Abstract
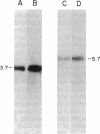
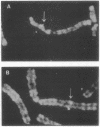
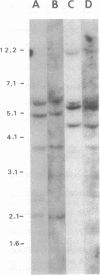
We report the isolation and sequencing of cDNAs encoding two human glutamate decarboxylases (GADs; L-glutamate 1-carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.15), GAD65 and GAD67. Human GAD65 cDNA encodes a Mr 65,000 polypeptide, with 585 amino acid residues, whereas human GAD67 encodes a Mr 67,000 polypeptide, with 594 amino acid residues. Both cDNAs direct the synthesis of enzymatically active GADs in bacterial expression systems. Each cDNA hybridizes to a single species of brain mRNA and to a specific set of restriction fragments in human genomic DNA. In situ hybridization of fluorescently labeled GAD probes to human chromosomes localizes the human GAD65 gene to chromosome 10p11.23 and the human GAD67 gene to chromosome 2q31. We conclude that GAD65 and GAD67 each derive from a single separate gene. The cDNAs we describe should allow the bacterial production of test antigens for the diagnosis and prediction of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Riley W. J. 64,000 Mr autoantibodies as predictors of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jun 9;335(8702):1357–1360. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Landin M., Kristensen J. K., Srikanta S., Bruining G. J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., de Beaufort C., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G., Lindgren F. Antibodies to a 64,000 Mr human islet cell antigen precede the clinical onset of insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):926–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI112903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Nielsen J. H., Marner B., Bilde T., Ludvigsson J., Lernmark A. Autoantibodies in newly diagnosed diabetic children immunoprecipitate human pancreatic islet cell proteins. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):167–169. doi: 10.1038/298167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banatvala J. E. Insulin-dependent (juvenile-onset, type 1) diabetes mellitus Coxsackie B viruses revisited. Prog Med Virol. 1987;34:33–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Connor E. Is insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus caused by coxsackievirus B infection? A review of the epidemiologic evidence. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):207–215. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum P., Jankovic J. Stiff-person syndrome: an autoimmune disease. Mov Disord. 1991;6(1):12–20. doi: 10.1002/mds.870060104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. W., Wyborski R. J., Gottlieb D. I. Developmentally regulated expression of an exon containing a stop codon in the gene for glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8771–8775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossa F., Martini F., Barra D., Voltattorni C. B., Minelli A., Turano C. The chymotryptic phosphopyridoxyl peptide of DOPA decarboxylase from pig kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91237-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breakefield X. O., Bressman S. B., Kramer P. L., Ozelius L., Moskowitz C., Tanzi R., Brin M. F., Hobbs W., Kaufman D., Tobin A. Linkage analysis in a family with dominantly inherited torsion dystonia: exclusion of the pro-opiomelanocortin and glutamic acid decarboxylase genes and other chromosomal regions using DNA polymorphisms. J Neurogenet. 1986 May;3(3):159–175. doi: 10.3109/01677068609106846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. C., Gottlieb D. I. Characterization of the proteins purified with monoclonal antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-02123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cram D. S., Barnett L. D., Joseph J. L., Harrison L. C. Cloning and partial nucleotide sequence of human glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA from brain and pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1239–1244. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdö S. L., Wolff J. R. gamma-Aminobutyric acid outside the mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):363–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Tillakaratne N. J., Feldblum S., Patel N., Tobin A. J. Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90077-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J. The structural and functional heterogeneity of glutamic acid decarboxylase: a review. Neurochem Res. 1991 Mar;16(3):215–226. doi: 10.1007/BF00966084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble D. R. The epidemiology of insulin dependent diabetes with particular reference to the relationship of virus infection to its etiology. Epidemiol Rev. 1980;2:49–70. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M., Reed-Fourquet L., Wu E., Wu J. Y. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of brain L-glutamate decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8491–8495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. R., Newby L. M., Kulkarni S. J. Drosophila GABAergic systems: sequence and expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):1068–1078. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. F., Legay F., Dumas S., Tappaz M., Mallet J. Molecular cloning, expression and in situ hybridization of rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase messenger RNA. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 14;73(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen A. E., Hagopian W. A., Grubin C. E., Dube S., Disteche C. M., Adler D. A., Bärmeier H., Mathewes S., Grant F. J., Foster D. Cloning and primary structure of a human islet isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase from chromosome 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8337–8341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katarova Z., Szabo G., Mugnaini E., Greenspan R. J. Molecular Identification of the 62 kd Form of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase from the Mouse. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(3):190–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Erlander M. G., Clare-Salzler M., Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Tobin A. J. Autoimmunity to two forms of glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):283–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI115573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Houser C. R., Tobin A. J. Two forms of the gamma-aminobutyric acid synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase have distinct intraneuronal distributions and cofactor interactions. J Neurochem. 1991 Feb;56(2):720–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., McGinnis J. F., Krieger N. R., Tobin A. J. Brain glutamate decarboxylase cloned in lambda gt-11: fusion protein produces gamma-aminobutyric acid. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1138–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.3518061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J. Glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA: nucleotide sequence encoding an enzymatically active fusion protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02768.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger N. R., Heller J. S. Localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase within laminae of the rat olfactory tubercle. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):299–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Tang C. J., Call K., Hermanson G., Evans G. A., Housman D., Ward D. C. High-resolution mapping of human chromosome 11 by in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.2294592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. L. Regulatory properties of brain glutamate decarboxylase. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1987 Sep;7(3):237–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00711302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelsen B. K., Petersen J. S., Boel E., Møldrup A., Dyrberg T., Madsen O. D. Cloning, characterization, and autoimmune recognition of rat islet glutamic acid decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8754–8758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Molecular mimicry and autoimmune disease. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):819–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Pelto-Huikko M., Metsis M., Söder O., Brene S., Skog S., Hökfelt T., Ritzén E. M. Expression of the neurotransmitter-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase in male germ cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4701–4711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reetz A., Solimena M., Matteoli M., Folli F., Takei K., De Camilli P. GABA and pancreatic beta-cells: colocalization of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and GABA with synaptic-like microvesicles suggests their role in GABA storage and secretion. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1275–1284. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08069.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Berggren P. O., Bokvist K., Ericson H., Möhler H., Ostenson C. G., Smith P. A. Glucose-inhibition of glucagon secretion involves activation of GABAA-receptor chloride channels. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):233–236. doi: 10.1038/341233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solimena M., Folli F., Aparisi R., Pozza G., De Camilli P. Autoantibodies to GABA-ergic neurons and pancreatic beta cells in stiff-man syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 31;322(22):1555–1560. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005313222202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spink D. C., Porter T. G., Wu S. J., Martin D. L. Characterization of three kinetically distinct forms of glutamate decarboxylase from pig brain. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 1;231(3):695–703. doi: 10.1042/bj2310695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Lewis K. A., Ruiz J. C., Rothenberg B., Zhao J., Evans G. A. Cosmid vectors for rapid genomic walking, restriction mapping, and gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyborski R. J., Bond R. W., Gottlieb D. I. Characterization of a cDNA coding for rat glutamic acid decarboxylase. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Aug;8(3):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. High resolution of human chromosomes. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1257746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]