Abstract
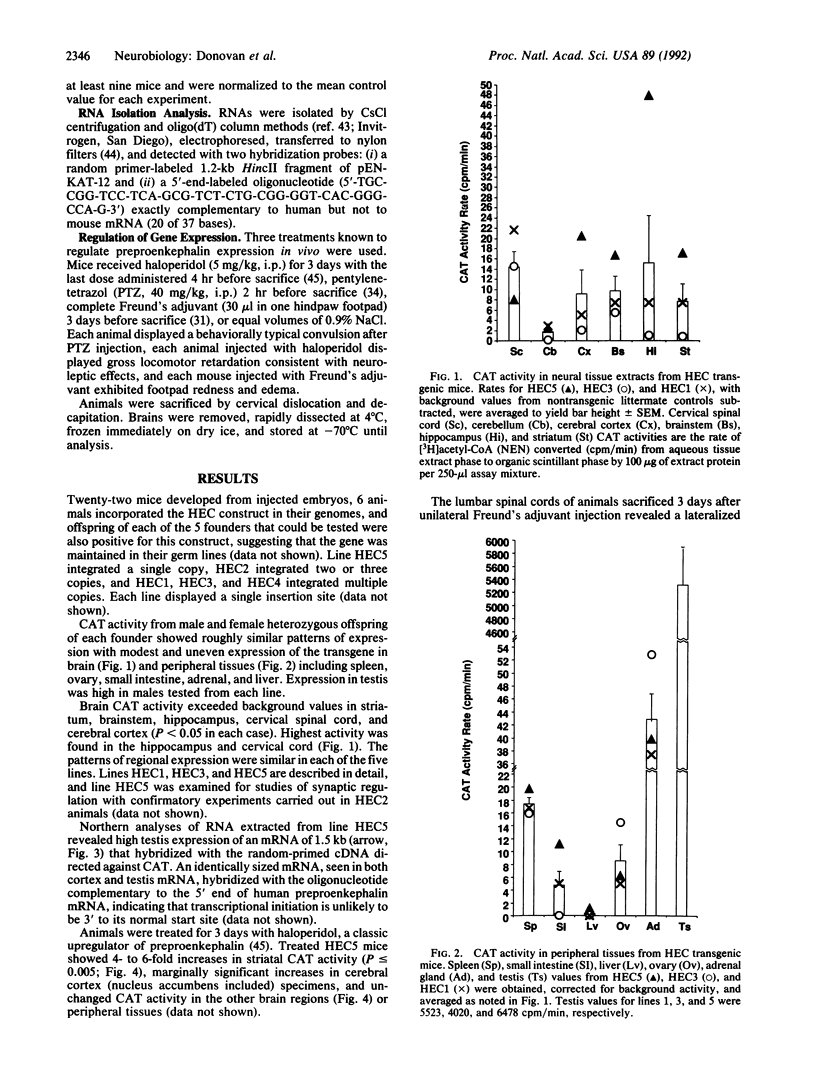
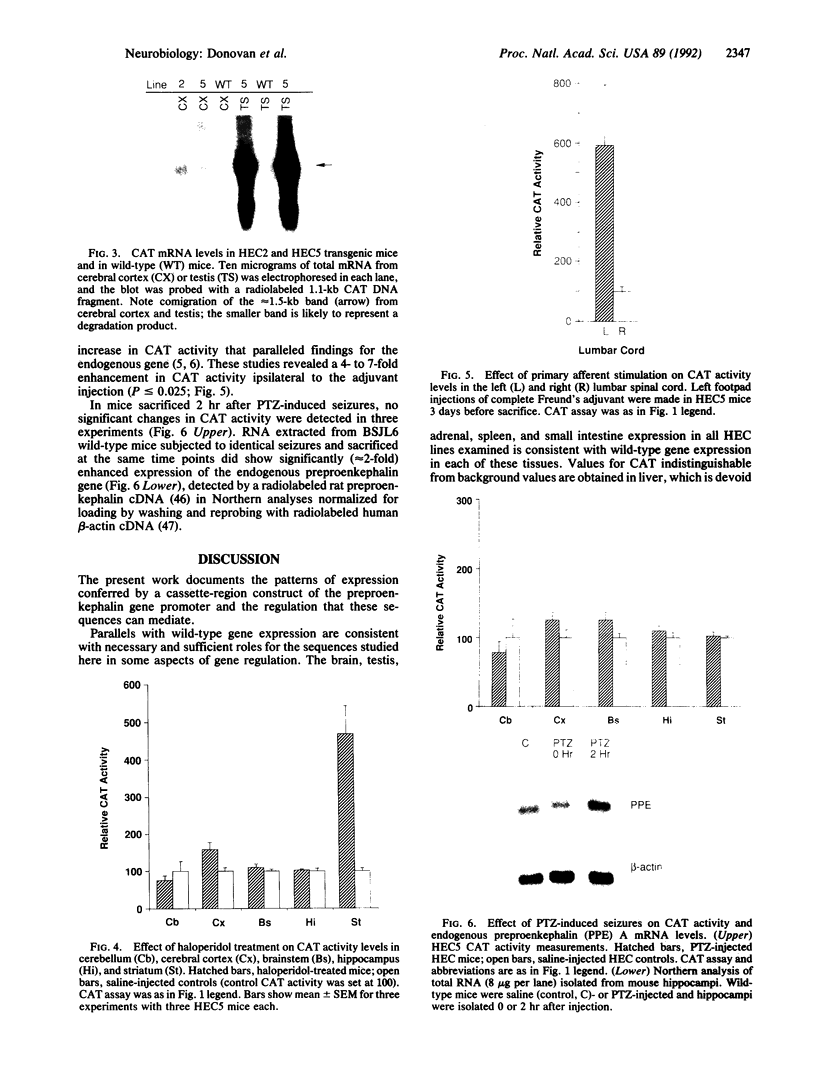
The preproenkephalin A gene is a neurotransmitter gene whose expression can be modulated "trans-synaptically" by changes in neuronal activity. DNA sequences lying within 200 base pairs of this gene's transcription start site resemble consensus binding sites for several transcription factor families. In nonneuronal cell cultures, this promoter region is sufficient to mediate gene responses to depolarization, phorbol esters, adenylate cyclase, and calcium fluxes. To assess the role that these cis-acting elements could play in preproenkephalin expression and regulation in vivo, the expression of a construct containing this 200-base-pair region fused to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene was examined in transgenic mice. This promoter confers modest expression in brain, adrenal, and small intestine, with substantially higher levels in testis. These elements confer trans-synaptic regulation in two well-studied models of trans-synaptic preproenkephalin upregulation but not in a third system, underscoring the specificity of the regulatory sequence elements implicated in the synaptic regulation of neuronal genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood M. E., Eberwine J. H., Erdelyi E., Evans C. J. Regulation of both preproenkephalin mRNA and its derived opioids by haloperidol--a method for measurement of peptides and mRNA in the same tissue extract. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Aug;8(3):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Allen J. M., Behringer R. R., Gelinas R. E., Palmiter R. D. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu H. M., Fischer W. H., Osborne T. F., Comb M. J. NF-I proteins from brain interact with the proenkephalin cAMP inducible enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Mermod N., Hyman S. E., Pearlberg J., Ross M. E., Goodman H. M. Proteins bound at adjacent DNA elements act synergistically to regulate human proenkephalin cAMP inducible transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3793–3805. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Grimes L., Shook J., Lee P. H., Hong J. S. Systemic administration of kainic acid differentially regulates the levels of prodynorphin and proenkephalin mRNA and peptides in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jan;9(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90132-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draisci G., Iadarola M. J. Temporal analysis of increases in c-fos, preprodynorphin and preproenkephalin mRNAs in rat spinal cord. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Jul;6(1):31–37. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. Seizures induce dramatic and distinctly different changes in enkephalin, dynorphin, and CCK immunoreactivities in mouse hippocampal mossy fibers. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):1852–1862. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-01852.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Tanese N., Fuchs E. Complementary DNA sequence of a human cytoplasmic actin. Interspecies divergence of 3' non-coding regions. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):673–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan R. E., Shivers B. D., Romano G. J., Howells R. D., Pfaff D. W. Localization of preproenkephalin mRNA in the rat brain and spinal cord by in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Apr 8;258(2):159–184. doi: 10.1002/cne.902580202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman S. E., Comb M., Lin Y. S., Pearlberg J., Green M. R., Goodman H. M. A common trans-acting factor is involved in transcriptional regulation of neurotransmitter genes by cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4225–4233. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman S. E., Comb M., Pearlberg J., Goodman H. M. An AP-2 element acts synergistically with the cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible enhancer of the human proenkephalin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):321–324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iadarola M. J., Douglass J., Civelli O., Naranjo J. R. Differential activation of spinal cord dynorphin and enkephalin neurons during hyperalgesia: evidence using cDNA hybridization. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 12;455(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iadarola M. J., Naranjo J. R., Duchemin A. M., Quach T. T. Expression of cholecystokinin and enkephalin mRNA in discrete brain regions. Peptides. 1989 May-Jun;10(3):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew D., Kilpatrick D. L. Expression and regulation of the proenkephalin gene in rat Sertoli cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;3(1):179–184. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauber A. H., Romano G. J., Mobbs C. V., Howells R. D., Pfaff D. W. Estradiol induction of proenkephalin messenger RNA in hypothalamus: dose-response and relation to reproductive behavior in the female rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Jun;8(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. H., Zhao D., Xie C. W., McGinty J. F., Mitchell C. L., Hong J. S. Changes of proenkephalin and prodynorphin mRNAs and related peptides in rat brain during the development of deep prepyriform cortex kindling. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Dec;6(4):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. J., Jiang H. K., Stachowiak M. S., Hudson P. M., Owyang V., Nanry K., Tilson H. A., Hong J. S. Influence of nigrostriatal dopaminergic tone on the biosynthesis of dynorphin and enkephalin in rat striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Aug;8(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90020-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Changes in hypothalamic preproenkephalin A mRNA following stress and opiate withdrawal. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):643–645. doi: 10.1038/328643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Influence of steroids on the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor and preproenkephalin mRNA responses to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4306–4310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lira S. A., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Glass C. K., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of rat growth hormone genomic sequences targeting pituitary expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4755–4759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menétrey D., Gannon A., Levine J. D., Basbaum A. I. Expression of c-fos protein in interneurons and projection neurons of the rat spinal cord in response to noxious somatic, articular, and visceral stimulation. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 8;285(2):177–195. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocchetti I., Schwartz J. P., Costa E. Use of mRNA hybridization and radioimmunoassay to study mechanisms of drug-induced accumulation of enkephalins in rat brain structures. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;28(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moneta M. E., Höllt V. Perforant path kindling induces differential alterations in the mRNA levels coding for prodynorphin and proenkephalin in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 14;110(3):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90859-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Feasey K. J., ten Bruggencate G., Herz A., Höllt V. Electrical stimulation in vivo increases the expression of proenkephalin mRNA and decreases the expression of prodynorphin mRNA in rat hippocampal granule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3226–3230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Höllt V., Herz A. Dopaminergic regulation of striatal proenkephalin mRNA and prodynorphin mRNA: contrasting effects of D1 and D2 antagonists. Neuroscience. 1988 May;25(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muffly K. E., Jin D. F., Okulicz W. C., Kilpatrick D. L. Gonadal steroids regulate proenkephalin gene expression in a tissue-specific manner within the female reproductive system. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;2(10):979–985. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-10-979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimori T., Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A., Uhl G. R. Preproenkephalin mRNA expression in nucleus caudalis neurons is enhanced by trigeminal stimulation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Nov;6(2-3):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand E., Popovici T., Fellmann D., Bloch B. Anatomical study of enkephalin gene expression in the rat forebrain following haloperidol treatment. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Dec 29;83(3):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrack B., Emmett M. R., Rao T. S., Kim H. S., Wood P. L. Increases in rat striatal preproenkephalin mRNA levels following chronic treatment with the depot neuroleptic, haloperidol decanoate. Life Sci. 1990;46(10):687–691. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90073-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Lira S. A., Swanson L., Borrelli E., Heyman R., Evans R. M. Transgenic mice: applications to the study of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:353–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seasholtz A., Comb M., Liston D., Martin M., Thomas G., Herbert E. Use of gene transfer approaches to study regulation of neuropeptide gene expression. Prog Brain Res. 1987;71:13–22. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61810-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Macgregor-Leon P. F., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Dynamic alterations occur in the levels and composition of transcription factor AP-1 complexes after seizure. Neuron. 1989 Sep;3(3):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90260-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morgan J. I., Curran T. Regulation of proenkephalin by Fos and Jun. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1622–1625. doi: 10.1126/science.2512642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang F., Costa E., Schwartz J. P. Increase of proenkephalin mRNA and enkephalin content of rat striatum after daily injection of haloperidol for 2 to 3 weeks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tecott L. H., Rubenstein J. L., Paxinos G., Evans C. J., Eberwine J. H., Valentino K. L. Developmental expression of proenkephalin mRNA and peptides in rat striatum. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(89)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay Y., Tretjakoff I., Peterson A., Antakly T., Zhang C. X., Drouin J. Pituitary-specific expression and glucocorticoid regulation of a proopiomelanocortin fusion gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8890–8894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Navia B., Douglas J. Differential expression of preproenkephalin and preprodynorphin mRNAs in striatal neurons: high levels of preproenkephalin expression depend on cerebral cortical afferents. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4755–4764. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Ryan J. P., Schwartz J. P. Morphine alters preproenkephalin gene expression. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 6;459(2):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90658-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Walther D., Nishimori T., Buzzi M. G., Moskowitz M. A. Jun B, c-jun, jun D and c-fos mRNAs in nucleus caudalis neurons: rapid selective enhancement by afferent stimulation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Sep;11(2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90115-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nguyen T., Kobierski L., Comb M., Hyman S. E. The effect of depolarization on expression of the human proenkephalin gene is synergistic with cAMP and dependent upon a cAMP-inducible enhancer. J Neurosci. 1990 Aug;10(8):2825–2833. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-08-02825.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wawrousek E. F., Chepelinsky A. B., McDermott J. B., Piatigorsky J. Regulation of the murine alpha A-crystallin promoter in transgenic mice. Dev Biol. 1990 Jan;137(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S., Evan G. I., Hunt S. P. Changing patterns of c-fos induction in spinal neurons following thermal cutaneous stimulation in the rat. Neuroscience. 1990;36(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie C. W., Lee P. H., Takeuchi K., Owyang V., Li S. J., Douglass J., Hong J. S. Single or repeated electroconvulsive shocks alter the levels of prodynorphin and proenkephalin mRNAs in rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1989 Jul;6(1):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(89)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Hong J. S., Sabol S. L. Electroconvulsive shock increases preproenkephalin messenger RNA abundance in rat hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):589–593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Maruyama K., Aizawa T., Yamamoto A. A new species of enkephalin precursor mRNA with a distinct 5'-untranslated region in haploid germ cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 27;246(1-2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Williams C., Sabol S. L. Rat brain preproenkephalin mRNA. cDNA cloning, primary structure, and distribution in the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14301–14308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. T., Porrino L. J., Iadarola M. J. Cocaine induces striatal c-fos-immunoreactive proteins via dopaminergic D1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1291–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]