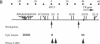Abstract
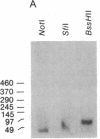
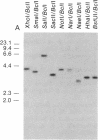
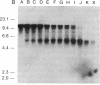
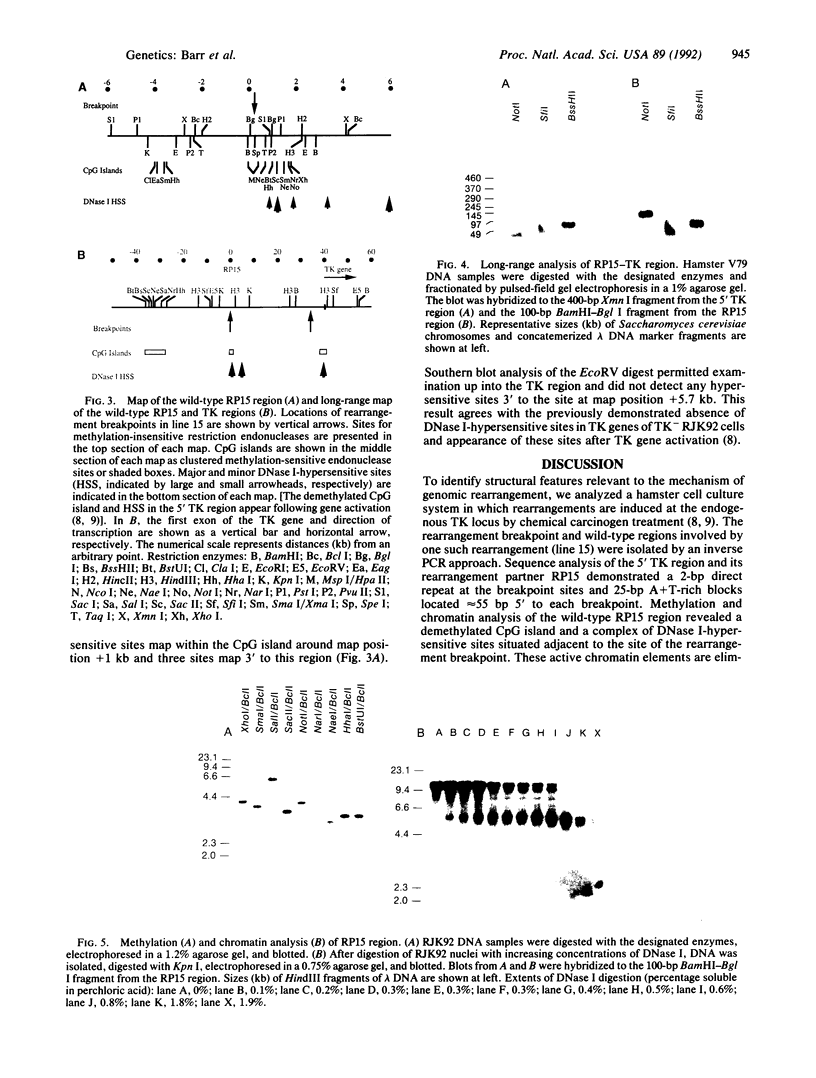
We have explored the mechanism of genomic rearrangement in a hamster fibroblast cell culture system in which rearrangements are induced 5' to the endogenous thymidine kinase gene by chemical carcinogen treatment. The wild-type region around one rearrangement breakpoint was cloned and sequenced. With this sequence information, the carcinogen-induced rearrangement was cloned from the corresponding rearranged cell line by the inverse polymerase chain reaction. After the breakpoint fragment was sequenced, the wild-type rearrangement partner (RP15) was isolated by a second inverse polymerase chain reaction of unrearranged DNA. Comparison of the sequence of the rearrangement breakpoint with the wild-type RP15 and 5' thymidine kinase gene regions revealed short repeats directly at the breakpoint, as well as nearby A + T-rich regions in each rearrangement partner. Pulsed-field electrophoresis analysis demonstrated that this rearrangement is an interstitial deletion of 35 kilobases. Southern blot analysis of the RP15 region in unrearranged parental cells showed a demethylated CpG island and a complex of DNase I-hypersensitive sites adjacent to the breakpoint in the region deleted by the rearrangement. Therefore, these studies reveal interesting sequence and chromatin features near the rearrangement breakpoints and suggest a role for nuclear organization in the mechanism of carcinogen-induced genomic rearrangement.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antequera F., Boyes J., Bird A. High levels of de novo methylation and altered chromatin structure at CpG islands in cell lines. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr F. G., Kastan M. B., Lieberman M. W. Distribution of 5-methyldeoxycytidine in products of staphylococcal nuclease digestion of nuclei and purified DNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Mar 12;24(6):1424–1428. doi: 10.1021/bi00327a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr F. G., Rajagopalan S., Lieberman M. W. Analysis of the rearrangements associated with carcinogen-induced activation of the hamster thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):129–135. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr F. G., Rajagopalan S., MacArthur C. A., Lieberman M. W. Genomic hypomethylation and far-5' sequence alterations are associated with carcinogen-induced activation of the hamster thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3023–3033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Alt F. W. Molecular characterization of the lymphoid V(D)J recombination activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10327–10330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Mengle-Gaw L., Kees U. R., Spurr N., Lavenir I., Forster A., Rabbitts T. H. Alternating purine-pyrimidine tracts may promote chromosomal translocations seen in a variety of human lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2621–2631. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning S., Dryja T. P. Short, direct repeats at the breakpoints of deletions of the retinoblastoma gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5044–5048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. J., Chen Z., Font M. P., d'Auriol L., Larsen C. J., Berger R. Structural alterations of the BCR and ABL genes in Ph1 positive acute leukemias with rearrangements in the BCR gene first intron: further evidence implicating Alu sequences in the chromosome translocation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7631–7642. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Ligation of EcoRI endonuclease-generated DNA fragments into linear and circular structures. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur C. A., Lieberman M. W. Different types of hypersensitive sites in the mouse metallothionein gene region. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2161–2165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Gerber A. S., Hartl D. L. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):621–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos P. C., Greenstein A. M., Gaffney R. A., Westbrook C. A., Wiedemann L. M. Characterization of the translocation breakpoint sequences in Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 Jan;1(3):233–239. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry A. O., Blasquez V. C., Garrard W. T. Dysfunction of chromosomal loop attachment sites: illegitimate recombination linked to matrix association regions and topoisomerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5497–5501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Rothstein R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triglia T., Peterson M. G., Kemp D. J. A procedure for in vitro amplification of DNA segments that lie outside the boundaries of known sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8186–8186. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Sklar J. Chromosomal translocations in lymphoid neoplasia: a reappraisal of the recombinase model. Cancer Cells. 1990 Jan;2(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb A., Collier D. A., Birshtein B. K., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA and intramolecular triplex formation at the site of an unequal sister chromatid exchange. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1352–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]