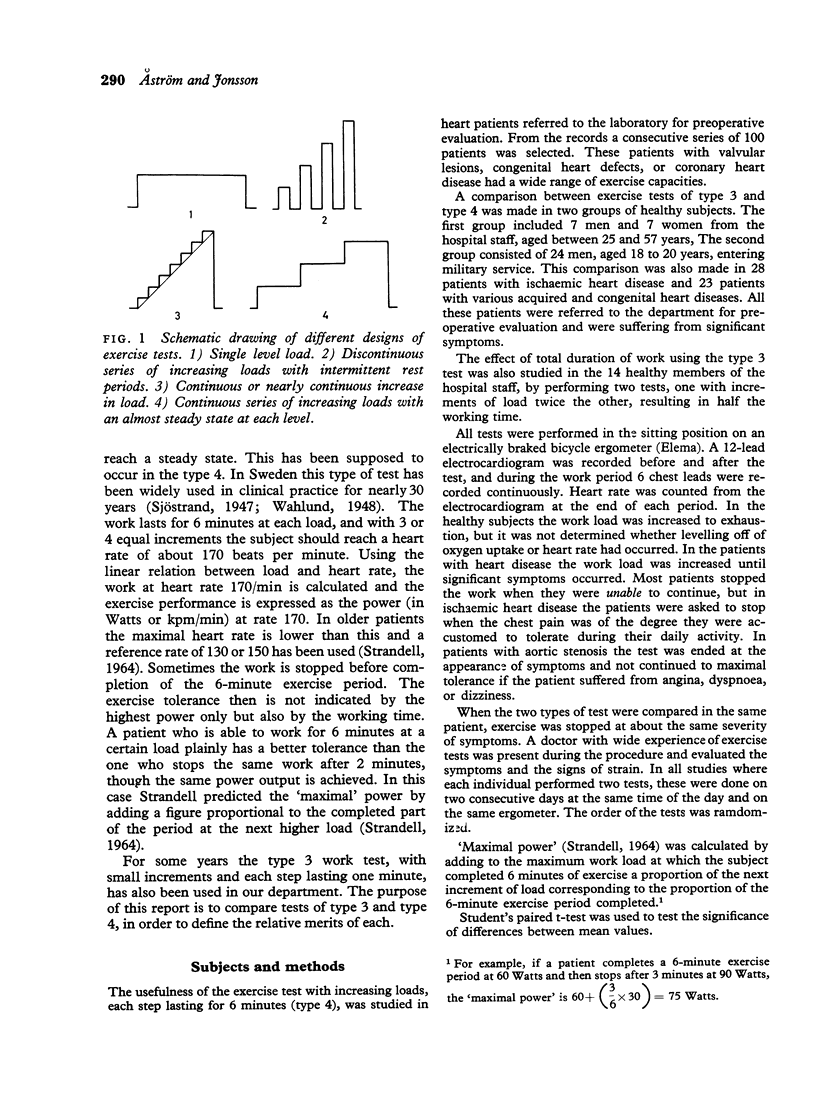
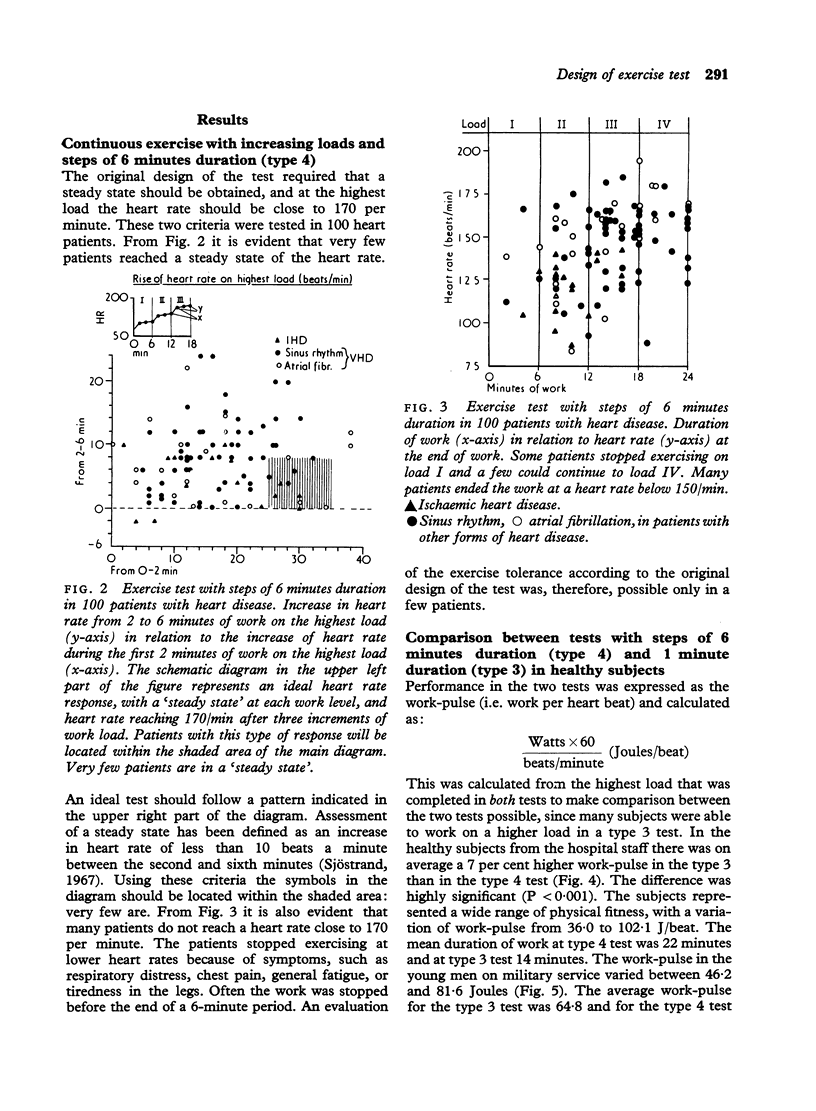
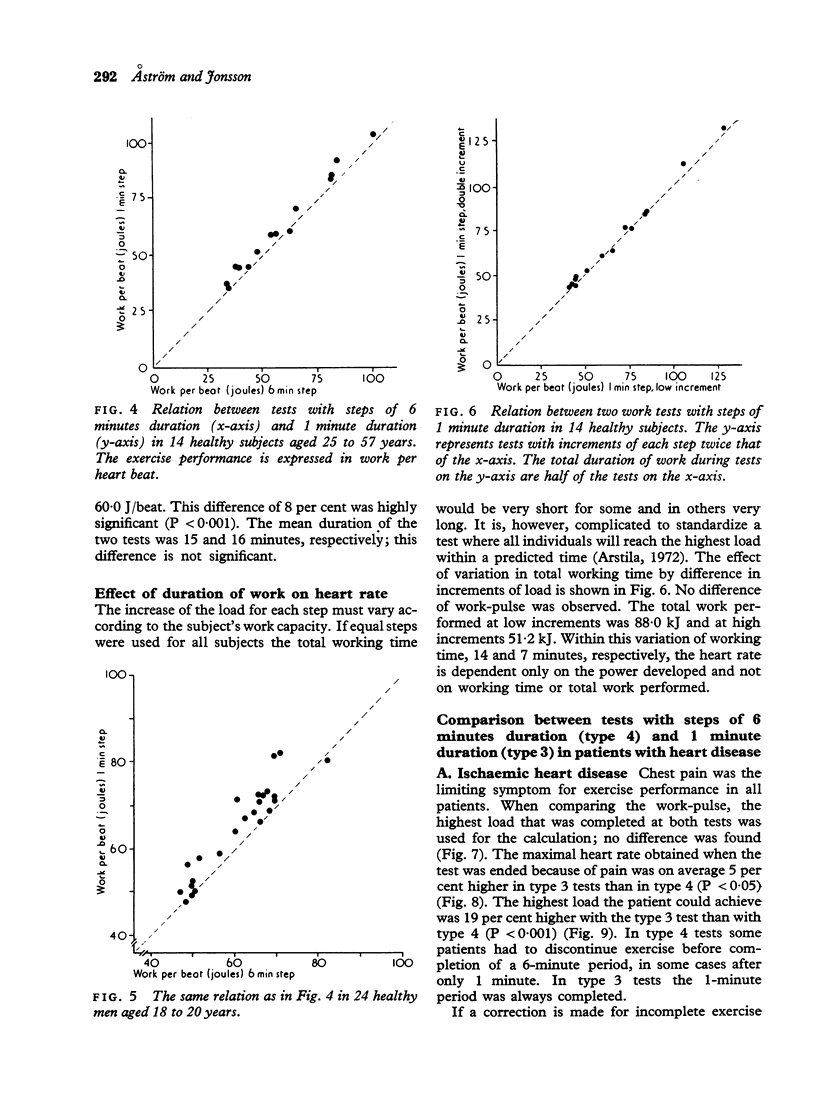
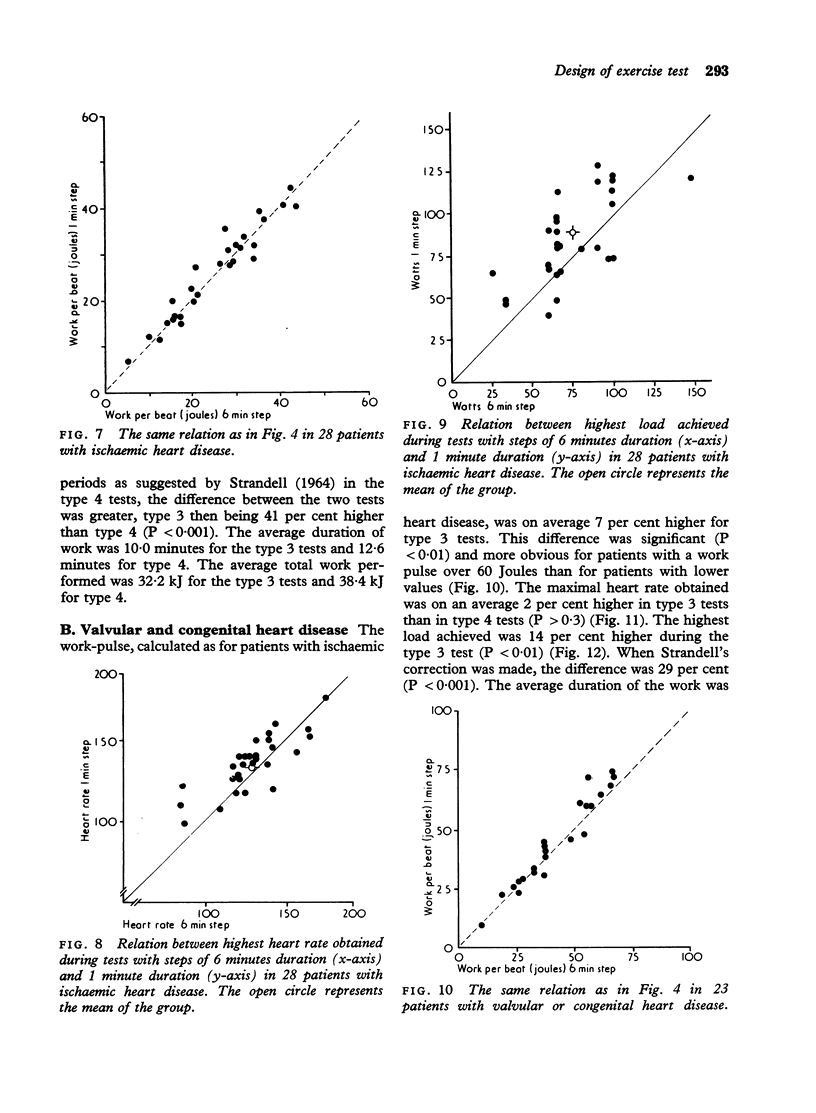
Abstract
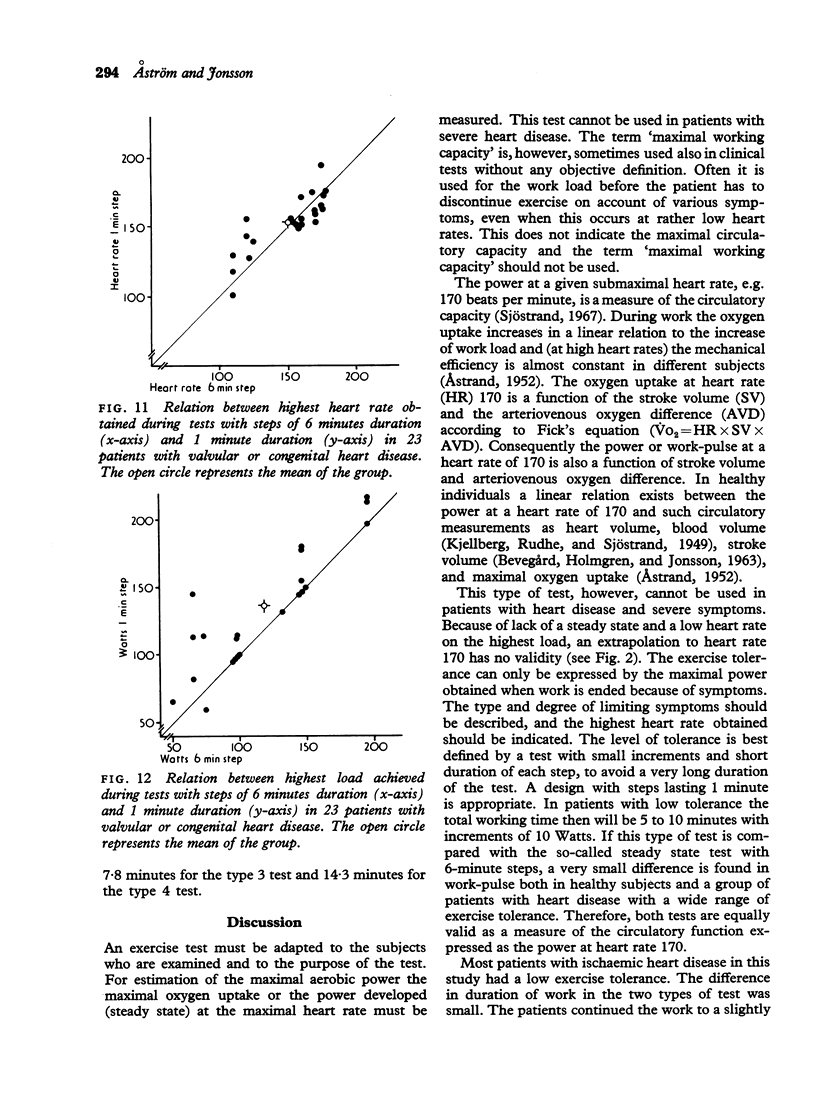
Estimation of exercise tolerance in patients with heart disease and significant symptoms can usually not be expressed in terms of maximal oxygen uptake or power at a fixed heart rate calculated from a 'steady state' exercise test. The exercise tolerance can be expressed only by the maximal power developed, when limited by symptoms. For this purpose the level of tolerance is better assessed by a test with small increments and short duration of each work load. In clinical practice this type of almost continuous increase in load was found to be particularly useful in patients with ischaemic heart disease. Comparative studies showed that the work per heart beat at equal loads is significantly higher in the test with continuous increase in load than in the test with steps of 6 minutes duration, both in normal subjects and in heart patients. The difference, however, is small (7%) and for practical purposes these tests have equal validity as a measure of the circulatory capacity.
Full text
PDF