Abstract
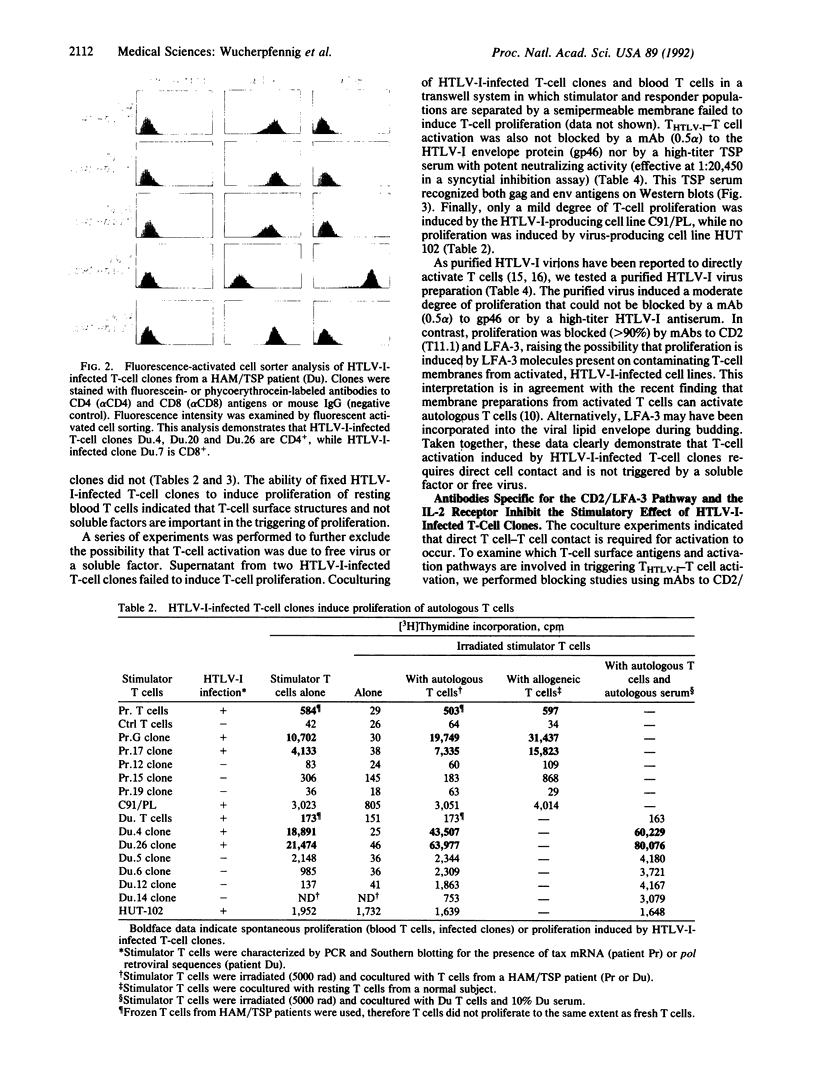
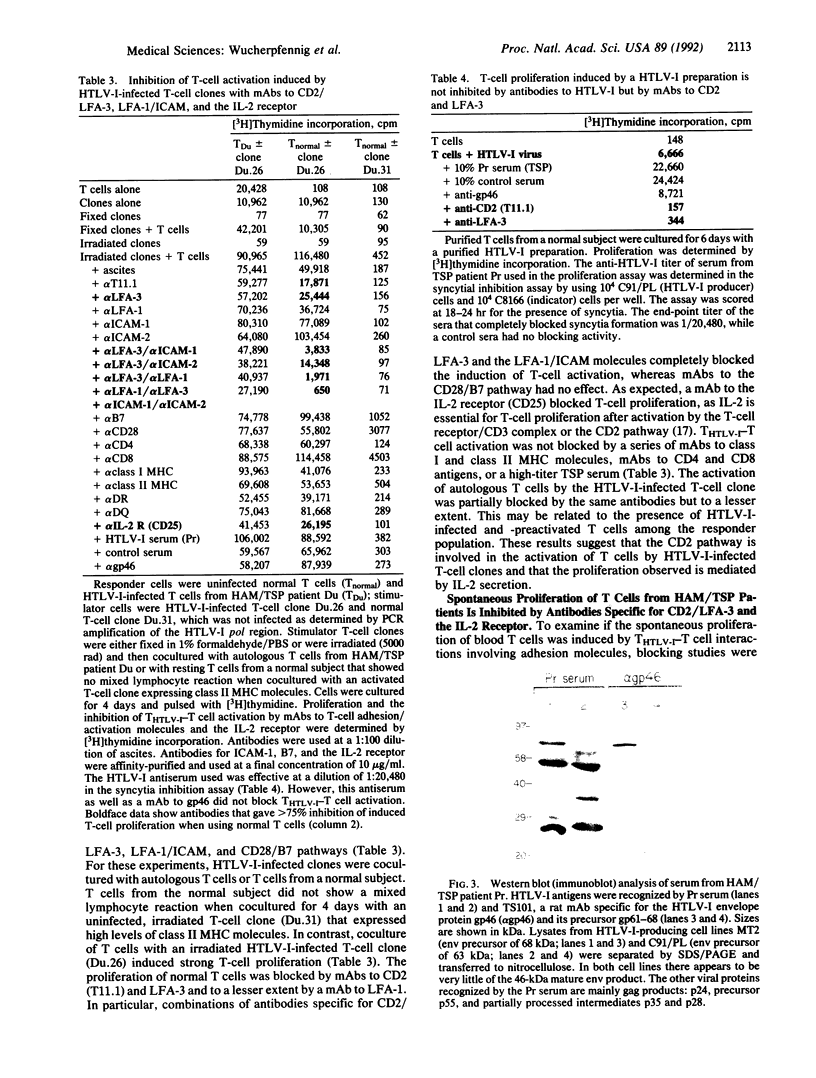
A unique feature of both human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) carriers and subjects with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP), a chronic inflammatory disease of the nervous system, is the presence of large numbers of activated T cells that spontaneously proliferate in vitro. We have investigated the mechanisms of T-cell activation by HTLV-I in freshly isolated blood T cells and in naturally infected T-cell clones obtained by direct single-cell cloning from patients with HAM/TSP. Both CD4+ and CD8+ HTLV-I-infected T-cell clones showed the unusual ability to proliferate in the absence of exogenous interleukin 2 (IL-2). Nevertheless, HTLV-I-infected clones were not transformed, as they required periodic restimulation with phytohemagglutinin and feeder cells for long-term growth. Irradiated or fixed HTLV-I-infected clones were found to induce the proliferation of blood T cells when cocultured, which we refer to as THTLV-1-T cell activation. This THTLV-1-T cell-mediated activation was blocked by monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against CD2/lymphocyte function-associated molecule 3 (LFA-3), LFA-1/intercellular cell-adhesion molecule (ICAM), and the IL-2 receptor but not by mAbs against class I or class II major histocompatibility complex molecules, HTLV-I gp46, or a high-titer HAM/TSP serum. Spontaneous proliferation of blood T cells from HAM/TSP patients could also be inhibited by mAbs to CD2/LFA-3, LFA-1/ICAM and to the IL-2 receptor (CD25). These results show at the clonal level that HTLV-I infection induces T-cell activation and that such activated T cells can in turn stimulate noninfected T cells by cognate THTLV-1-T cell interactions involving the CD2 pathway.
Full text
PDF


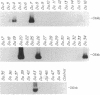
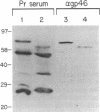
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhagavati S., Ehrlich G., Kula R. W., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Udani V., Poiesz B. J. Detection of human T-cell lymphoma/leukemia virus type I DNA and antigen in spinal fluid and blood of patients with chronic progressive myelopathy. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 5;318(18):1141–1147. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805053181801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brod S. A., Purvee M., Benjamin D., Hafler D. A. T-T cell interactions are mediated by adhesion molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2259–2268. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodon M. D., Bernard A., Gazzolo L. Peripheral T-lymphocyte activation by human T-cell leukemia virus type I interferes with the CD2 but not with the CD3/TCR pathway. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5413–5419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5413-5419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzolo L., Duc Dodon M. Direct activation of resting T lymphocytes by human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):714–717. doi: 10.1038/326714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Duby A. D., Lee S. J., Benjamin D., Seidman J. G., Weiner H. L. Oligoclonal T lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1313–1322. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Tiefenthaler G., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Meuer S. C. Alternative pathway activation of T cells by binding of CD2 to its cell-surface ligand. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):298–301. doi: 10.1038/326298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Kira J., Fujii N., Goto I., Yamamoto N. Increases in helper inducer T cells and activated T cells in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol. 1989 Aug;26(2):257–262. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Gupta A., Mattson D., Mingioli E., McFarlin D. E. Immunological studies in tropical spastic paraparesis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):149–156. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Raine C. S., Mingioli E. S., McFarlin D. E. Isolation of an HTLV-1-like retrovirus from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):540–543. doi: 10.1038/331540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson S., Shida H., McFarlin D. E., Fauci A. S., Koenig S. Circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for HTLV-I pX in patients with HTLV-I associated neurological disease. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):245–248. doi: 10.1038/348245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Shimoyama M., Tobinai K., Ito M., Ito S., Ikeda S., Tajima K., Shimotohno K., Sugimura T. Detection of mRNA for the tax1/rex1 gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells of adult T-cell leukemia patients and viral carriers by using the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5620–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Kinoshita K., Ban N., Yamada Y., Shiku H. Activated T-lymphocytes with polyclonal gammopathy in patients with human T-lymphotropic virus type I--associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol. 1988 Aug;24(2):280–282. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osame M., Matsumoto M., Usuku K., Izumo S., Ijichi N., Amitani H., Tara M., Igata A. Chronic progressive myelopathy associated with elevated antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I and adult T-cell leukemialike cells. Ann Neurol. 1987 Feb;21(2):117–122. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PCR analysis of DNA from multiple sclerosis patients for the presence of HTLV-I. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):821–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. H., Edwards A. J., Cruickshank J. K., Rudge P., Dalgleish A. G. In vivo cellular tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5682–5687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5682-5687.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tendler C. L., Greenberg S. J., Blattner W. A., Manns A., Murphy E., Fleisher T., Hanchard B., Morgan O., Burton J. D., Nelson D. L. Transactivation of interleukin 2 and its receptor induces immune activation in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy: pathogenic implications and a rationale for immunotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5218–5222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The structure, function, and expression of interleukin-2 receptors on normal and malignant lymphocytes. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):727–732. doi: 10.1126/science.3008337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Fierz W. T cell approach to demyelinating diseases. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1985;8(1-2):97–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00197249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Miyoshi I., Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]