Abstract
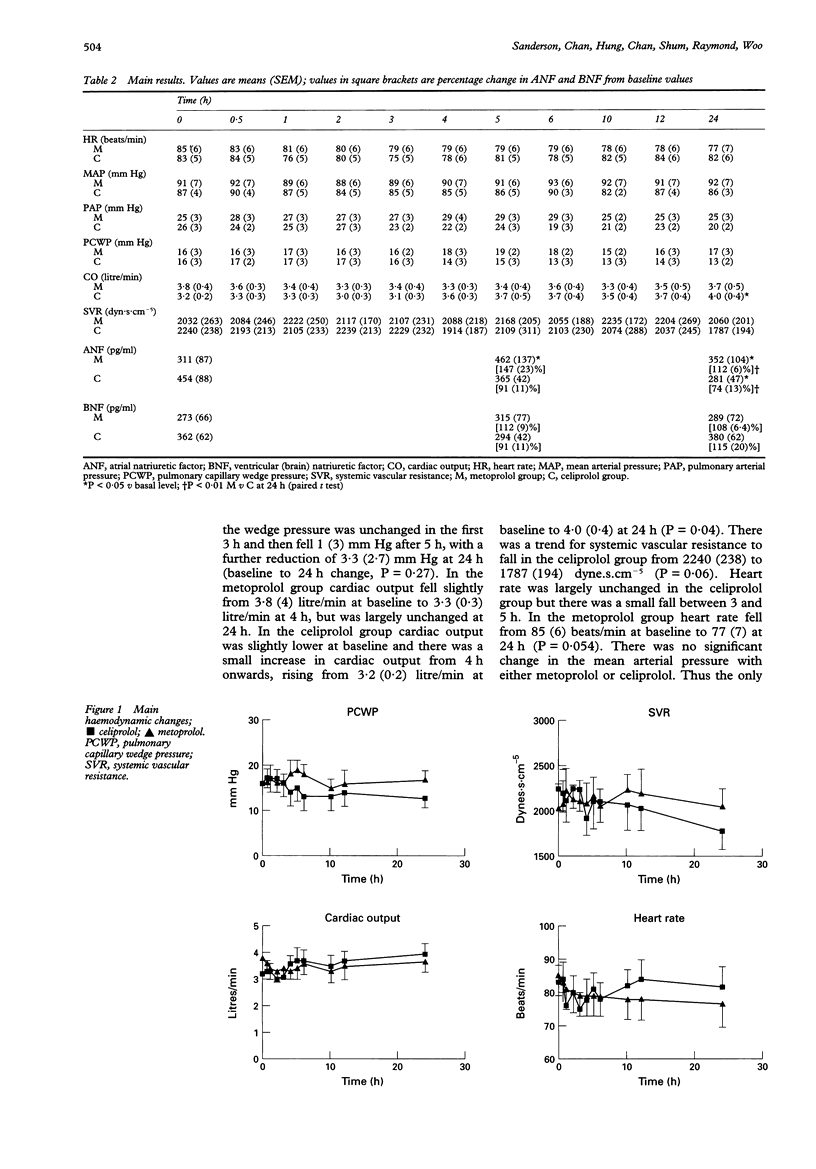
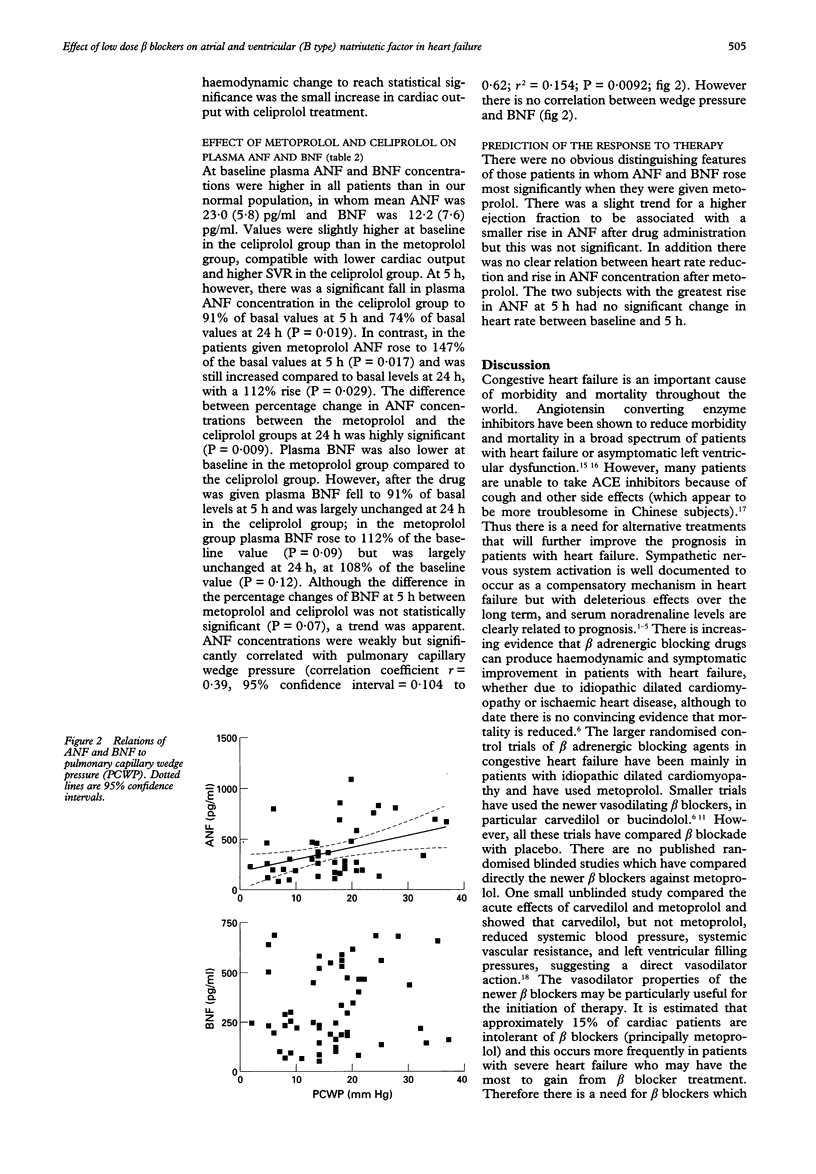
OBJECTIVES--This study examines the acute effects of two differing beta adrenergic blocking agents (metoprolol and a third generation vasodilating beta blocker) on plasma concentrations of atrial natriuretic factor (ANF), brain (ventricular) natriuretic factor (BNF), and haemodynamic variables in patients with heart failure. SETTING--University teaching hospital. METHODS--20 patients with impaired left ventricular systolic function [ejection fraction 32 (SEM 2.3)%] were randomised in a double blind manner to receive either oral metoprolol 6.25 mg twice daily or celiprolol 25 mg daily. Haemodynamic variables were evaluated by Swan-Ganz pulmonary artery catheter over 24 hours. ANF and BNF concentrations were measured at baseline, 5 h, and 24 h by radioimmunoassay. RESULTS--At baseline ANF and BNF concentrations were considerably raised compared to the normal range. Treatment with metoprolol caused ANF to rise further to 147% of the basal level at 5 h (P = 0.017) and 112% at 24 h (P = 0.029). This was associated with a small but non-significant rise in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure. Cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance were unchanged at 24 h. In contrast, after celiprolol ANF fell to 90% of basal levels at 5 h and to 74% of basal level at 24 h (P = 0.019), associated with a small but non-significant fall in pulmonary capillary wedge pressure [-3.3 (2.7) mm Hg] and systemic vascular resistance, and rise in cardiac output from 3.2 (0.2) to 4.0 (0.4) l/min (P = 0.04). BNF concentrations rose to 112% of baseline at 5 h (P = 0.09) after metoprolol but fell slightly, to 91% of baseline values, after celiprolol (NS). CONCLUSIONS--Metoprolol, even in very low doses (6.25 mg), produced a rise in ANF and BNF, although minimal haemodynamic changes were detected. In contrast, a vasodilating beta blocker was associated with a significant fall in ANF and BNF and a small rise in cardiac output. This study confirms both the advantages of vasodilating beta blockers over metoprolol for initial treatment of heart failure and the usefulness of ANF and BNF measurements for the assessment of drug effects in heart failure compared to traditional haemodynamic measurements.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohn J. N., Levine T. B., Olivari M. T., Garberg V., Lura D., Francis G. S., Simon A. B., Rector T. Plasma norepinephrine as a guide to prognosis in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 27;311(13):819–823. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409273111303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughty R. N., MacMahon S., Sharpe N. Beta-blockers in heart failure: promising or proved? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Mar 1;23(3):814–821. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90773-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. A., Ferro A., Dickerson J. E., Brown M. J. Beta adrenoreceptor subtype cross regulation in the human heart. Br Heart J. 1993 Apr;69(4):332–337. doi: 10.1136/hrt.69.4.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leimbach W. N., Jr, Wallin B. G., Victor R. G., Aylward P. E., Sundlöf G., Mark A. L. Direct evidence from intraneural recordings for increased central sympathetic outflow in patients with heart failure. Circulation. 1986 May;73(5):913–919. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.5.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milano C. A., Allen L. F., Rockman H. A., Dolber P. C., McMinn T. R., Chien K. R., Johnson T. D., Bond R. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Enhanced myocardial function in transgenic mice overexpressing the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):582–586. doi: 10.1126/science.8160017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motwani J. G., McAlpine H., Kennedy N., Struthers A. D. Plasma brain natriuretic peptide as an indicator for angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition after myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1993 May 1;341(8853):1109–1113. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)93126-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okrucká A., Pechán J., Balazovjech I. The effect of short-term celiprolol therapy on platelet function in essential hypertension. Cardiology. 1993;82(6):399–404. doi: 10.1159/000175893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer M., Medina N., Yushak M. Hemodynamic changes mimicking a vasodilator drug response in the absence of drug therapy after right heart catheterization in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 1985 Apr;71(4):761–766. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.71.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine A. E., Erne P., Bürgisser E., Müller F. B., Bolli P., Burkart F., Bühler F. R. Atrial natriuretic peptide and atrial pressure in patients with congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):533–537. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Hambrecht R., Schlierf G., Niebauer J., Hauer K., Neumann J., Hoberg E., Drinkmann A., Bacher F., Grunze M. Regular physical exercise and low-fat diet. Effects on progression of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1992 Jul;86(1):1–11. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.86.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfers R. F., Adler S., Daul A., Zeitler G., Vogelsang M., Zerkowski H. R., Brodde O. E. Positive inotropic effects of the beta 2-adrenoceptor agonist terbutaline in the human heart: effects of long-term beta 1-adrenoceptor antagonist treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 Apr;23(5):1224–1233. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephen S. A. Unwanted effects of propranolol. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Sep;18(3):463–472. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vliet P. D., Burchell H. B., Titus J. L. Focal myocarditis associated with pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 19;274(20):1102–1108. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605192742002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waagstein F., Caidahl K., Wallentin I., Bergh C. H., Hjalmarson A. Long-term beta-blockade in dilated cardiomyopathy. Effects of short- and long-term metoprolol treatment followed by withdrawal and readministration of metoprolol. Circulation. 1989 Sep;80(3):551–563. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.3.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waagstein F., Hjalmarson A., Varnauskas E., Wallentin I. Effect of chronic beta-adrenergic receptor blockade in congestive cardiomyopathy. Br Heart J. 1975 Oct;37(10):1022–1036. doi: 10.1136/hrt.37.10.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Heublein D. M., Perrella M. A., Lerman A., Rodeheffer R. J., McGregor C. G., Edwards W. D., Schaff H. V., Burnett J. C., Jr Natriuretic peptide system in human heart failure. Circulation. 1993 Sep;88(3):1004–1009. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.3.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo K. S., Norris R. M., Nicholls G. Racial difference in incidence of cough with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (a tale of two cities). Am J Cardiol. 1995 May 1;75(14):967–968. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(99)80703-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura M., Yasue H., Tanaka H., Kikuta K., Sumida H., Kato H., Jougasaki M., Nakao K. Responses of plasma concentrations of A type natriuretic peptide and B type natriuretic peptide to alacepril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, in patients with congestive heart failure. Br Heart J. 1994 Dec;72(6):528–533. doi: 10.1136/hrt.72.6.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


