Abstract
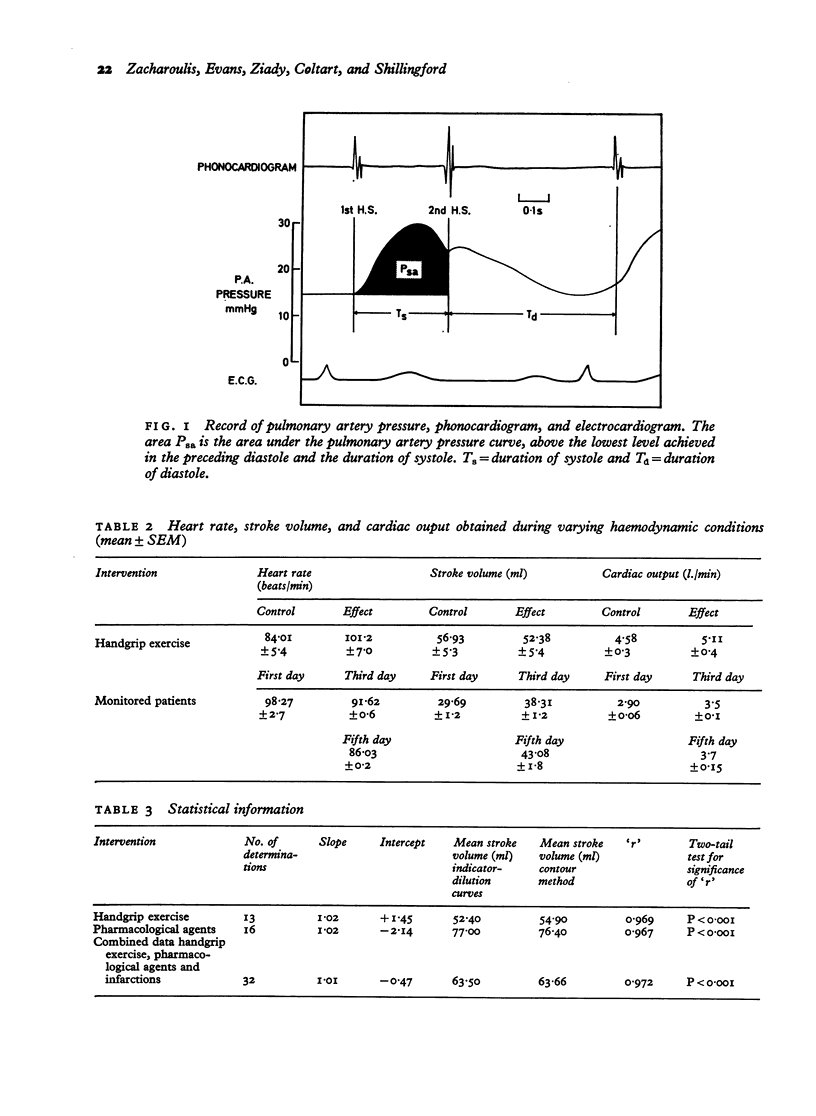
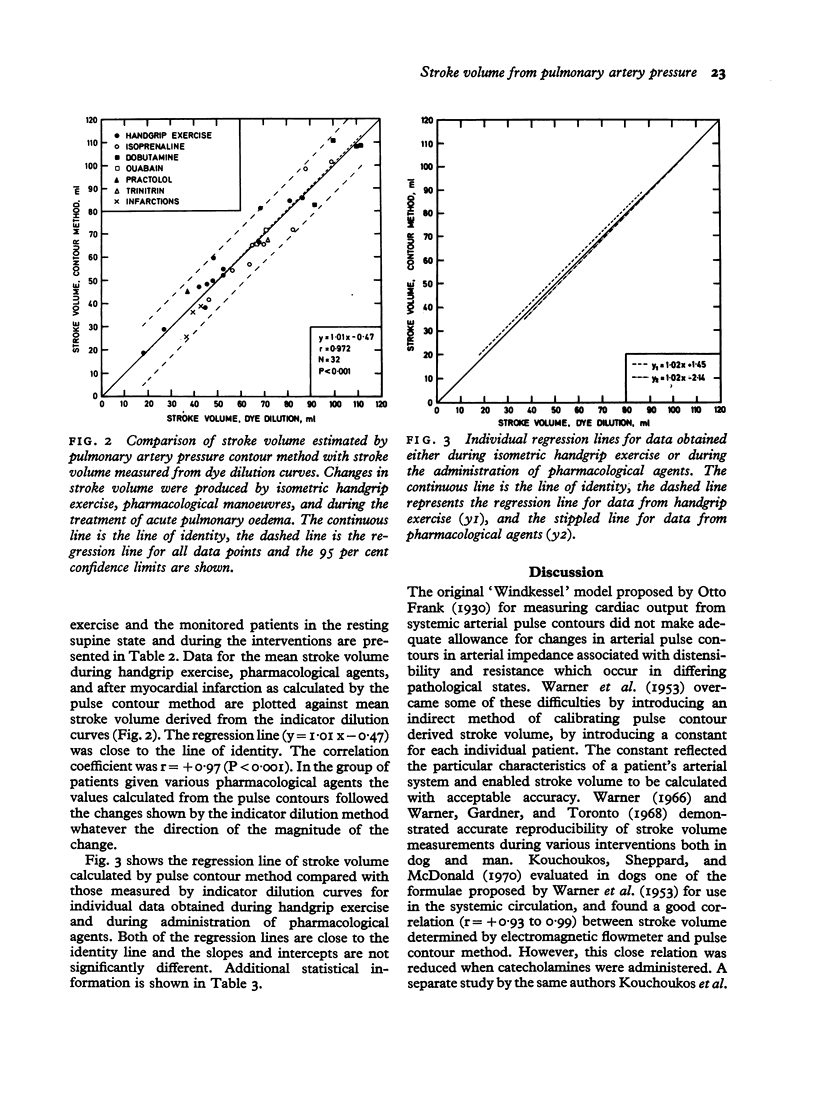
Stroke volume was determined from the pulmonary artery pressure record by application of the pulse contour method. Pulmonary artery pressure records were obtained in 17 patients using a high fidelity catheter-tip pressure transducer and simultaneous measurements of cardiac output were obtained from indicator dilution curves. The formula used was SV = KP sa (i plus T s/Td) where Psa is the planimetered area beneath the systolic portion of the pulmonary artery pressure curve. Ts and Td are the durations of systole and diastole, and K is a constant. Stroke volume was altered by isometric handgrip exercise and/or pharmacological agents in 15 patients. Serial measurementswere made in 2 patients in acute pulmonary oedema after myocardial infarction. Comparison of a wide range of values of stroke volume by the pulse contour method with those obtained from dye dilution curves showed a good correlation (r plus 0.97, P smaller than 0.001) regression line y = 1.01 times - 0.47. Measurement of stroke volume from the pulmonary artery pressure contour is a technique of potential value in serial haemodynamic monitoring.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderman E. L., Branzi A., Sanders W., Brown B. W., Harrison D. C. Evaluation of the pulse-contour method of determining stroke volume in man. Circulation. 1972 Sep;46(3):546–558. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.46.3.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starmer C. F., McHale P. A., Cobb F. R., Greenfield J. C., Jr Evaluation of several methods for computing stroke volume from central aortic pressure. Circ Res. 1973 Aug;33(2):139–148. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenson R., Crouse L., Harrison D. C. Computer measurement of cardiac output by dye dilution: comparison of computer, Fick, and Dow techniques. Cardiovasc Res. 1972 Jul;6(4):449–456. doi: 10.1093/cvr/6.4.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER H. R., SWAN H. J. C., CONNOLLY D. C., TOMPKINS R. G., WOOD E. H. Quantitation of beat-to-beat changes in stroke volume from the aortic pulse contour in man. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Mar;5(9):495–507. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.5.9.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner H. R. The role of computers in medical research. JAMA. 1966 Jun 13;196(11):944–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


