Abstract
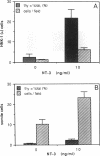
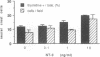
Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) promotes the survival and induces neurite outgrowth from a subset of neural crest (NC) and placode-derived neurons. We now report that this growth factor regulates the proliferation of cultured NC progenitor cells grown in a serum-free defined medium. In cultures of somites containing NC cells at migratory stages, NT-3 promotes a 2- to 8.4-fold increase in the number of NC cells incorporating [3H]thymidine into nuclei and a 1.8- to 4.8-fold increase in NC cell number compared to controls without added factor. NT-3 also promoted, to a lesser extent, the proliferation of NC cells in homogeneous cultures established from NC clusters. In addition to its effect on NC cells, NT-3 was mitogenic to somite cells in the mixed NC/somite cultures. These data demonstrate that NT-3 can act directly on the NC cells. They also indicate that the response of NC cells to NT-3 may be modulated by the presence of somitic cells. We suggest that NT-3 may be one of the central nervous system-derived factors that mediate NC cell proliferation in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1525–1534. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner-Fraser M. Analysis of the early stages of trunk neural crest migration in avian embryos using monoclonal antibody HNK-1. Dev Biol. 1986 May;115(1):44–55. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner-Fraser M., Stern C. Effects of mesodermal tissues on avian neural crest cell migration. Dev Biol. 1991 Feb;143(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90071-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo E., McKay R. Proliferation and differentiation of neuronal stem cells regulated by nerve growth factor. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):762–765. doi: 10.1038/347762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Tapley P., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Lamballe F., Kovary K., Klein R., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. The trk tyrosine protein kinase mediates the mitogenic properties of nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90149-s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. M., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. The response of chick sensory neurons to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):1897–1904. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-01897.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass D. J., Nye S. H., Hantzopoulos P., Macchi M. J., Squinto S. P., Goldfarb M., Yancopoulos G. D. TrkB mediates BDNF/NT-3-dependent survival and proliferation in fibroblasts lacking the low affinity NGF receptor. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90629-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. S., Kalcheim C. Normal segmentation and size of the primary sympathetic ganglia depend upon the alternation of rostrocaudal properties of the somites. Development. 1991 May;112(1):327–334. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. S., Teillet M. A., Kalcheim C. The microenvironment created by grafting rostral half-somites is mitogenic for neural crest cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4476–4480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Fibroblast growth factor and its involvement in developmental processes. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1990;24:57–93. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn A., Leibrock J., Bailey K., Barde Y. A. Identification and characterization of a novel member of the nerve growth factor/brain-derived neurotrophic factor family. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):339–341. doi: 10.1038/344339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalcheim C., Barde Y. A., Thoenen H., Le Douarin N. M. In vivo effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on the survival of developing dorsal root ganglion cells. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2871–2873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalcheim C. Basic fibroblast growth factor stimulates survival of nonneuronal cells developing from trunk neural crest. Dev Biol. 1989 Jul;134(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalcheim C., Gendreau M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulates survival and neuronal differentiation in cultured avian neural crest. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 1;469(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90171-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalcheim C., Le Douarin N. M. Requirement of a neural tube signal for the differentiation of neural crest cells into dorsal root ganglia. Dev Biol. 1986 Aug;116(2):451–466. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalcheim C., Teillet M. A. Consequences of somite manipulation on the pattern of dorsal root ganglion development. Development. 1989 May;106(1):85–93. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. J., Stern C. D. Segmentation in the vertebrate nervous system. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):786–789. doi: 10.1038/310786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Nanduri V., Jing S. A., Lamballe F., Tapley P., Bryant S., Cordon-Cardo C., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90628-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier T. E., Bronner-Fraser M. A spatial and temporal analysis of dorsal root and sympathetic ganglion formation in the avian embryo. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):99–112. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90192-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Lievre C. S., Schweizer G. G., Ziller C. M., Le Douarin N. M. Restrictions of developmental capabilities in neural crest cell derivatives as tested by in vivo transplantation experiments. Dev Biol. 1980 Jun 15;77(2):362–378. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillien L. E., Claude P. Nerve growth factor is a mitogen for cultured chromaffin cells. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):632–634. doi: 10.1038/317632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay R. M., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Placode and neural crest-derived sensory neurons are responsive at early developmental stages to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring J. F., Erickson C. A. Neural crest cell migratory pathways in the trunk of the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):220–236. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90154-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring J., Glimelius B., Erickson C., Weston J. A. Analysis of developmentally homogeneous neural crest cell populations in vitro. I. Formation, morphology and differentiative behavior. Dev Biol. 1981 Feb;82(1):86–94. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90430-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Friedman B., Alderson R. F., Wiegand S. J., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. NT-3, BDNF, and NGF in the developing rat nervous system: parallel as well as reciprocal patterns of expression. Neuron. 1990 Oct;5(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Squinto S., Ip N. Y., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1446–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. S., Sharma A., de Vellis J., Bradshaw R. A. Basic fibroblast growth factor supports the survival of cerebral cortical neurons in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7537–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgreen D. F., Scheel M., Kastner V. Morphogenesis of sclerotome and neural crest in avian embryos. In vivo and in vitro studies on the role of notochordal extracellular material. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;244(2):299–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00219205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickmann M., Fawcett J. W., Keynes R. J. The migration of neural crest cells and the growth of motor axons through the rostral half of the chick somite. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Dec;90:437–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Moscatelli D. Recent developments in the cell biology of basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Goeddel D. V., Nguyen T., Lewis M., Shih A., Laramee G. R., Nikolics K., Winslow J. W. Primary structure and biological activity of a novel human neurotrophic factor. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):767–773. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90203-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer G., Ayer-Le Lièvre C., Le Douarin N. M. Restrictions of developmental capacities in the dorsal root ganglia during the course of development. Cell Differ. 1983 Nov;13(3):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(83)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieber-Blum M. Role of the neurotrophic factors BDNF and NGF in the commitment of pluripotent neural crest cells. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):949–955. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90235-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., Burton L. E., Stanton B. R., Kaplan D. R., Hunter T. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):895–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Stitt T. N., Aldrich T. H., Davis S., Bianco S. M., Radziejewski C., Glass D. J., Masiakowski P., Furth M. E., Valenzuela D. M. trkB encodes a functional receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 but not nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90395-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teillet M. A., Kalcheim C., Le Douarin N. M. Formation of the dorsal root ganglia in the avian embryo: segmental origin and migratory behavior of neural crest progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 1987 Apr;120(2):329–347. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teillet M. A., Le Douarin N. M. Consequences of neural tube and notochord excision on the development of the peripheral nervous system in the chick embryo. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):192–211. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Reichert-Preibsch H., Schmidt R., Pettmann B., Labourdette G., Sensenbrenner M. Astroglial and fibroblast growth factors have neurotrophic functions for cultured peripheral and central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walicke P. A. Basic and acidic fibroblast growth factors have trophic effects on neurons from multiple CNS regions. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2618–2627. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02618.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]