Abstract
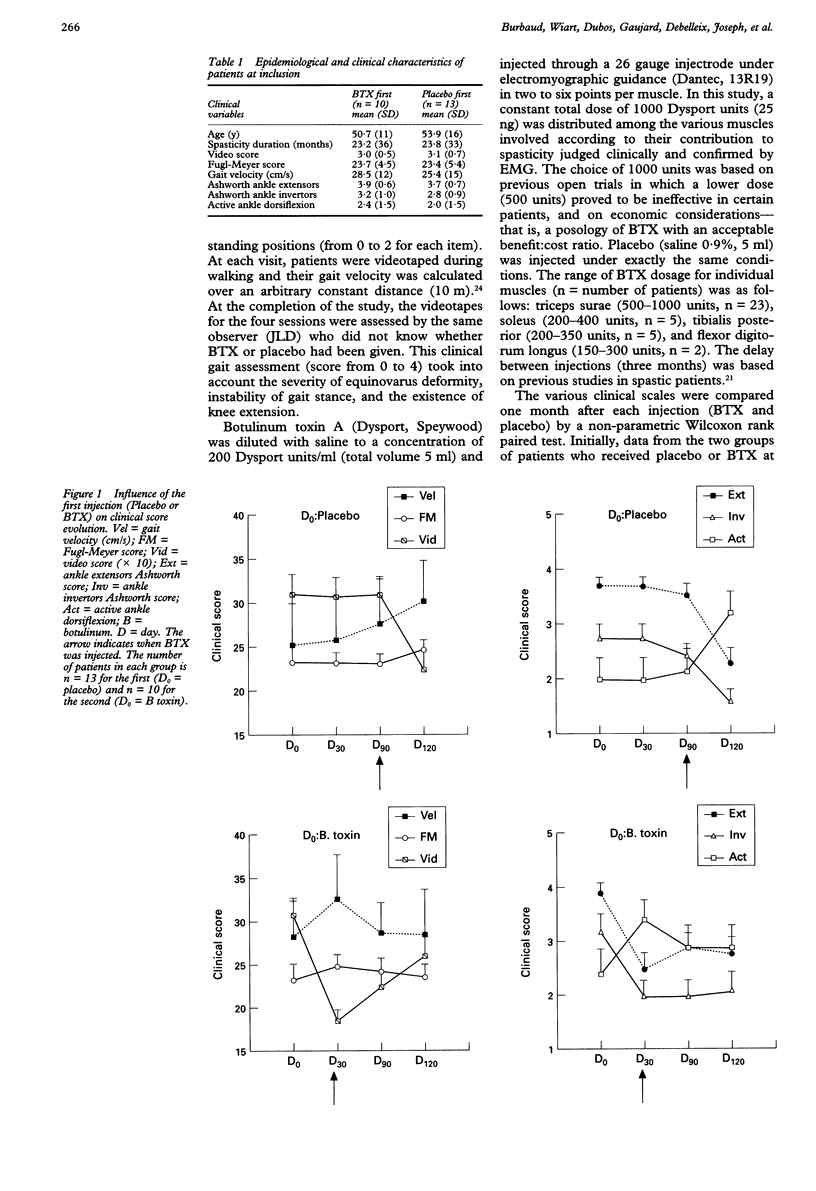
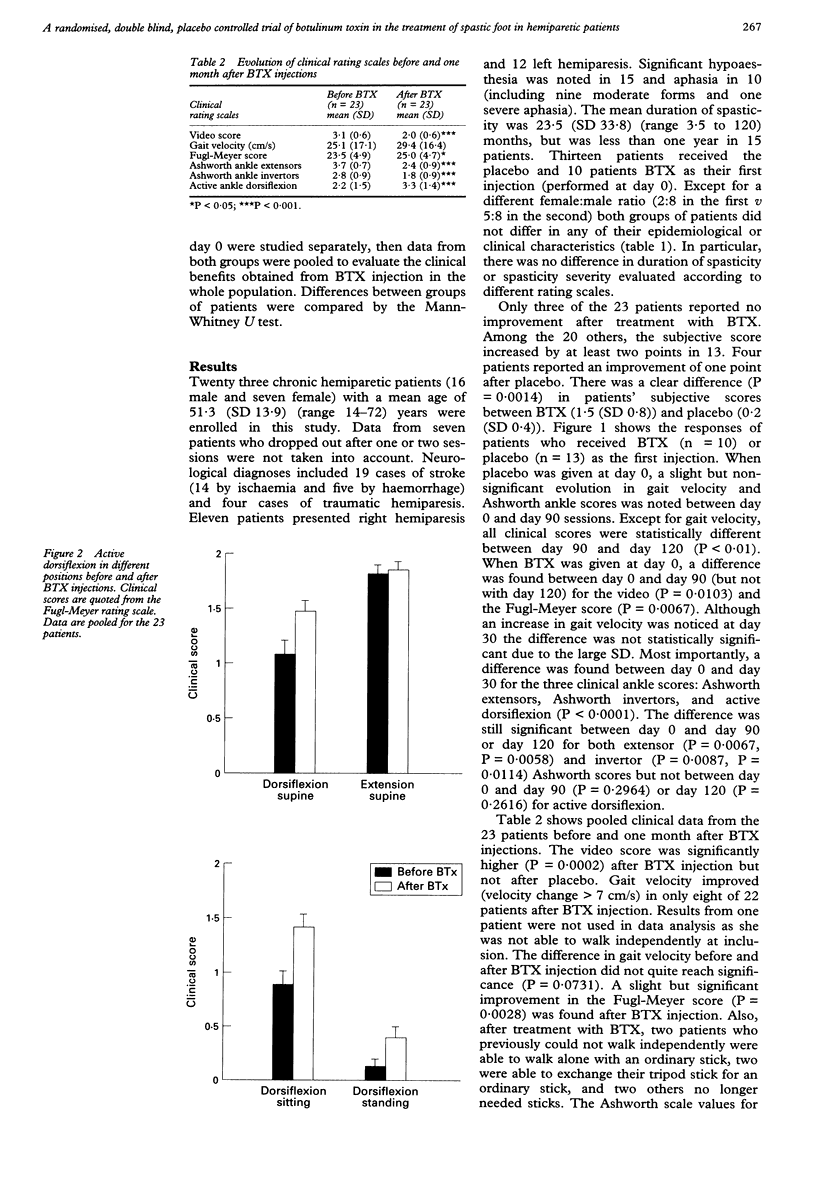
OBJECTIVE: To confirm the apparent effectiveness of botulinum toxin (BTX) in hemiparetic patients with ankle plantar flexors and foot invertor spasticity. METHODS: Twenty three hemiparetic patients with spasticity of the ankle plantar flexors and foot invertors were included in a randomised double blind, placebo controlled study with BTX. Patients were examined on days 0, 30, 90, and 120 and received one injection of BTX and one of placebo in a random order at day 0 and day 90. RESULTS: Patients reported a clear subjective improvement in foot spasticity after BTX (P = 0.0014) but not after placebo. Significant changes were noted in Ashworth scale values for ankle extensors (P < 0.0001) and invertors (P = 0.0002), and for active ankle dorsiflexion (P = 0.0001). Gait velocity was slightly but not significantly (P = 0.0731) improved after BTX injections. The severity of spasticity did not modify treatment efficacy, but BTX was less effective in patients with longer duration of spasticity (P = 0.0081). CONCLUSION: The efficacy of BTX injections in the treatment of spastic foot suggests that BTX may be particularly useful during the first year after a stroke.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohannon R. W., Smith M. B. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther. 1987 Feb;67(2):206–207. doi: 10.1093/ptj/67.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg-Stein J., Pine Z. M., Miller J. R., Brin M. F. Botulinum toxin for the treatment of spasticity in multiple sclerosis. New observations. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 1993 Dec;72(6):364–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove A. P., Graham H. K. Botulinum toxin A prevents the development of contractures in the hereditary spastic mouse. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1994 May;36(5):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1994.tb11863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das T. K., Park D. M. Botulinum toxin in treating spasticity. Br J Clin Pract. 1989 Nov;43(11):401–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dengler R., Neyer U., Wohlfarth K., Bettig U., Janzik H. H. Local botulinum toxin in the treatment of spastic drop foot. J Neurol. 1992 Aug;239(7):375–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00812153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne J. W., Heye N., Dunne S. L. Treatment of chronic limb spasticity with botulinum toxin A. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Feb;58(2):232–235. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.2.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fugl-Meyer A. R., Jäskö L., Leyman I., Olsson S., Steglind S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. 1. a method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1975;7(1):13–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene P., Fahn S., Diamond B. Development of resistance to botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis. Mov Disord. 1994 Mar;9(2):213–217. doi: 10.1002/mds.870090216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz D. A., Looman J. E., Tiberio A., Ketterling K., Kreitsch R. K., Colwill J. C., Grin O. D., Jr The management of paralytic spasticity. Neurosurgery. 1990 Feb;26(2):300–306. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199002000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse S., Lücke D., Malezic M., Bertelt C., Friedrich H., Gregoric M., Mauritz K. H. Botulinum toxin treatment for lower limb extensor spasticity in chronic hemiparetic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Nov;57(11):1321–1324. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.11.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koman L. A., Mooney J. F., 3rd, Smith B., Goodman A., Mulvaney T. Management of cerebral palsy with botulinum-A toxin: preliminary investigation. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993 Jul-Aug;13(4):489–495. doi: 10.1097/01241398-199307000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konstanzer A., Ceballos-Baumann A. O., Dressnandt J., Conrad B. Lokale Injektionsbehandlung mit Botulinum-Toxin A bei schwerer Arm- und Beinspastik. Nervenarzt. 1993 Aug;64(8):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mémin B., Pollak P., Hommel M., Perret J. Traitement de la spasticité par la toxine botulique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1992;148(3):212–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Savoy S. M., Corcos D., Latash M., Gottlieb G., Parke B., Kroin J. S. Intrathecal baclofen for severe spinal spasticity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 8;320(23):1517–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906083202303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrillo C. R., Knoploch S. Phenol block of the tibial nerve for spasticity: a long-term follow-up study. Int Disabil Stud. 1988;10(3):97–100. doi: 10.3109/09638288809164120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow B. J., Tsui J. K., Bhatt M. H., Varelas M., Hashimoto S. A., Calne D. B. Treatment of spasticity with botulinum toxin: a double-blind study. Ann Neurol. 1990 Oct;28(4):512–515. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thilmann A. F., Fellows S. J., Garms E. The mechanism of spastic muscle hypertonus. Variation in reflex gain over the time course of spasticity. Brain. 1991 Feb;114(Pt 1A):233–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. R., Delwaide P. J. Drug therapy: spasticity (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 1;304(1):28–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101013040107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. R., Delwaide P. J. Drug therapy: spasticity (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 8;304(2):96–99. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101083040207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M., Sebald M., Bathien N., de Recondo J., Rondot P. Botulinum antibodies in dystonic patients treated with type A botulinum toxin: frequency and significance. Neurology. 1993 Sep;43(9):1715–1718. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.9.1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


