Abstract
In this study we examined whether the arrest of DNA polymerase alpha (pol alpha)-catalyzed DNA synthesis at template pause sites entails terminal nucleotide misincorporation. An approach was developed to identify the 3'-terminal nucleotide in nascent DNA chains that accumulate at pause sites. A radioactive 5'-end-labeled primer was annealed to a bacteriophage M13mp2 single-stranded DNA template and elongated by pol alpha. Individual DNA chains that were accumulated at pause sites were resolved by sequencing gel electrophoresis, isolated, and purified. These DNA chains were elongated by pol alpha by using four annealed synthetic DNA templates, each of which contained a different nucleotide at the position opposite the 3' terminus of the arrested chain. Owing to the high preference of pol alpha for matched-over-mismatched primer termini, only those templates that contain a nucleotide that is complementary to the 3' terminus of the isolated pause-site chain are copied. Electrophoresis of product DNA showed the extent of copying of each template and thus identified the 3'-terminal nucleotide of the pause-site chains. We found that product DNA chains terminate with a noncomplementary 3'-terminal nucleotide opposite pause sites within the sequence 3'-d(AAAA)-5' at positions 6272-6269 of the M13mp2 genome. pol alpha catalyzed misincorporation of dG or dA into the 3' terminus of nascent chains opposite two of the M13mp2 template dA residues. A similar analysis of a different pause site did not reveal significant misincorporation opposite template dC. These results suggest that some but not all sites at which pol alpha pauses may constitute loci of mutagenesis.
Full text
PDF

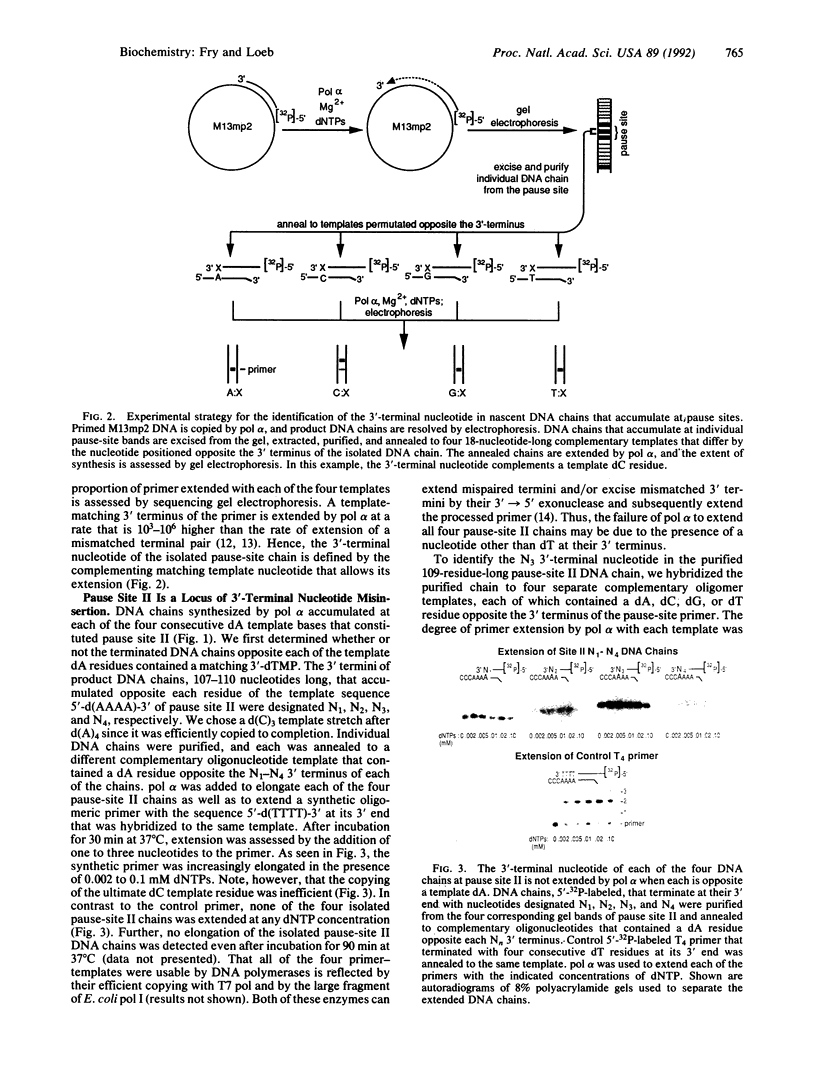
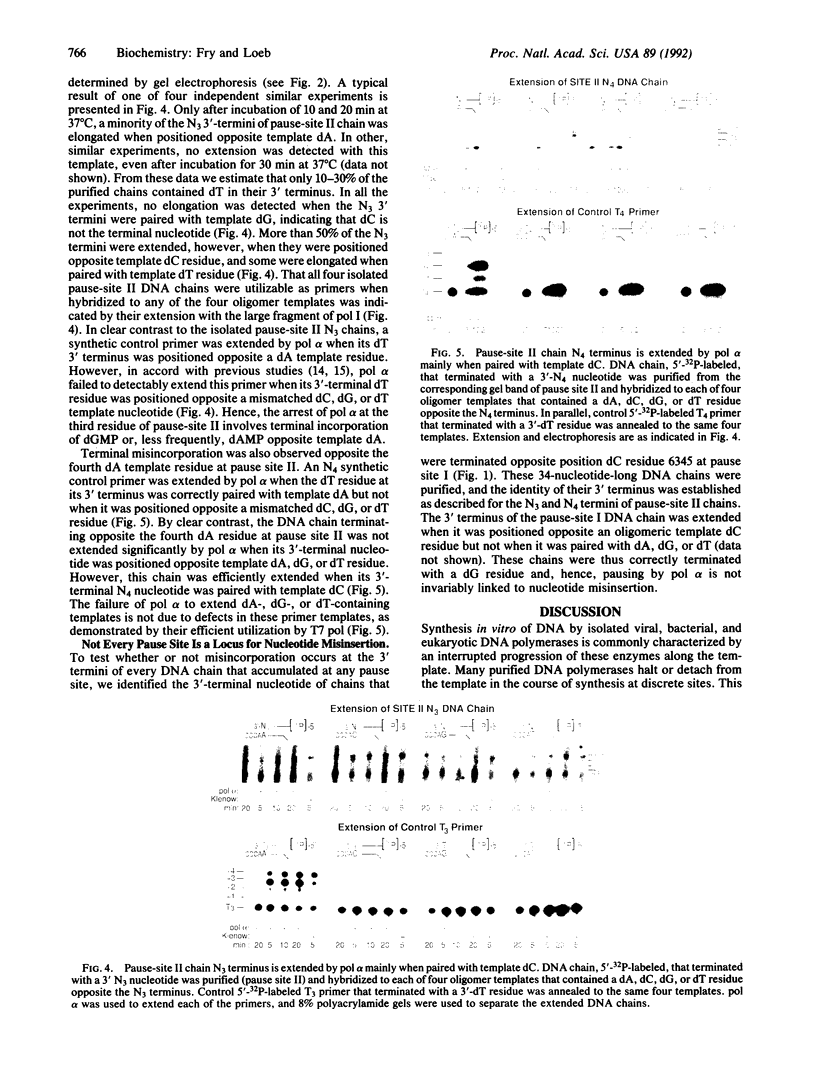

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbotts J., SenGupta D. N., Zon G., Wilson S. H. Studies on the mechanism of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I large fragment. Effect of template sequence and substrate variation on termination of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15094–15103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asna N., Weisman-Shomer P., Waldman E., Fry M. Factor C from rabbit liver. A new poly(dC) and poly[d(G-C)] template-selective stimulatory protein of DNA polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5245–5252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Abbotts J., Roberts J. D., Wilson S. H., Kunkel T. A. Specificity and mechanism of error-prone replication by human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16948–16956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Joyce C. M., Fitzgerald M. P., Kunkel T. A. The fidelity of DNA synthesis catalyzed by derivatives of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13878–13887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Johanson K. O., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Size classes of products synthesized processively by two subassemblies of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5692–5699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M., Weisman-Shomer P., Lapidot J., Sharf R. Template-selective stimulation of diverse DNA polymerases by the murine DNA-binding protein factor D. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8861–8867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosse F., Krauss G. Replication of M13mp7 single-stranded DNA in vitro by the 9-S DNA polymerase alpha from calf thymus. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillebrand G. G., Beattie K. L. Influence of template primary and secondary structure on the rate and fidelity of DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3116–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J. The energy relay: a proofreading scheme based on dynamic cooperativity and lacking all characteristic symptoms of kinetic proofreading in DNA replication and protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5248–5252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Escherichia coli thioredoxin stabilizes complexes of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase and primed templates. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16224–16232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Clayton D. A. Template-directed pausing in in vitro DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase a from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., DiFrancesco R. A., Lehman I. R. The DNA polymerase-primase from drosophila melanogaster embryos. Rate and fidelity of polymerization on single-stranded DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9314–9319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Alexander P. S. The base substitution fidelity of eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Mispairing frequencies, site preferences, insertion preferences, and base substitution by dislocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K. Recent studies of the fidelity of DNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. The mutational specificity of DNA polymerases-alpha and -gamma during in vitro DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12866–12874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaDuca R. J., Fay P. J., Chuang C., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Site-specific pausing of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis catalyzed by four forms of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5177–5188. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelman L. V., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. Base mispair extension kinetics. Comparison of DNA polymerase alpha and reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2338–2346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrino F. W., Loeb L. A. Differential extension of 3' mispairs is a major contribution to the high fidelity of calf thymus DNA polymerase-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2898–2905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrino F. W., Preston B. D., Sandell L. L., Loeb L. A. Extension of mismatched 3' termini of DNA is a major determinant of the infidelity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8343–8347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharf R., Weisman-Shomer P., Fry M. Rabbit liver factor D, a poly(thymidine) template stimulatory protein of DNA polymerases: purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2990–2997. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Huber H. E., Richardson C. C. Escherichia coli thioredoxin confers processivity on the DNA polymerase activity of the gene 5 protein of bacteriophage T7. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16212–16223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. T., DePamphilis M. L. Specific sequences in native DNA that arrest synthesis by DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2075–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman-Shomer P., Dube D. K., Perrino F. W., Stokes K., Loeb L. A., Fry M. Sequence specificity of pausing by DNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1149–1156. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. J., Loeb L. A., Fry M. Synthesis of DNA by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase is preferentially blocked at template oligo(deoxyadenosine) tracts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18682–18689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong P. J., Grosovsky A. J., Glickman B. W. Spectrum of spontaneous mutation at the APRT locus of Chinese hamster ovary cells: an analysis at the DNA sequence level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]