Abstract
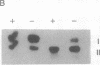
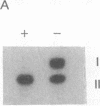
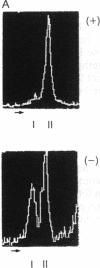
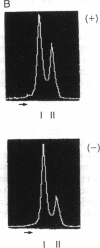
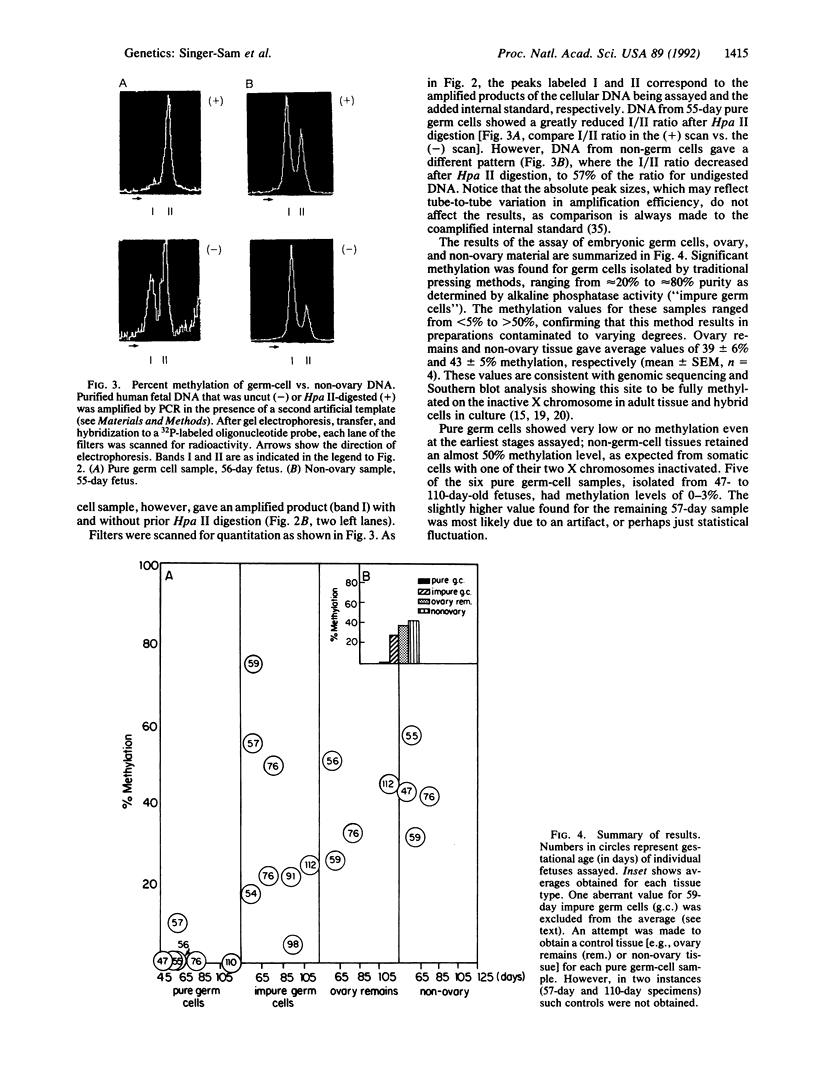
Hpa II site H8 is in the CpG-rich 5' untranslated region of the human X chromosome-linked gene for phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1). It is the only Hpa II site in the CpG "island" whose methylation pattern is perfectly correlated with transcriptional silence of this gene. We measured DNA methylation at site H8 in fetal oogonia and oocytes and found, using a quantitative assay based on the polymerase chain reaction, that purified germ cells isolated by micromanipulation were unmethylated in 47-day to 110-day fetuses, whereas ovaries depleted of germ cells and non-ovary tissues were methylated. We conclude that site H8 is unmethylated in germ cells prior to the onset of meiosis and reactivation of the X chromosome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andina R. J. A study of X chromosome regulation during oogenesis in the mouse. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jan;111(1):211–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER T. G. A QUANTITATIVE AND CYTOLOGICAL STUDY OF GERM CELLS IN HUMAN OVARIES. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1963 Oct 22;158:417–433. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1963.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLANDAU R. J., WHITE B. J., RUMERY R. E. OBSERVATIONS ON THE MOVEMENTS OF THE LIVING PRIMORDIAL GERM CELLS IN THE MOUSE. Fertil Steril. 1963 Sep-Oct;14:482–489. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)34981-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIQUOINE A. D. The identification, origin, and migration of the primordial germ cells in the mouse embryo. Anat Rec. 1954 Feb;118(2):135–146. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091180202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H., Razin A. DNA methylation and development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 24;1049(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90076-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaillet J. R., Vogt T. F., Beier D. R., Leder P. Parental-specific methylation of an imprinted transgene is established during gametogenesis and progressively changes during embryogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90140-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. J., Migeon B. R. Sex difference in methylation of single-copy genes in human meiotic germ cells: implications for X chromosome inactivation, parental imprinting, and origin of CpG mutations. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 May;16(3):267–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01233363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebensperger C., Studer R., Epplen J. T. Specific amplification of the ZFY gene to screen sex in man. Hum Genet. 1989 Jun;82(3):289–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00291174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Andina R., Gant N. Ontogeny of X-chromosome inactivation in the female germ line. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 15;91(2):454–457. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Liskay R. M., Campbell B. K., Sparkes R., Gant N. Evidence for two functional X chromosomes in human oocytes. Cell Differ. 1972 Oct;1(4):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(72)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartler S. M., Rivest M., Cole R. E. Cytological evidence for an inactive X chromosome in murine oogonia. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;28(3):203–207. doi: 10.1159/000131531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen R. S., Ellis N. A., Gartler S. M. Demethylation of specific sites in the 5' region of the inactive X-linked human phosphoglycerate kinase gene correlates with the appearance of nuclease sensitivity and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4692–4699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanpierre M. A rapid method for the purification of DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9611–9611. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith D. H., Singer-Sam J., Riggs A. D. Active X chromosome DNA is unmethylated at eight CCGG sites clustered in a guanine-plus-cytosine-rich island at the 5' end of the gene for phosphoglycerate kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4122–4125. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzer P. G., Chapman V. M. X chromosome reactivation in oocytes of Mus caroli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3093–3097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock L. F., Takagi N., Martin G. R. Methylation of the Hprt gene on the inactive X occurs after chromosome inactivation. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKAY D. G., HERTIG A. T., ADAMS E. C., DANZIGER S. Histochemical observations on the germ cells of human embryos. Anat Rec. 1953 Oct;117(2):201–219. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon B. R. Insights into X chromosome inactivation from studies of species variation, DNA methylation and replication, and vice versa. Genet Res. 1990 Oct-Dec;56(2-3):91–98. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300035151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Boubelik M., Lehnert S. Temporal and regional changes in DNA methylation in the embryonic, extraembryonic and germ cell lineages during mouse embryo development. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):371–382. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., McLaren A. X-chromosome activity in foetal germ cells of the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Jun;63:75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa G. J., Zaia J. A., Spallone P. A., Stephens D. A., Kaplan B. E., Wallace R. B., Rossi J. J. Direct detection of HIV-1 RNA from AIDS and ARC patient samples. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):287–295. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer M. S., Berta P., Sinclair A. H., Pym B., Goodfellow P. N. Comparison of human ZFY and ZFX transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1681–1685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Hansen R. S., Gartler S. M., Riggs A. D. Polymerase chain reaction-aided genomic sequencing of an X chromosome-linked CpG island: methylation patterns suggest clonal inheritance, CpG site autonomy, and an explanation of activity state stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8252–8256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Mueller P. R., Wold B., Riggs A. D. Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2814502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Tanguay R. L., Steigerwald S. D., Riggs A. D. In vivo footprint and methylation analysis by PCR-aided genomic sequencing: comparison of active and inactive X chromosomal DNA at the CpG island and promoter of human PGK-1. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1277–1287. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and cell memory. Cell Biophys. 1989 Aug-Oct;15(1-2):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02991574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J. P., Clark H. J., Chapman V. M., Rossant J. Differences in DNA methylation during oogenesis and spermatogenesis and their persistence during early embryogenesis in the mouse. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1039–1046. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Sam J., Grant M., LeBon J. M., Okuyama K., Chapman V., Monk M., Riggs A. D. Use of a HpaII-polymerase chain reaction assay to study DNA methylation in the Pgk-1 CpG island of mouse embryos at the time of X-chromosome inactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4987–4989. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Sam J., Keith D. H., Tani K., Simmer R. L., Shively L., Lindsay S., Yoshida A., Riggs A. D. Sequence of the promoter region of the gene for human X-linked 3-phosphoglycerate kinase. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):409–417. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Sam J., LeBon J. M., Tanguay R. L., Riggs A. D. A quantitative HpaII-PCR assay to measure methylation of DNA from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):687–687. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham D. G. Culture of mouse ova. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1971 Jun;14:7–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Singer-Sam J., Flores J. C., Riggs A. D. DNA binding factors for the CpG-rich island containing the promoter of the human X-linked PGK gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Sep;14(5):461–472. doi: 10.1007/BF01534712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]