Abstract
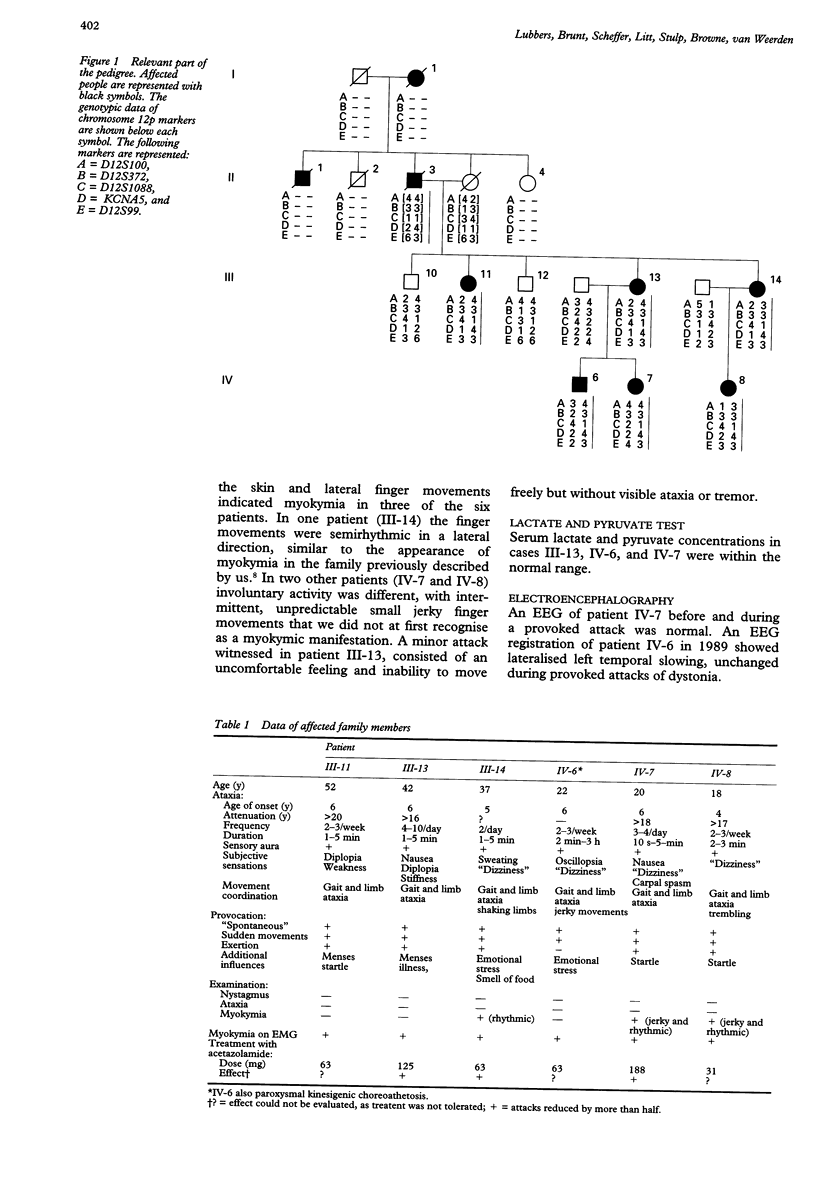
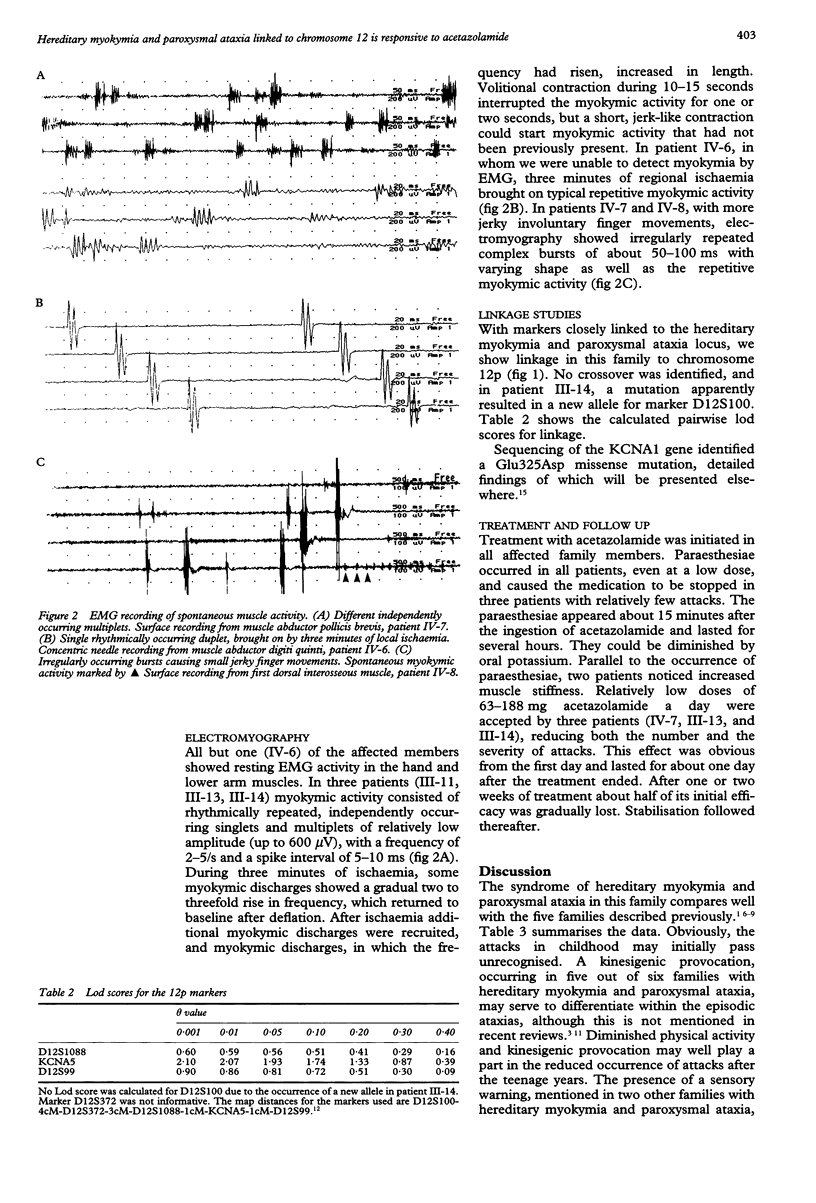
A sixth family with autosomal dominantly inherited myokymia and paroxysmal ataxia is described. The syndrome in this family is linked to the recently discovered locus for inherited myokymia and paroxysmal ataxia on the human chromosome 12p, and a missense mutation is shown in the KCNA1 gene. The attacks of ataxia in this family compare well with those of previously described families and similarly are precipitated by kinesigenic stimuli, exertion, and startle. Responsiveness of these attacks to low dose acetazolamide is confirmed, but some loss of efficacy occurs with prolonged treatment, and side effects are notable. Although not all affected family members showed myokymia on clinical examination, electromyography invariably showed myokymic discharges, in one patient only after a short provocation with regional ischaemia. One affected family member also had attacks of paroxysmal kinesigenic choreoathetosis, responsive to carbamazepine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Browne D. L., Gancher S. T., Nutt J. G., Brunt E. R., Smith E. A., Kramer P., Litt M. Episodic ataxia/myokymia syndrome is associated with point mutations in the human potassium channel gene, KCNA1. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):136–140. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunt E. R., van Weerden T. W. Familial paroxysmal kinesigenic ataxia and continuous myokymia. Brain. 1990 Oct;113(Pt 5):1361–1382. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.5.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake M. E., Jr, Jackson R. D., Miller C. A. Paroxysmal choreoathetosis after head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Jul;49(7):837–838. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.7.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gancher S. T., Nutt J. G. Autosomal dominant episodic ataxia: a heterogeneous syndrome. Mov Disord. 1986;1(4):239–253. doi: 10.1002/mds.870010404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff-Radford N. R. A recessively inherited ataxia with episodes of dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 May;49(5):591–594. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.5.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs R. C., Moxley R. T., 3rd, Lafrance R. A., McQuillen J. Hereditary paroxysmal ataxia: response to acetazolamide. Neurology. 1978 Dec;28(12):1259–1264. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.12.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson P. A., Martinez L. B., Cassidy R. Contractures, continuous muscle discharges, and titubation. Ann Neurol. 1977 Feb;1(2):120–124. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Kramer P., Browne D., Gancher S., Brunt E. R., Root D., Phromchotikul T., Dubay C. J., Nutt J. A gene for episodic ataxia/myokymia maps to chromosome 12p13. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;55(4):702–709. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Fahn S. Paroxysmal dystonic choreoathetosis in a patient with familial ataxia. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1184–1186. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptácek L. Ion channel shake-down. Nat Genet. 1994 Oct;8(2):111–112. doi: 10.1038/ng1094-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. C., Howes J. L., Celinski M. J., Allman R. G. Kinesigenic choreoathetosis due to brain injury. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Nov;14(4):626–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin J. J. Paroxysmal choreoathetosis following head injury. Ann Neurol. 1977 Nov;2(5):447–448. doi: 10.1002/ana.410020520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanDyke D. H., Griggs R. C., Murphy M. J., Goldstein M. N. Hereditary myokymia and periodic ataxia. J Neurol Sci. 1975 May;25(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf P. Familiäre episodische Ataxie. Nervenarzt. 1980 Jun;51(6):355–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierz S., Meessen S., Jerusalem F. Lactat- und Pyruvatblutspiegel in der Diagnostik mitochondrialer Myopathien. Nervenarzt. 1989 Sep;60(9):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


