Abstract
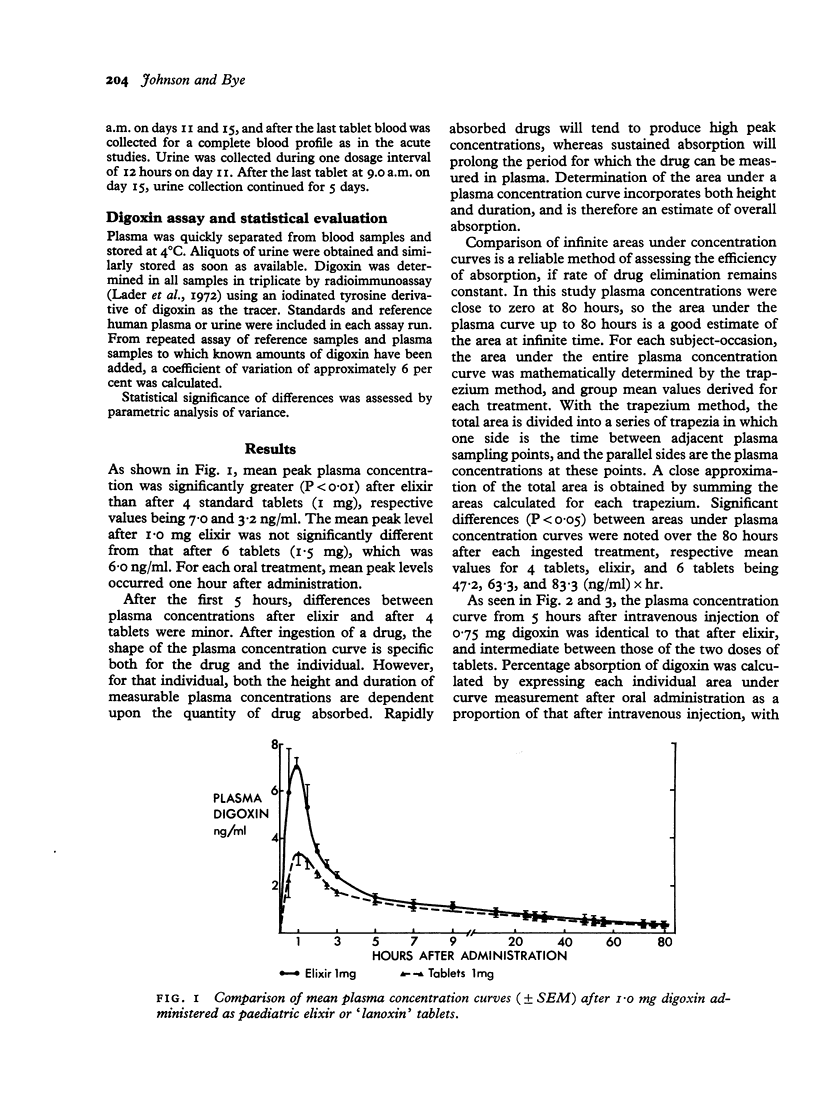
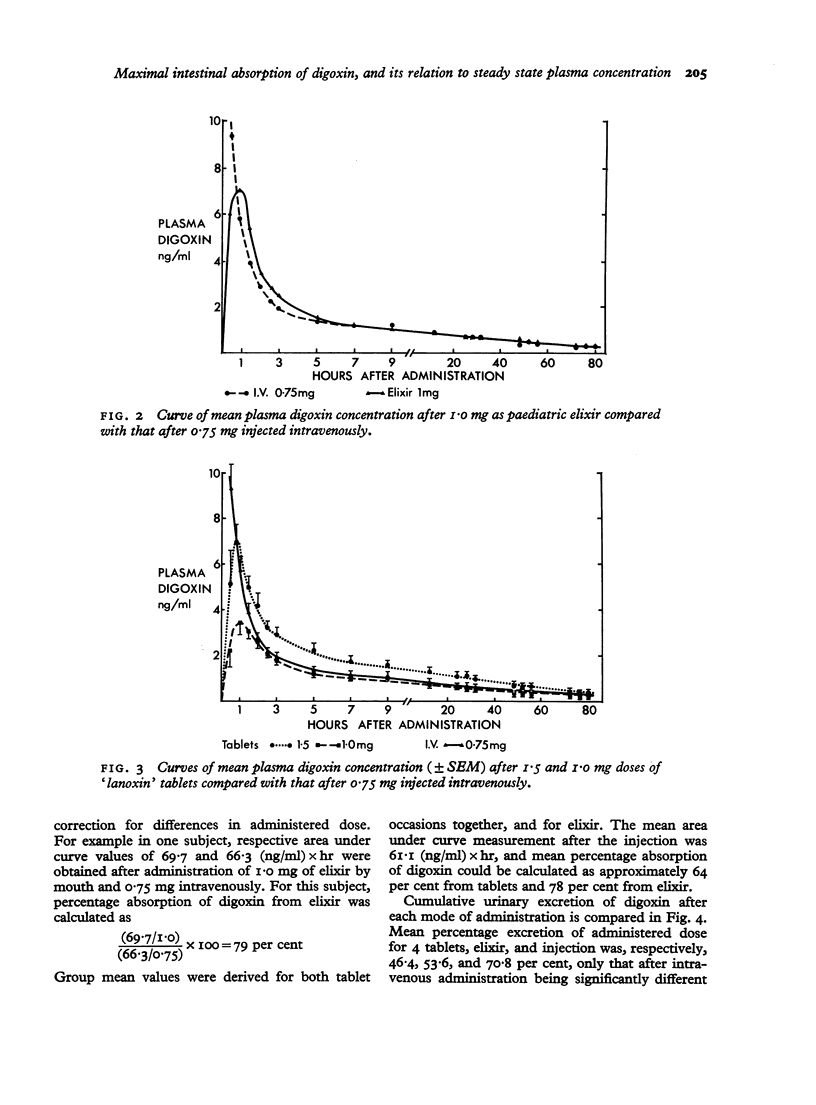
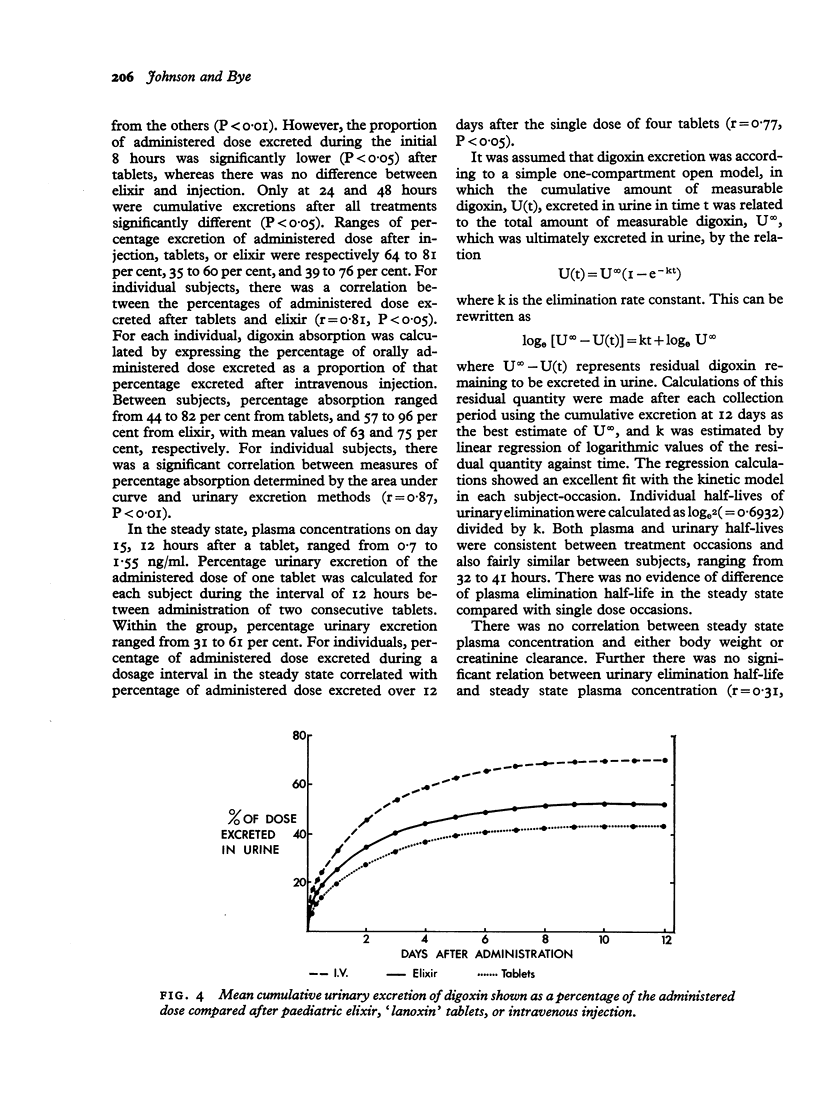
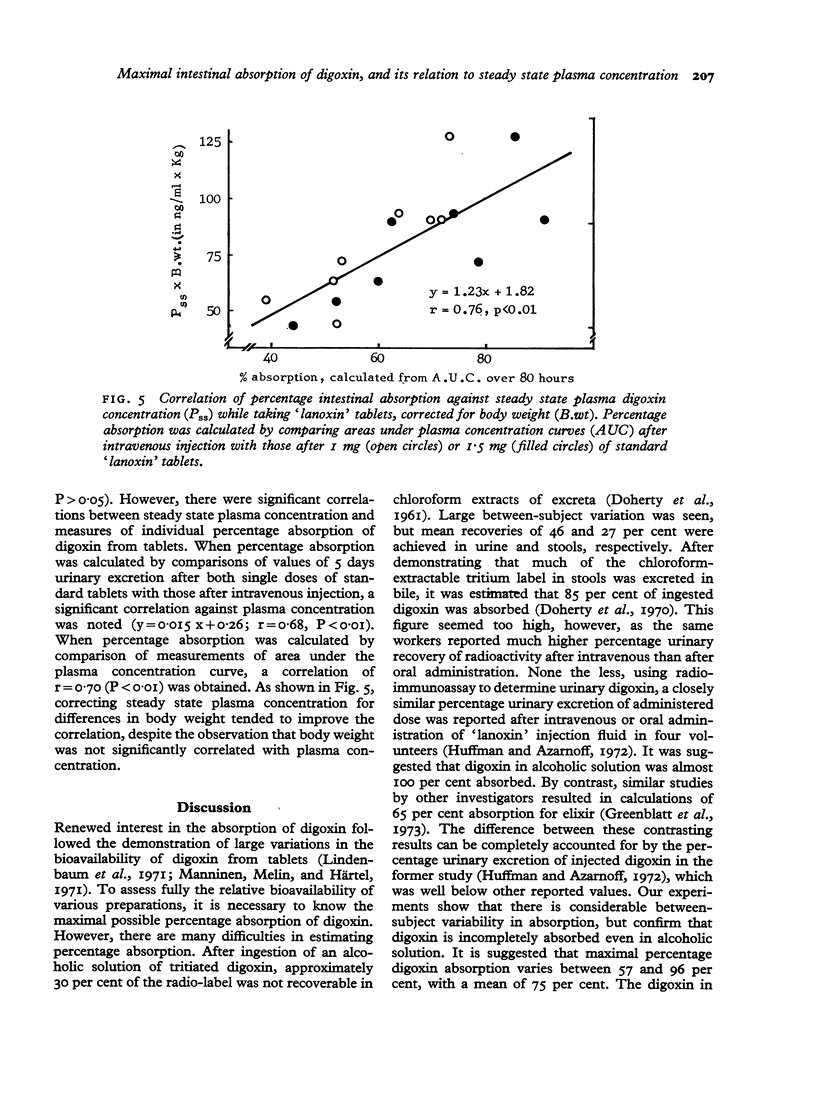
In a group of 8 volunteers, peak plasma digoxin concentrations and areas under 80-hour plasma concentration curves were significantly greater after 1 mg digoxin in paediatric elixir than after 4 0,25 mg tablets. Mean cumulative urinary excretion of digoxin over 12 days was 46.4 per cent after tablets, 53.6 per cent after elixir, and 70.8 per cent after intravenous injection. Mean percentage absorption was estimated to be 63 per cent from tablets and 75 per cent from elixir, but considerable between-subject variation was noted. Individual estimates of percentage absorption were significantly correlated with plasma concentrations in the steady state. Computer programmes to relate steady state plasma concentration to oral digoxin dosage take no account of absorptive capacity, are limited to gross approximations, and cannot replace determination of plasma concentration to assess the degree of digitalization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlain D. A., White R. J., Howard M. R., Smith T. W. Plasma digoxin concentrations in patients with atrial fibrillation. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 22;3(5720):429–432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5720.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOHERTY J. E., PERKINS W. H., MITCHELL G. K. Tritiated digoxin studies in human subjects. Arch Intern Med. 1961 Oct;108:531–539. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1961.03620100023004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. E., Flanigan W. J., Murphy M. L., Bulloch R. T., Dalrymple G. L., Beard O. W., Perkins W. H. Tritiated digoxin. XIV. Enterohepatic circulation, absorption, and excretion studies in human volunteers. Circulation. 1970 Nov;42(5):867–873. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.42.5.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLD H., CATTELL M., GREINER T., HANLON L. W., KWIT N. T., MODELL W., COTLOVE E., BENTON J., OTTO H. L. Clinical pharmacology of digoxin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Sep;109(1):45–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffman D. H., Azarnoff D. L. Absorption of orally given digoxin preparations. JAMA. 1972 Nov 20;222(8):957–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelliffe R. W., Buell J., Kalaba R. Reducation of digitalis toxicity by computer-assisted glycoside dosage regimens. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Dec;77(6):891–906. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-6-891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. F., Greer H., McCrerie J., Bye C., Fowle A. Rate of dissolution of digoxin tablets as a predictor of absorption. Lancet. 1973 Jun 30;1(7818):1473–1475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91811-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum J., Butler V. P., Jr, Murphy J. E., Cresswell R. M. Correlation of digoxin-tablet dissolution-rate with biological availability. Lancet. 1973 Jun 2;1(7814):1215–1217. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum J., Mellow M. H., Blackstone M. O., Butler V. P., Jr Variation in biologic availability of digoxin from four preparations. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 9;285(24):1344–1347. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112092852403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manninen V., Melin J., Hartel G. Serum-digoxin concentrations during treatment with different preparations. Lancet. 1971 Oct 23;2(7730):934–935. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92560-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck C. C., Sheiner L. B., Martin C. M., Combs D. T., Melmon K. L. Computer-assisted digoxin therapy. N Engl J Med. 1973 Aug 30;289(9):441–446. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197308302890902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfors A. Plasma digoxin concentration--its relation to digoxin dosage and clinical effects in patients with atrial fibrillation. Br Heart J. 1972 Apr;34(4):383–391. doi: 10.1136/hrt.34.4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


