Abstract
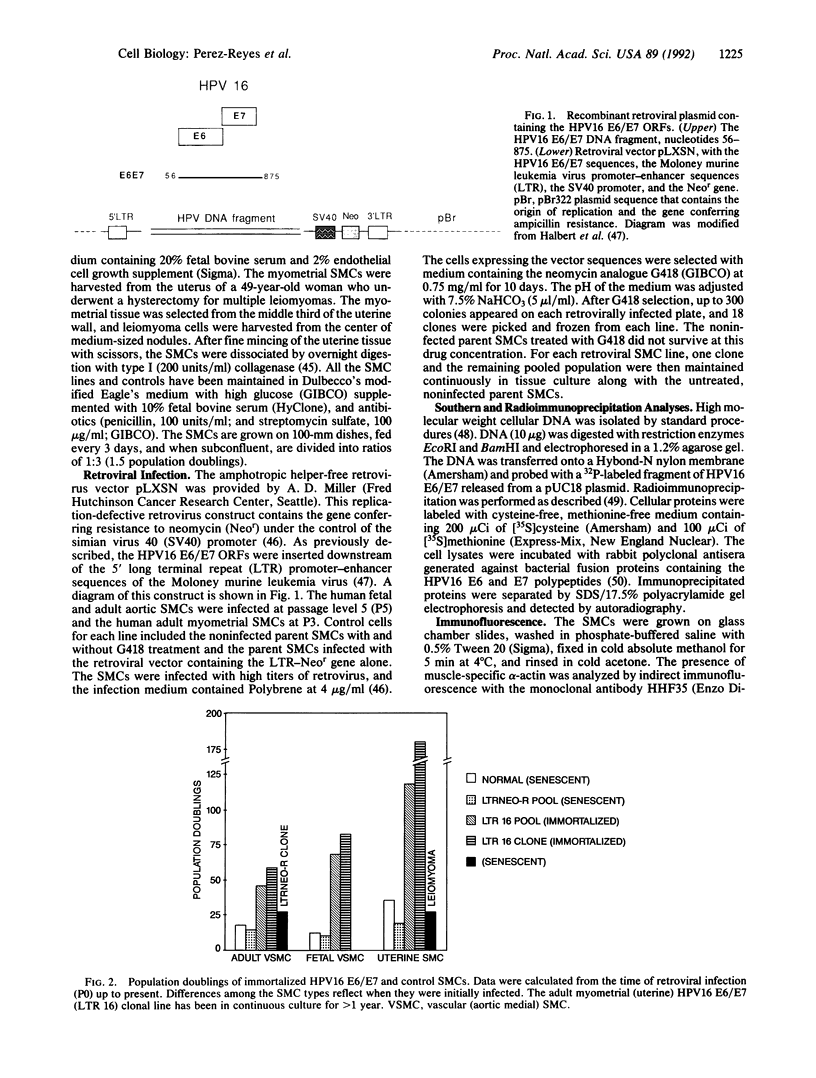
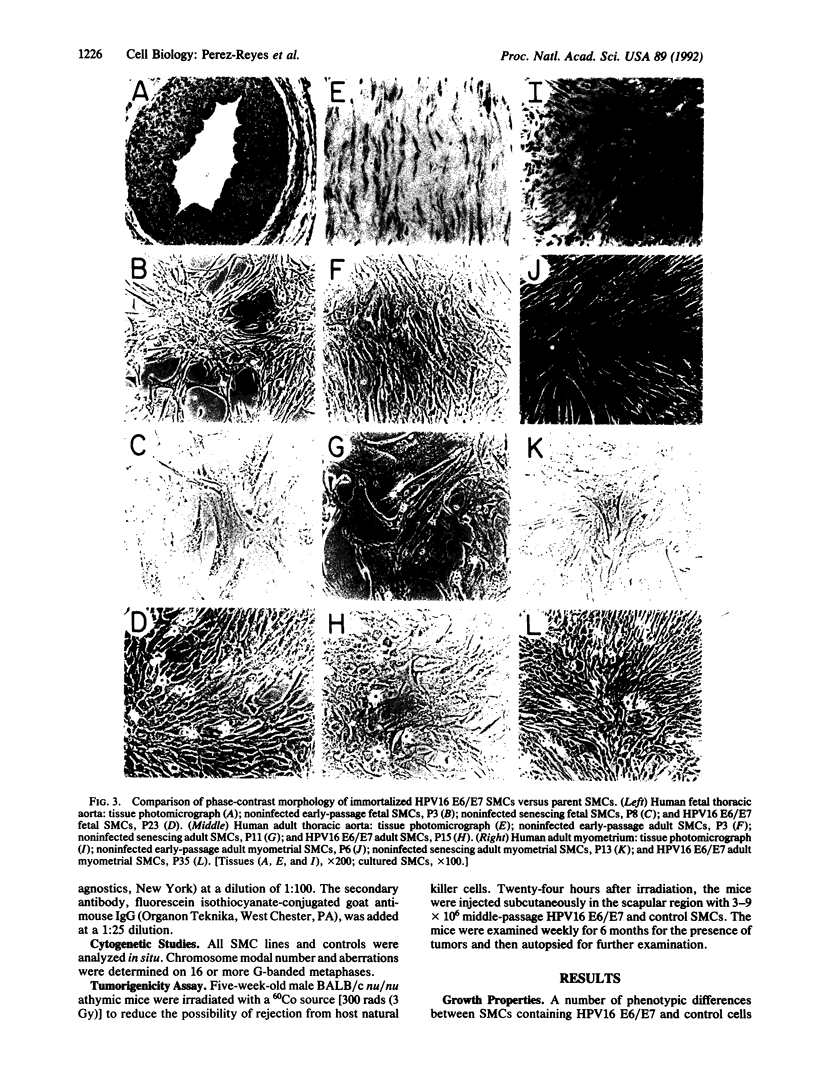
Primary human aortic and myometrial smooth muscle cells (SMCs) were immortalized using an amphotropic recombinant retroviral construct containing the E6 and E7 open reading frames (ORFs) of human papillomavirus type 16. The SMCs expressing the E6/E7 ORFs have considerably elevated growth rates when compared with nonimmortalized control cells and show no signs of senescence with long-term passage. The first SMC line derived in this study has been maintained in continuous tissue culture for greater than 1 year (greater than 180 population doublings). The immortalized SMCs have decreased cell size and decreased content of muscle-specific alpha-actin filaments as determined by indirect immunofluorescence. Southern blot analysis has demonstrated the stable integration of the E6/E7 ORFs in the retrovirally infected cells, and radioimmunoprecipitation has confirmed the continued expression of the E6 and E7 genes. Cytogenetic studies of the SMC lines have revealed essentially diploid populations except for the myometrial clonal line, which became aneuploid at late passage (greater than 125 doublings). These cell lines were not tumorigenic in nude mice.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam E., Melnick J. L., Probtsfield J. L., Petrie B. L., Burek J., Bailey K. R., McCollum C. H., DeBakey M. E. High levels of cytomegalovirus antibody in patients requiring vascular surgery for atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1987 Aug 8;2(8554):291–293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90888-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Barrett T., McDougall J. K. Viruses in the etiology of atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6386–6389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Benditt J. M. Evidence for a monoclonal origin of human atherosclerotic plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1753–1756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Gown A. M. Atheroma: the artery wall and the environment. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1980;21:55–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P. Origins of human atherosclerotic plaques. The role of altered gene expression. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Oct;112(10):997–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casalone R., Granata P., Minelli E., Portentoso P., Giudici A., Righi R., Castelli P., Socrate A., Frigerio B. Cytogenetic analysis reveals clonal proliferation of smooth muscle cells in atherosclerotic plaques. Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;87(2):139–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00204169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etingin O. R., Hajjar D. P. Evidence for cytokine regulation of cholesterol metabolism in herpesvirus-infected arterial cells by the lipoxygenase pathway. J Lipid Res. 1990 Feb;31(2):299–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant C. G., Fabricant J., Litrenta M. M., Minick C. R. Virus-induced atherosclerosis. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):335–340. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant C. G., Fabricant J., Minick C. R., Litrenta M. M. Herpesvirus-induced atherosclerosis in chickens. Fed Proc. 1983 May 15;42(8):2476–2479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant C. G., Hajjar D. P., Minick C. R., Fabricant J. Herpesvirus infection enhances cholesterol and cholesteryl ester accumulation in cultured arterial smooth muscle cells. Am J Pathol. 1981 Nov;105(2):176–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayed Y. M., Tsibris J. C., Langenberg P. W., Robertson A. L., Jr Human uterine leiomyoma cells: binding and growth responses to epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and insulin. Lab Invest. 1989 Jan;60(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. The oncogenic potential of herpes simplex viruses: evidence for a 'hit-and-run' mechanism. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):21–24. doi: 10.1038/302021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grattan M. T., Moreno-Cabral C. E., Starnes V. A., Oyer P. E., Stinson E. B., Shumway N. E. Cytomegalovirus infection is associated with cardiac allograft rejection and atherosclerosis. JAMA. 1989 Jun 23;261(24):3561–3566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUST M. D., MORE R. H., MOVAT H. Z. The role of smooth muscle cells in the fibrogenesis of arteriosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1960 Oct;37:377–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Fabricant C. G., Minick C. R., Fabricant J. Virus-induced atherosclerosis. Herpesvirus infection alters aortic cholesterol metabolism and accumulation. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jan;122(1):62–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Falcone D. J., Fabricant C. G., Fabricant J. Altered cholesteryl ester cycle is associated with lipid accumulation in herpesvirus-infected arterial smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6124–6128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P. Herpesvirus infection prevents activation of cytoplasmic cholesteryl esterase in arterial smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7611–7614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Nicholson A. C., Hajjar K. A., Sando G. N., Summers B. D. Decreased messenger RNA translation in herpesvirus-infected arterial cells: effects on cholesteryl ester hydrolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3366–3370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar D. P., Pomerantz K. B., Falcone D. J., Weksler B. B., Grant A. J. Herpes simplex virus infection in human arterial cells. Implications in arteriosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Nov;80(5):1317–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI113208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert C. L., Demers G. W., Galloway D. A. The E7 gene of human papillomavirus type 16 is sufficient for immortalization of human epithelial cells. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):473–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.473-478.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. G., Daemen M., Bruggeman C. A. Cytomegalovirus nucleic acid distribution within the human vascular tree. Am J Pathol. 1991 Mar;138(3):563–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. G., Dormans P. H., Kitslaar P., Bosman F., Bruggeman C. A. The presence of cytomegalovirus nucleic acids in arterial walls of atherosclerotic and nonatherosclerotic patients. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1151–1157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix M. G., Salimans M. M., van Boven C. P., Bruggeman C. A. High prevalence of latently present cytomegalovirus in arterial walls of patients suffering from grade III atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):23–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenison S. A., Yu X. P., Valentine J. M., Koutsky L. A., Christiansen A. E., Beckmann A. M., Galloway D. A. Evidence of prevalent genital-type human papillomavirus infections in adults and children. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):60–69. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K., Cone R. Immortalization of primary human epithelial cells by cloned cervical carcinoma DNA containing human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7 open reading frames. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1261–1266. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand A., Greenspan P., Nagpal M. L., Nachtigal S. A., Nachtigal M. Characterization of human vascular smooth muscle cells transformed by the early genetic region of SV40 virus. Am J Pathol. 1991 Sep;139(3):629–640. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limon J., Dal Cin P., Sandberg A. A. Application of long-term collagenase disaggregation for the cytogenetic analysis of human solid tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Dec;23(4):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder D., Gartler S. M. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mosaicism: utilization as a cell marker in the study of leiomyomas. Science. 1965 Oct 1;150(3692):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3692.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majesky M. W., Reidy M. A., Benditt E. P., Juchau M. R. Focal smooth muscle proliferation in the aortic intima produced by an initiation-promotion sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald K., Rector T. S., Braulin E. A., Kubo S. H., Olivari M. T. Association of coronary artery disease in cardiac transplant recipients with cytomegalovirus infection. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Aug 1;64(5):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Petrie B. L., Dreesman G. R., Burek J., McCollum C. H., DeBakey M. E. Cytomegalovirus antigen within human arterial smooth muscle cells. Lancet. 1983 Sep 17;2(8351):644–647. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Bender M. A., Harris E. A., Kaleko M., Gelinas R. E. Design of retrovirus vectors for transfer and expression of the human beta-globin gene. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4337–4345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4337-4345.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minick C. R., Fabricant C. G., Fabricant J., Litrenta M. M. Atheroarteriosclerosis induced by infection with a herpesvirus. Am J Pathol. 1979 Sep;96(3):673–706. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss N. S., Benditt E. P. Human atherosclerotic plaque cells and leiomyoma cells. Comparison of in vitro growth characteristics. Am J Pathol. 1975 Feb;78(2):175–190. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Werness B. A., Dyson N., Phelps W. C., Harlow E., Howley P. M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4099–4105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachtigal M., Legrand A., Greenspan P., Nachtigal S. A., Nagpal M. L. Immortalization of rabbit vascular smooth muscle cells after transfection with a fragment of the BglII N region of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA. Intervirology. 1990;31(2-4):166–174. doi: 10.1159/000150151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachtigal M., Legrand A., Nagpal M. L., Nachtigal S. A., Greenspan P. Transformation of rabbit vascular smooth muscle cells by transfection with the early region of SV40 DNA. Am J Pathol. 1990 Feb;136(2):297–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nibert M., Heim S. Uterine leiomyoma cytogenetics. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 May;2(1):3–13. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870020103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson T. A., Dillman J. M., Solez K., Heptinstall R. H. Clonal characteristics in layers of human atherosclerotic plaques. A study of the selection hypothesis of monoclonality. Am J Pathol. 1978 Oct;93(1):93–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie B. L., Adam E., Melnick J. L. Association of herpesvirus/cytomegalovirus infections with human atherosclerosis. Prog Med Virol. 1988;35:21–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie B. L., Melnick J. L., Adam E., Burek J., McCollum C. H., DeBakey M. E. Nucleic acid sequences of cytomegalovirus in cells cultured from human arterial tissue. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):158–159. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F. Rat vascular smooth muscle cells immortalized with SV40 large T antigen possess defined smooth muscle cell characteristics including growth inhibition by heparin. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Feb;142(2):342–351. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041420217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein M. S., Friedman A. J., Barbieri R. L., Pavelka K., Fletcher J. A., Morton C. C. Cytogenetic abnormalities in uterine leiomyomata. Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jun;77(6):923–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis--an update. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 20;314(8):488–500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602203140806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Wight T. N., Strandness E., Thiele B. Human atherosclerosis. I. Cell constitution and characteristics of advanced lesions of the superficial femoral artery. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jan;114(1):79–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Campbell G. R., Campbell J. H. Replication of smooth muscle cells in vascular disease. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):427–444. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern C., Kazmierczak B., Thode B., Rommel B., Bartnitzke S., Dal Cin P., van de Ven W., Van den Berghe H., Bullerdiek J. Leiomyoma cells with 12q15 aberrations can be transformed in vitro and show a relatively stable karyotype during precrisis period. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1991 Jul 15;54(2):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(91)90210-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. A., Reiner J. M., Janakidevi K., Florentin R. A., Lee K. T. Population dynamics of arterial cells during atherogenesis. X. Study of monotypism in atherosclerotic lesions of black women heterozygous for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD). Exp Mol Pathol. 1979 Dec;31(3):367–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(79)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Tippens D., Gordon D., Ross R., Gown A. M. HHF35, a muscle-actin-specific monoclonal antibody. I. Immunocytochemical and biochemical characterization. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jan;126(1):51–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Kanda T., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 transformation of primary human embryonic fibroblasts requires expression of open reading frames E6 and E7. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):965–969. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.965-969.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werness B. A., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins with p53. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):76–79. doi: 10.1126/science.2157286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiroya H. M., Ghosh L., Yang R., Robertson A. L., Jr Herpesviridae in the coronary arteries and aorta of young trauma victims. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jan;130(1):71–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]