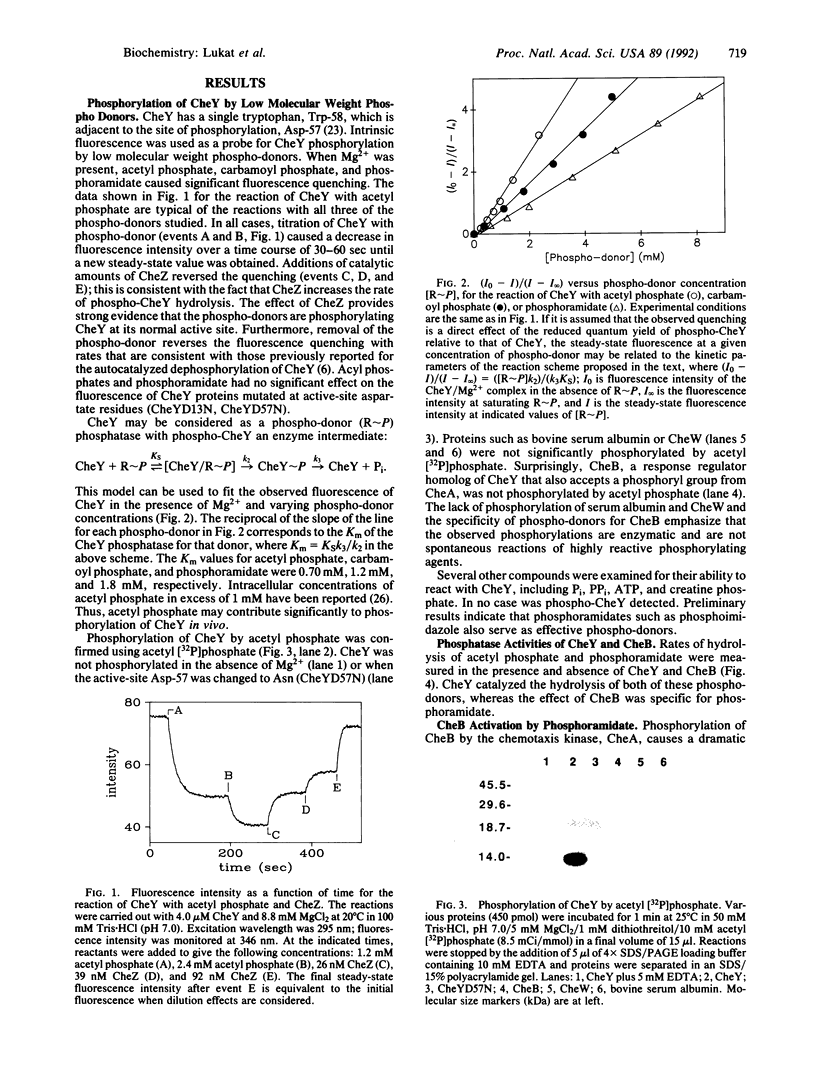
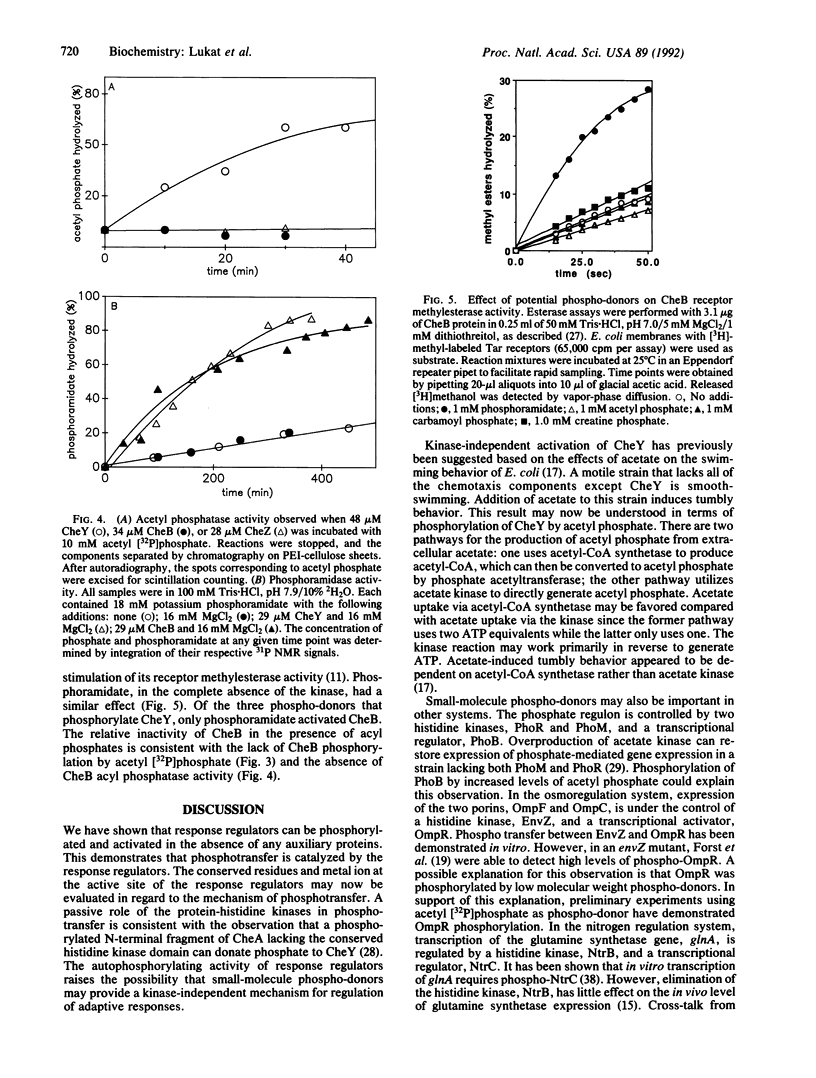
Bacterial motility and gene expression are controlled by a family of phosphorylated response regulators whose activities are modulated by an associated family of protein-histidine kinases. In chemotaxis there are two response regulators, CheY and CheB, that receive phosphoryl groups from the histidine kinase, CheA. Here we show that the response regulators catalyze their own phosphorylation in that both CheY and CheB can be phosphorylated in the complete absence of any auxiliary protein. Both CheY and CheB use the N-phosphoryl group in phosphoramidate (NH2PO3(2-)) as a phospho-donor. This enzymatic activity probably reflects the general ability of response regulators to accept phosphoryl groups from phosphohistidines in their associated kinases. It provides a general method for the study of activated response regulators in the absence of kinase proteins. CheY can also use intermediary metabolites such as acetyl phosphate and carbamoyl phosphate as phospho-donors. These reactions may provide a mechanism to modulate cell behavior in response to altered metabolic states.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Epstein W. Phosphotransferase-system enzymes as chemoreceptors for certain sugars in Escherichia coli chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2895–2899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amemura M., Makino K., Shinagawa H., Nakata A. Cross talk to the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli by PhoM protein: PhoM is a histidine protein kinase and catalyzes phosphorylation of PhoB and PhoM-open reading frame 2. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6300–6307. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6300-6307.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backman K. C., Chen Y. M., Ueno-Nishio S., Magasanik B. The product of glnL is not essential for regulation of bacterial nitrogen assimilation. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):516–519. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.516-519.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley A. L., Jencks W. P. Acetyl phosphate as a substrate for the calcium ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13997–14004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borczuk A., Staub A., Stock J. Demethylation of bacterial chemoreceptors is inhibited by attractant stimuli in the complete absence of the regulatory domain of the demethylating enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 30;141(3):918–923. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. The dynamics of protein phosphorylation in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1339–1348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90429-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno R., Pahel G., Magasanik B. Role of glnB and glnD gene products in regulation of the glnALG operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):816–822. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.816-822.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a bacterial sensing protein and effects of its elevated expression. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):398–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.398-405.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Delgado J., Rampersaud A., Inouye M. In vivo phosphorylation of OmpR, the transcription activator of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3473–3477. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3473-3477.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. K., Meadow N. D., Roseman S. Phosphate transfer between acetate kinase and enzyme I of the bacterial phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13498–13503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerra M., Robinson J. D., Steinberg M. Differential effects of substrates on three transport modes of the Na+/K(+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 30;1023(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90011-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Histidine phosphorylation and phosphoryl group transfer in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):139–143. doi: 10.1038/336139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Kaplan N., Simon M. I. Phosphorylation of three proteins in the signaling pathway of bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. G. Micromethod for the measurement of acetyl phosphate and acetyl coenzyme A. Methods Enzymol. 1986;122:43–50. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)22146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jencks W. P. The utilization of binding energy in coupled vectorial processes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1980;51:75–106. doi: 10.1002/9780470122969.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. Y., Makino K., Shinagawa H., Nakata A. Overproduction of acetate kinase activates the phosphate regulon in the absence of the phoR and phoM functions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2245–2249. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2245-2249.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., Lee B. H., Mottonen J. M., Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Roles of the highly conserved aspartate and lysine residues in the response regulator of bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8348–8354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Divalent metal ion binding to the CheY protein and its significance to phosphotransfer in bacterial chemotaxis. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5436–5442. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Stock J. Phosphorylation of an N-terminal regulatory domain activates the CheB methylesterase in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17337–17342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Ninfa E. G., Lupas A. N., Stock A., Magasanik B., Stock J. Crosstalk between bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction proteins and regulators of transcription of the Ntr regulon: evidence that nitrogen assimilation and chemotaxis are controlled by a common phosphotransfer mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5492–5496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa E. G., Stock A., Mowbray S., Stock J. Reconstitution of the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction system from purified components. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9764–9770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwano M., Taylor B. L. Novel sensory adaptation mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis to oxygen and phosphotransferase substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmedo G., Ninfa E. G., Stock J., Youngman P. Novel mutations that alter the regulation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Evidence that phosphorylation of regulatory protein SpoOA controls the initiation of sporulation. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):359–372. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Stock A. M., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the site of phosphorylation of the chemotaxis response regulator protein, CheY. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21770–21778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simms S. A., Keane M. G., Stock J. Multiple forms of the CheB methylesterase in bacterial chemosensing. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10161–10168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M., Stock J. B., Schutt C. E. Three-dimensional structure of CheY, the response regulator of bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):745–749. doi: 10.1038/337745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Purification and characterization of the CheZ protein of bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3301–3311. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3301-3311.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A., Koshland D. E., Jr, Stock J. Homologies between the Salmonella typhimurium CheY protein and proteins involved in the regulation of chemotaxis, membrane protein synthesis, and sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7989–7993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Lukat G. S., Stock A. M. Bacterial chemotaxis and the molecular logic of intracellular signal transduction networks. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:109–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Twenty questions concerning the reaction cycle of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(2):123–151. doi: 10.3109/10409238409113603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Conley M. P., Berg H. C. Acetyladenylate plays a role in controlling the direction of flagellar rotation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6711–6715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]