Abstract
Mice overexpressing B cell activating factor of the TNF family (BAFF) develop systemic autoimmunity characterized by class-switched anti-nuclear antibodies. Transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI) signals are critical for BAFF-mediated autoimmunity, but the B cell developmental subsets undergoing TACI-dependent activation in settings of excess BAFF remains unclear. We now report that, whereas surface TACI expression is usually limited to mature B cells, excess BAFF promotes the expansion of TACI-expressing transitional B cells. TACIhi transitional cells from BAFF-Tg mice are characterized by an activated, cycling phenotype; and the TACIhi cell subset is specifically enriched for autoreactivity, expresses activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and T-bet and exhibits evidence of somatic hypermutation. Consistent with a potential contribution to BAFF-mediated humoral autoimmunity, TACIhi transitional B cells from BAFF-Tg mice spontaneously produce class-switched autoantibodies ex vivo. These combined findings highlight a novel mechanism whereby BAFF promotes humoral autoimmunity via direct, TACI-dependent activation of transitional B cells.
INTRODUCTION
Although over-expression of the B cell survival cytokine, BAFF, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of SLE in both murine models and human studies (1), the underlying mechanisms whereby BAFF promotes breaks in B cell tolerance and autoantibody (autoAb) production are unclear. BAFF, and the related cytokine APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand), are TNF-family cytokines with important roles in promoting peripheral B cell survival, development and activation. BAFF exerts its impact on B cells by binding to both the BAFF receptor (BAFF-R) and TACI, while APRIL binds TACI and the B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) (1). Since BAFF-R deletion causes loss of peripheral B cells beyond the transitional stage (2), this receptor was anticipated to be the major contributor to the autoimmune phenotype of BAFF-Tg mice. However, a recent study demonstrated that TACI deletion prevents humoral autoimmunity in BAFF-Tg mice (3); an observation we confirm in this current report.
Importantly, the specific B cell subset that is the target of TACI-dependent activation during BAFF-mediated autoimmunity is not known. Developing B cells progress through transitional stages in the spleen prior to entering follicular mature (FM) and marginal zone (MZ) B cell compartments; a process impacted by developmental cues including B cell receptor (BCR) and BAFF-mediated signals. Although mature FM and MZ B cells are most frequently implicated in generation of antibody responses, direct activation of transitional B cells has been described (4, 5), suggesting a potential physiologic explanation for immature B cell transit in the periphery.
In this context, we now report the surprising observation that transitional B cells are an important source of serum autoAb in BAFF-Tg mice. Mechanistically, self-ligand engagement promotes TACI upregulation on a subset of autoreactive transitional B cells, resulting in TACI-dependent activation and class-switched autoAb production in high BAFF settings. By identifying transitional B cells as the dominant splenic B cell subset promoting BAFF-mediated autoimmunity, our findings have important implications for the understanding of SLE pathogenesis and B cell autoimmunity in other high BAFF settings, including the events following therapeutic B cell depletion or stem cell transplantation. In addition, while the proportion of TACI+ transitional B cells was markedly expanded in BAFF-Tg mice, we detected a distinct TACI+ transitional subset in wild-type mice at physiologic serum BAFF levels. Since infectious challenge can promote local BAFF generation (6), we predict that TACI-dependent activation of transitional B cells also contributes to rapid, T-independent antibody responses to blood-borne pathogens.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice
C57BL/6, BAFF-Tg (7), Taci−/− (8), Baffr−/−(9), Rag2.GFP-Tg (10), and Nur77.GFP-Tg (11) mice and relevant murine crosses were bred and maintained in the specific pathogen-free (SPF) animal facility of Seattle Children’s Research Institute (Seattle, WA). All animal studies were conducted in accordance with Seattle Children’s Research Institute IACUC approved protocols. Mice were sacrificed at 3–6 months of age.
Antibodies
Anti-murine antibodies include: B220 (RA3-6B2), CD138 (281-2), CD21 (7G6), CD24 (M1/69), CD80 (16-10A1), CD86 (GL1), CD5 (53-7.3) from BD Biosciences; CD19 (ID3), CD44 (IM7), CD21 (7E9), CD23 (B3B4), CD24 (M1/69), TACI (1A1) from BioLegend; CD11c (N418), TACI (8F10-3), AA4.1 (AA4.1), AID (mAID-2), T-bet (4B10), CD11b (M1/70) from eBioscience; B220 (RA3-6B2) from Life Technologies; TACI (166010) from R&D Systems; goat anti-mouse IgM-, IgG-, IgA-, IgG1-, IgG2b-, IgG2c-, IgG3-HRP conjugated, unlabeled, or isotype, IgG2c (1079-02) from Southern Biotechnology.
Measurement of autoAb
Hep-2 anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) immunofluorescence and specific autoAb ELISAs were performed, as described (12).
Spleen immunofluorescence staining
Acetone-fixed splenic sections were stained with B220-PE, CD3-APC and IgG2c-FITC, as described (12).
Flow Cytometry, cell sorting and in vitro B cell culture
Single cell splenocytes or peritoneal cells were stained with fluorescence-labeled antibodies for flow cytometry analysis; intra-cellular staining performed using a fixation/permeabilization kit (BD Biosciences); and intra-nuclear staining performed using the FOXP3 Fix/Perm Buffer set (BioLegend). Cell sorting was performed on CD43 –depleted splenocytes, using a FACSAria II sorter (BD Biosciences), with the following sort gates: FM, CD24intCD21int; MZ, CD21hiCD23lo; and, transitional (T1/T2), CD24hiCD21lo-int, with BAFF-Tg T1/T2 further subdivided as TACIlo and TACIhi. Sorted B cell subsets were cultured in RPMI at 2 × 105 cells/well in a 96-well plate with or without R848 (5ng/mL) at 37°C for 72 hours prior to collection of supernatant for Ab ELISA.
RT-PCR and KREC analysis
RT-PCR was performed with murine β2-microglobulin (B2M) as control using the following primers: B2M 5’-CTTCAGTCGTCAGCATGGCTCG-3’ (forward); 5’-GCAGTTCAGTATGTTCGGCTTCCC-3’ (reverse). Taci 5’-ACCCCCAGTGTGCAGTAGAG-3’ (forward); RP, 5’-GGAGGTGGAAGTCAGGT CAG-3’ (reverse). Aicd 5’-CCTCCTGCTCACTGGACTTC-3’ (forward); 5’-GGCTGAGGTTAGGGTTCCAT-3’ (reverse). Tbx21 5’-GGTGTCTGGGAAGCTGAGAG-3’ (forward); 5’-CCACATCCACAAACATCCTG-3’ (reverse). Igg2c 5’-GGGAATTCGAGGTGCAGCTGCAGGAGTCTGG-3’ (forward); 5’-GCTCAGGGAAATAACCCTTGAC-3’ (reverse). Replication history of sorted B cell subsets was determined by KREC analysis (13).
Single cell BCR cloning
Single cell BCR cloning was performed as described (14). Briefly, Ig heavy and light (κ and λ) gene transcripts from sorted single GFPhi and GFPlo T2 (CD21intCD24hi) cells from Rag2-GFP.BAFF-Tg mice where cloned into human IGG1, IGK, or IGL expression vectors, transfected into HEK293T cells, and monoclonal antibodies purified from culture supernatants using protein A–agarose beads.
Statistical Evaluation
P-values were calculated by two-tailed Student’s t test; by Mann Whitney U test; or by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test (GraphPad Software, Inc.).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Humoral autoimmunity in BAFF-Tg mice requires TACI
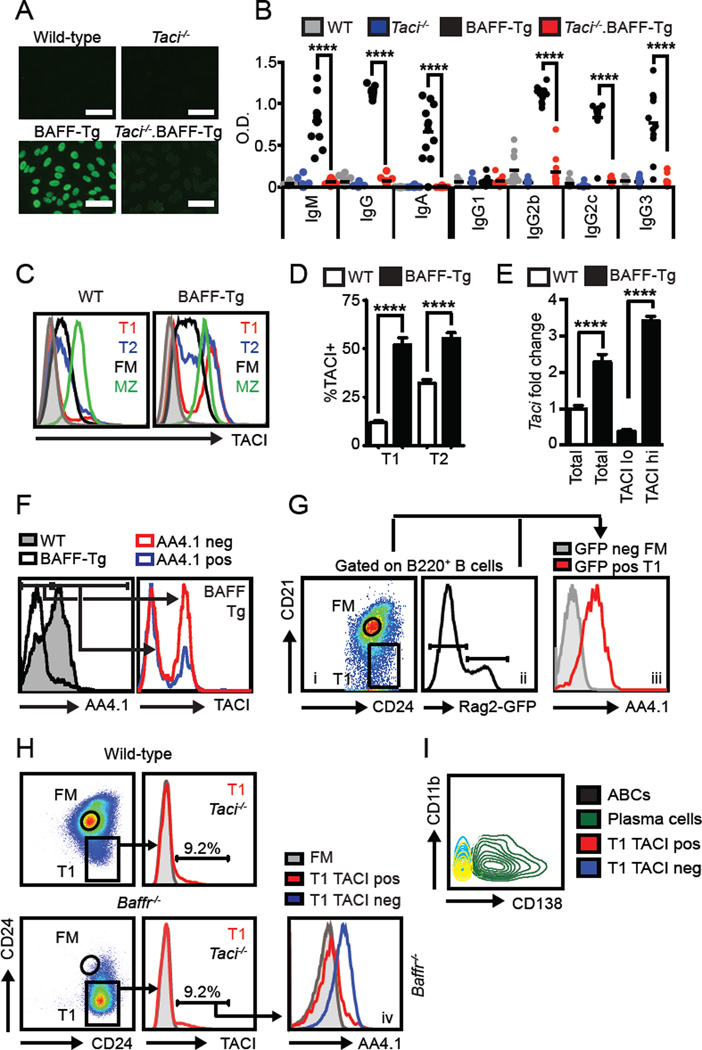
BAFF-Tg autoimmunity is T cell-independent, but requires the signaling adaptor MyD88 (15). Because TLR signals are critical for humoral autoimmunity, lack of disease in Myd88−/−.BAFF-Tg mice has been presumed secondary to absent MyD88-dependent TLR activation (16). However, since TACI also signals via MyD88 (17), loss of TACI signals might also explain this phenotype. Although TACI has been proposed to act as a negative regulator of BAFF signaling in B cells (18, 19), Taci−/−.BAFF-Tg mice exhibited a striking loss of IgG anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) and RNA-associated Sm/RNP autoAb across the spectrum of Ab isotypes and Ig subclasses (Fig. 1A, B), without impacting BAFF-Tg B cell expansion (Supplemental Fig. 1A). In keeping with this idea, Figgett et al. recently reported decreased autoimmunity in irradiated BAFF-Tg mice reconstituted with Taci−/− BM (3). Together, these observations demonstrate that TACI is required for development of humoral autoimmunity in BAFF-Tg mice.
Figure 1. TACI deletion prevents BAFF-Tg autoimmunity; and excess BAFF promotes sTACI on transitional B cells.
(A) Representative IgG HEp2-ANA staining. Bars, 50µm. (B) Isotype-specific anti-Sm/RNP Ab from 12-week-old WT (grey), Taci−/− (blue), BAFF-Tg (black) and Taci−/−.BAFF-Tg (red) mice. (C) Splenic B cell subset sTACI levels from wild-type (left) and BAFF-Tg (right) mice. Grey histogram: Taci−/− B cells. (D) % sTACI+ T1 and T2 B cells. (E) Taci mRNA transcript (fold change vs. WT T1/T2) from sorted WT and BAFF-Tg T1/T2 B cells (CD21lo/midCD24hi) as well as BAFF-Tg TACI+ vs. TACI− T1/T2 subsets. (F) Left panel: AA4.1 surface expression in WT (shaded) and BAFF-Tg (line) T1 B cells. Right panel: BAFF-Tg sTACI expression in AA4.1+ (blue) vs. AA4.1− (red) T1 B cells. (G) Left panel: Rag2-GFP reporter T1 and FM gating. Middle panel: Rag2-GFP histogram showing GFPneg and GFPpos gates. Right panel: Overlaid histograms of AA4.1 expression in Rag2-GFPpos T1 (red) and Rag2-GFPneg FM (grey) B cells. (H) T1 and FM gating (left), and T1 sTACI expression (right; Taci−/− B cells grey) in 12-week-old WT (upper) and Baffr−/− (lower) mice. Number equals % in TACI+ gate. Lower right panel: AA4.1 expression on Baffr−/− TACIhi T1 (red), Baffr−/− TACIlo T1 (blue) and WT FM (grey) B cells. (I) Overlaid flow plots demonstrating that TACIhi transitional cells (red) from BAFF-Tg mice are not CD138+ plasma cells (green) or CD11b+CD11c+ age-associated B cells (black; CD11c not shown). (A–I) Data representative of WT (n=16), Taci−/− (n=12), BAFF-Tg (n=15) and Taci−/−.BAFF-Tg (n=14) from ≥2 independent experiments/sorts. Error bars indicate SEM; **, P<0.01; ****, P<0.0001; by two-tailed Student’s t test.
Excess BAFF promotes TACI expression by a subset of transitional B cells
To begin to understand how TACI signals might promote BAFF-Tg autoimmunity, we first assessed surface TACI (sTACI) expression on developing B cell subsets in WT and BAFF-Tg mice. Consistent with prior reports, sTACI in WT mice was low on transitional (T1, CD21loCD24hi; T2, CD21intCD24hi) B cells, but increased in mature (FM and MZ) B cells. Whereas sTACI in FM and MZ B cells did not differ significantly between WT and BAFF-Tg mice, a prominent sub-population of T1 and T2 B cells in BAFF-Tg mice expressed sTACI at levels exceeding that of previously reported TACI+ MZ B cells (Fig. 1C, D; Supplemental Fig. 1B). As predicted, BAFF-R (BR3) levels were increased in mature (FM and MZ) relative to transitional T1 B cells in WT mice (data not shown). However, we were not able to compare BAFF-R expression between the TACIhi and TACIlo transitional subsets in BAFF-Tg mice, since BAFF-R is markedly decreased on splenic B cells from BAFF-Tg mice, consistent with physiologic receptor downregulation in the setting of high serum BAFF levels (20).
Increased sTACI correlated with a greater abundance of Taci transcripts, consistent with transcriptional regulation of TACI in a subset of BAFF-Tg transitional B cells (Fig. 1E). While the proportion of TACIhi transitional cells was significantly increased in BAFF-Tg mice, a distinct subset of WT transitional cells also expressed higher levels of sTACI (Fig. 1C, D). This prominent expansion of TACI+ T1/T2 B cells in BAFF-Tg mice suggested that transitional cells might directly contribute to TACI-dependent humoral autoimmunity.
Notably, relative to WT transitional cells, BAFF-Tg T1 and T2 transitional cells exhibit reduced CD93 (AA4.1); a marker commonly used to define transitional B cells (21). In addition, the AA4.1neg transitional subset was predominantly TACIhi (Fig. 1F); findings that suggested that TACI+ cells within the CD21lo or CD21intCD24hi gate might be derived from mature, rather than transitional B cells (21). However, several lines of evidence strongly supported the conclusion that TACI+ B cells within the CD21loCD24hi and CD21intCD24hi gates are derived from immature, transitional B cells. First, using Rag2-GFP reporter mice (10) to label recent BM emigrants, we consistently observed lack of AA4.1 expression on a subset of transitional B cells at physiologic BAFF levels (Fig. 1G); indicating that absent AA4.1 expression per se does not imply a non-transitional origin for TACI+ T1 B cells. Moreover, Rag2-GFP+ T1 B cells with lower GFP expression (i.e. the subset of T1 B cells that have transited through cell cycle leading to ~50% dilution in the GFP signal) exhibit lower AA4.1 and increased sTACI, consistent with reciprocal regulation of these surface markers on early transitional B cells (Supplemental Fig. 1C). Second, TACI+ T1 B cells lacking AA4.1 expression develop in BAFF receptor-null (Baffr−/−) mice at equivalent proportions to WT mice (Fig. 1H), despite the marked reduction in mature B cells in this strain (9). Third, BAFF-Tg TACI+ transitional B cells lacked both the plasma cell marker, CD138+ as well as the “age-associated B cell” markers, CD11b and CD11c (22), indicating that this population is distinct from previously-described activated B cell subsets in autoimmunity (Fig. 1 I). Fourth, splenic TACI+ transitional B cells in BAFF-Tg mice were distinct from peritoneal B1b cells recently hypothesized to promote BAFF-mediated autoimmunity (23) (Supplemental Fig. 1D). Finally, the expansion of TACI+ transitional B cells in BAFF-Tg mice precedes the development of autoimmunity, arguing against the accumulation of TACI+ autoreactive B cells derived from mature B cell subsets (Supplemental Fig. 1E). Together, these data highlight the surprising observation that excess BAFF promotes the expansion of sTACI-expressing transitional B cells.
TACI expression marks an activated, proliferative subset of transitional B cells
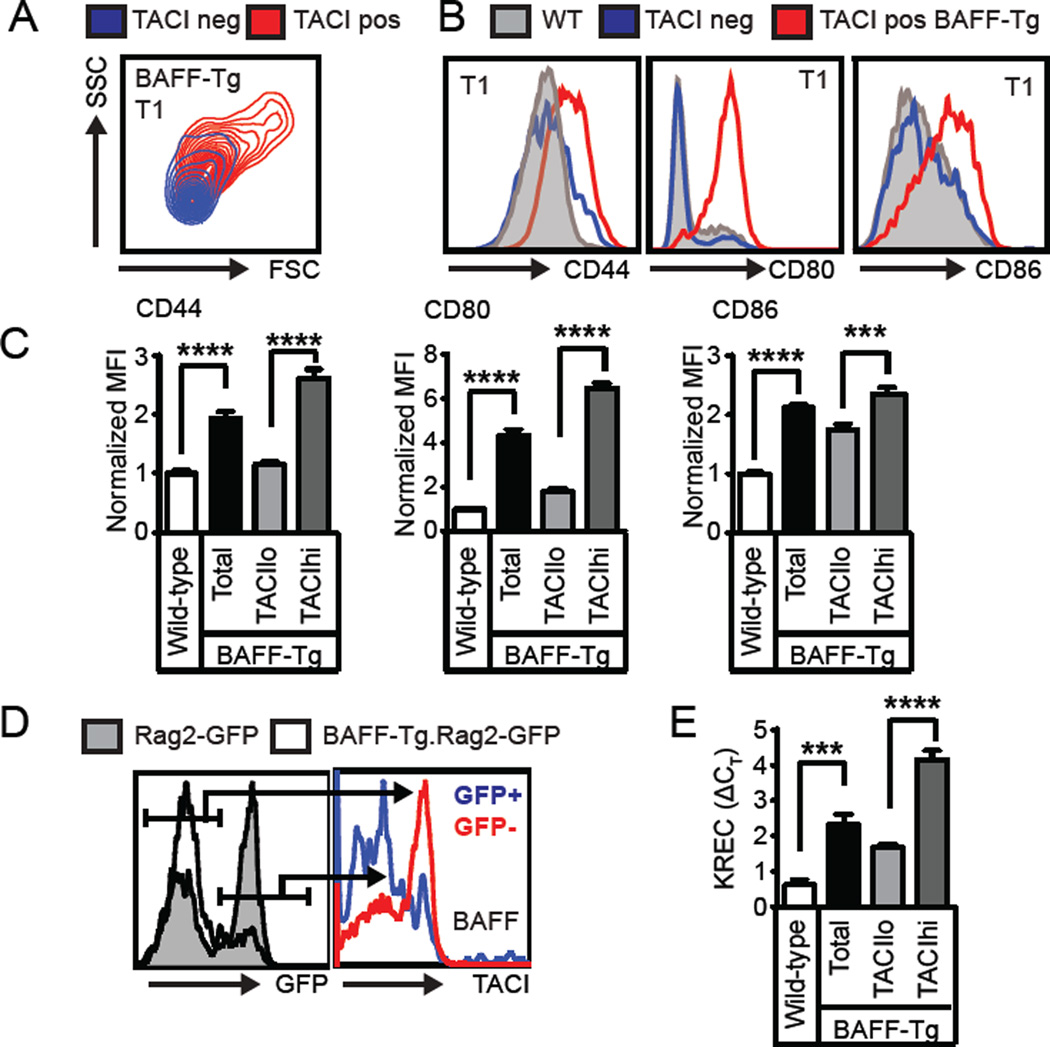
Based on these findings, we next sought to better define the phenotype of the TACIhi transitional cell population. BAFF-Tg TACIhi transitional cells were significantly larger than BAFF-Tg TACI− or WT transitional cells, implying increased activation (Fig. 2A). Consistent with this idea, BAFF-Tg transitional cells exhibited increased CD44, CD80 and CD86 expression; and this increase in activation markers was specific to the TACIhi subset (Fig. 2B, C). Notably, the TACI+ T1 subset from WT and Baffr−/− mice exhibited a similar activated phenotype (Supplemental Fig. 1F).
Figure 2. TACIhi transitional cells exhibit an activated, cycling phenotype.
(A) Overlaid flow plots from TACIlo (blue) and TACIhi (red) BAFF-Tg T1 B cells showing cell size by forward (FSC)/side scatter (SSC). (B) Left panels: Representative overlaid histograms of surface activation markers from WT (grey), TACIlo BAFF-Tg (blue) and TACIhi BAFF-Tg (red) T1 B cells. (C) Activation marker MFI in WT and BAFF-Tg T1 B cell subsets. (D) Left panel: Histogram of T1 GFP expression in Rag2-GFP (shaded) and BAFF-Tg.Rag2-GFP (line) mice. Right panel: sTACI expression in GFP+ (blue) vs. GFP− (red) T1 B cells from BAFF-Tg.Rag2-GFP mouse. (E) KREC analysis of sorted WT and BAFF-Tg T1/T2 B cells (CD21lo/midCD24hi), as well as BAFF-Tg TACIlo and TACIhi T1/T2 B cells. (A–E) Data representative of ≥2 independent experiments involving WT (n=9), BAFF-Tg (n=9), Rag2-GFP (n=5) and BAFF-Tg.Rag2-GFP (n=7) mice; error bars indicate SEM; ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001, by two-tailed Student’s t test.
To address whether this activated subset is cycling in vivo, we crossed BAFF-Tg with Rag2-GFP reporter mice to allow quantification of transitional cell proliferation by GFP dilution (10). Relative to WT Rag2-GFP reporter cells, an increased proportion of BAFF-Tg transitional cells were GFPneg. The BAFF-Tg GFPneg (i.e. divided) subset was sTACIhi, while GFPpos cells were TACIlo (Fig. 2D). Consistent with these findings, BAFF-Tg transitional cells had proliferated based on KREC analysis, with the average number of cell divisions increased in TACIhi vs. TACIlo cells (Fig. 2E) (13). Together, these data demonstrate that excess BAFF promotes transitional B cell activation and proliferation and that sTACI marks this activated, cycling subset.
TACI expression correlates with BCR engagement in transitional B cells
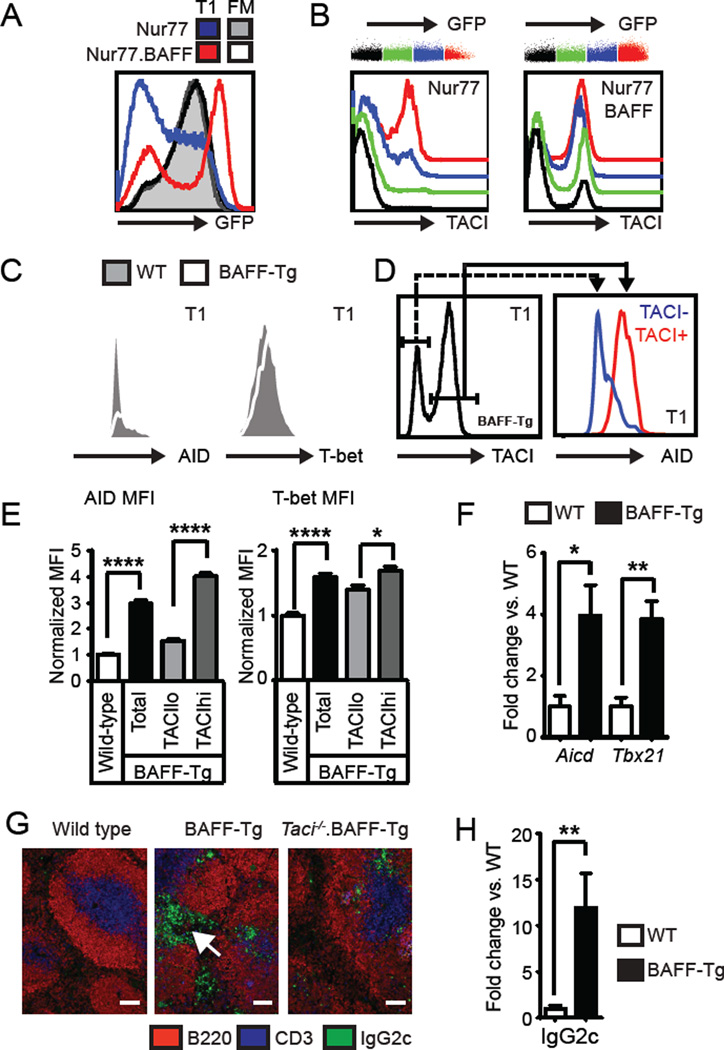
Since BCR ligation upregulates TACI on mature B cells (24), we next assessed whether BCR signal strength correlates with sTACI expression using the Nur77-GFP reporter strain where BCR signals activate GFP expression under control of the Nur77 regulatory region. In this model, mature FM and MZ B cells expressing a diverse (non-transgenic) BCR repertoire are predominantly GFPhi, while transitional cells exhibit a range of GFP expression dependent upon with the relative strength of BCR engagement by self-ligand (11). Notably, whereas GFP expression in FM and MZ B cells did not differ between Nur77 and Nur77.BAFF-Tg mice, excess BAFF increased the proportion of GFPhi cells in the transitional compartment (Fig. 3A; and not shown). Subdividing transitional cells according to relative GFP expression demonstrated a correlation between BCR signal strength and sTACI on transitional cells in both Nur77 and Nur77.BAFF-Tg mice, with relatively greater increases in sTACI in Nur77.BAFF-Tg mice (Fig. 3B).
Figure 3. BCR engagement promotes sTACI, AID and T-bet expression by BAFF-Tg transitional B cells.
(A) Left panel: Overlaid histograms showing Nur77-GFP expression in T1 and FM B cells from Nurr77-GFP (T1, blue; FM; grey shaded) and Nur77-GFP.BAFF-Tg (T1, red; FM; black line) mice. (B) T1 B cells were subdivided into color bins based on relative Nur77-GFP expression. Representative histograms of sTACI expression in overlaid GFP color bins from Nur77-GFP (left panel) and Nur77-GFP.BAFF-Tg (right panel) mice. (C) Representative histograms of T1 AID (left) and T-bet (right) intracellular staining in WT (shaded) and BAFF-Tg (line) mice. (D) AID levels in TACIlo (blue) vs. TACIhi (red) T1 B cells from representative BAFF-Tg mouse. (E) AID (left) and T-bet (right) expression in WT and BAFF-Tg T1 B cell subsets. (F) Aicd and Tbx21 mRNA transcript from sorted WT (□) and BAFF-Tg (■) T1/T2 B cells (fold change vs. WT). (G) Splenic immunofluorescence staining showing prominent extrafollicular IgG2c+ cells (arrow) in BAFF-Tg mice, that are absent in Taci−/−.BAFF-Tg. Bars, 100µm. (H) IgG2c (Iγ2c) mRNA transcript from sorted WT (□) and BAFF-Tg (■) T1/T2 B cells (fold change vs. WT). (A–H) Data representative of ≥2 independent experiments involving Nur77 (n=4), Nur77-GFP.BAFF-Tg (n=4), WT (n=9), BAFF-Tg (n=9); error bars indicate SEM; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ****, P<0.0001, by two-tailed Student’s t test.
BAFF-Tg TACIhi transitional cells express AID and T-bet
Dysregulated TLR7 signals can directly activate transitional B cells in TLR7-transgenic mice (5), resulting in transitional cell expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) and T-bet, a T-box transcription factor required for CSR to IgG2a/c (25). Strikingly, transitional B cells expressed AID and T-bet in BAFF-Tg mice, and this change was specific to TACIhi cells (Fig. 3C–E). In addition, Q-PCR analysis demonstrated increased Aicd (encoding AID) and Tbx21 (encoding T-bet) mRNA transcripts in sorted BAFF-Tg transitional cells (Fig. 3F). Consistent with the role for AID and T-bet in CSR, we observed prominent extra-follicular IgG2c+ cells within the splenic red pulp in BAFF-Tg mice. In contrast, IgG2c+ cells were much less abundant and restricted to the follicles in Taci−/−.BAFF-Tg mice (Fig. 3G). While the primary B cell subset(s) contributing to this extra-follicular IgG2c+ population remains to be definitely identified, transitional B cells in BAFF-Tg mice expressed abundant IgG2c mRNA transcripts (Fig. 3H), implying that the TACIhi transitional subset directly contributes to this activated population.
TACIhi cells are enriched for self-reactivity, exhibit somatic hypermutation and spontaneously produce class-switched autoAb
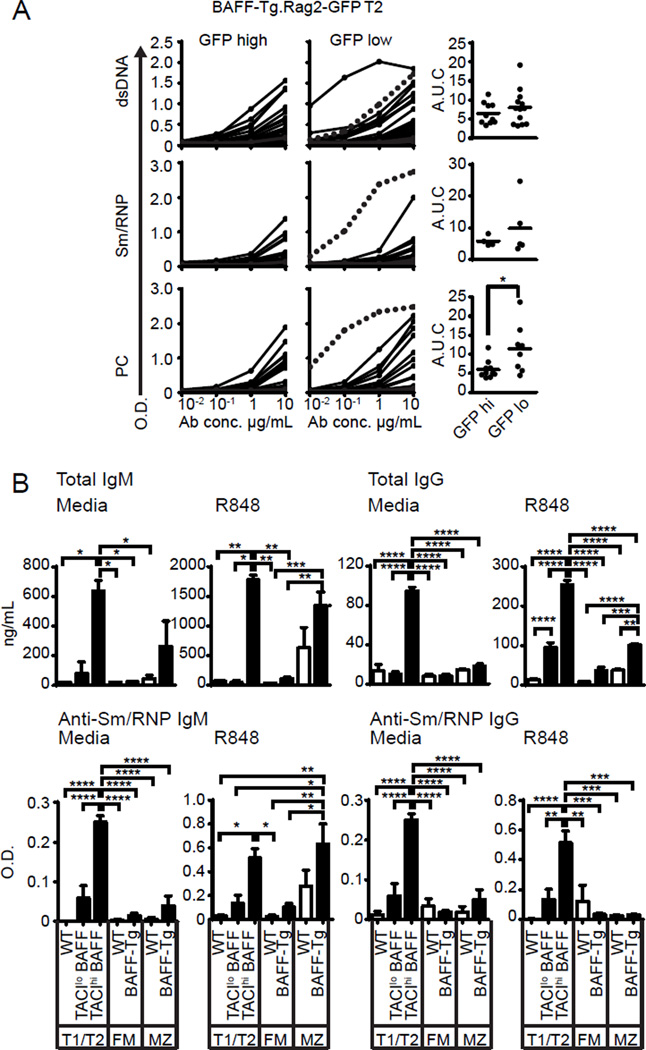
Despite central tolerance mechanisms, a significant proportion of early transitional cells exhibit auto- or poly-reactivity (26). To test the hypothesis that the novel TACIhi transitional subset is enriched for autoreactivity, we cloned BCRs from single GFPlo vs. GFPhi T2 B cells sorted from Rag2-GFP.BAFF-Tg mice; an approach designed to directly assess the relative self-reactivity in cycling vs non-cycling B cells, respectively. Consistent with our hypothesis, BCRs cloned from GFPlo (i.e. divided, TACIhi) T2 B cells exhibited reactivity to a panel of autoantigens, including significantly increased reactivity with phosphorylcholine (PC) and a trend towards greater dsDNA and Sm/RNP reactivity (Fig. 4A).
Figure 4. The cycling, TACIhi transitional cells subset is enriched for self-reactivity and spontaneously produces class-switched autoAb.
(A) Rag2-GFP.BAFF-Tg T2 B cell single cell cloning. Left panels: Serial dilution curves of cloned GFPlo (n=43) and GFPhi (n=37) BCR reactivity against dsDNA, Sm/RNP and phosphorylcholine (PC) by ELISA. Right panel: AUC of reactive antibodies (defined as BCR with reactivity > threshold of 0.5 O.D.) to respective self-antigen. (B) Bar graphs showing total Ig concentrations (upper) and anti-Sm/RNP Ab (lower) in supernatants from sorted B cell subsets from WT (□) and BAFF-Tg (■) mice, cultured for 72 hours in RPMI media or stimulated with R848 (5ng/mL). Data pooled from ≥2 independent sorts. Error bars indicate SEM; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001, by two-tailed Student’s t test (A), and one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test (B).
Strikingly, BCRs from the cycling GFPlo transitional subset demonstrated increased immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy and light chain mutation frequency, whereas mutations were rare in GFPhi BAFF-Tg T2 B cells, BAFF-Tg MZ B cells and in BCRs from naïve control B cells (Table I). Observed mutations were characteristic of AID-mediated somatic hypermutation (SHM), in that nucleotide substitutions were biased for G to A and C to T transitions; and were predominantly localized to complementary determining regions (CDRs) (Supplemental Fig. 2A,B). Interestingly, one T2 GFPlo derived mAb exhibiting polyreactivity to PC, Sm/RNP and dsDNA (Fig. 4A; highly-reactive clone highlighted with dashed line), contained the greatest number of replacement mutations [4 total; heavy chain S64I (CDR2), M91I (FWR3); kappa light chain S14F (FWR1), N56D (CDR2)]. Together, these data indicate that engagement of self-antigen by autoreactive transitional B cells is sufficient to promote AID-mediated SHM in setting of BAFF excess.
Table I.
BCR mutation frequency in B cell subsets1
| Sequences | ≥1 mutation | ≥2 mutation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT FM | 236 | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| WT MZ | 199 | 1.51% | 0.0% |
| BAFF-Tg MZ | 221 | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Rag2-GFP.BAFF-Tg T1/T2 GFPpos | 118 | 1.69% | 0.0% |
| Rag2-GFP.BAFF-Tg T1/T2 GFPneg | 192 | 18.75%* † ¶ # | 11.98%* † ¶ |
Total number of sequences analyzed and heavy and light chains (κ and λ) mutation frequency in single-cell sorted B cells from indicated subsets. P<0.0001 mutated sequences in Rag2-GFP.BAFF-Tg GFPlo T1/T2 BCRs vs.
WT FM;
WT MZ;
BAFF-Tg MZ; and
Rag2-GFP.BAFF-Tg GFPhi BCRs.
Finally, to address whether this autoreactive transitional subset contributes to BAFF-Tg autoAb, we quantified ex vivo Ig production by sorted WT and BAFF-Tg B cell subsets. While both BAFF-Tg TACIhi transitional B cells, and to a lesser extent MZ B cells, produced IgM, only the BAFF-Tg TACIhi transitional cell subset spontaneously produced class-switched IgG. Further, addition of the TLR7 ligand, R848, markedly increased IgM and IgG by BAFF-Tg TACIhi transitional cells. Although TLR7 activation increased MZ IgM secretion, R848 exerted minimal impact of IgG formation by FM, MZ or TACIlo transitional cells (Fig. 4B; upper panel). Importantly, secreted Ab exhibited reactivity to the RNA-associated antigen Sm/RNP, with both TACIhi transitional and MZ subsets from BAFF-Tg producing anti-Sm/RNP IgM. Remarkably, only BAFF-Tg transitional cells produced class-switched Sm/RNP IgG Ab ex vivo, and the TACIhi transitional subset was the dominant source for anti-Sm/RNP IgG, both spontaneously and after R848 stimulation (Fig. 4B; lower panel). Thus, although the MZ is enriched for autoreactive specificities and expanded in BAFF-Tg mice (27, 28), TACI-expressing transitional cells from BAFF-Tg mice produce markedly greater levels of class-switched IgG autoAb ex vivo.
In summary, our results demonstrate a critical role for TACI in the pathogenesis of BAFF-mediated humoral autoimmunity and identify a distinct subpopulation of activated, cycling transitional B cells enriched for autoreactive BCR specificities and characterized by prominent sTACI expression. Excess BAFF has previously been shown to rescue low-affinity, autoreactive B cell clones from deletion at the transitional stage, suggesting that BAFF promotes autoimmunity by skewing the mature B cell compartment towards autoreactivity (20, 29). Our combined in vivo and in vitro observations strongly support a complimentary model wherein direct activation of transitional B cells generates a pool of IgG antibody secreting cells (ASCs) that produce pathogenic autoAb in BAFF-Tg mice, highlighting the significant and surprising contribution of TACIhi transitional cells to BAFF-mediated autoimmunity. Although serum BAFF levels in BAFF-Tg mice likely exceed that of the majority of patients with SLE and other autoimmune disorders, we predict that our findings may inform disease pathogenesis in the subset of subjects characterized by the highest BAFF levels. In addition, dysregulated transitional B cell activation is likely to be relevant in other clinical scenarios, including autoimmune disease relapse after treatment with B cell-depletion therapies and de novo humoral autoimmunity following stem cell transplantation. Importantly, while our data have focused on events leading to loss of B cell tolerance, the developmental program identified here is more likely to have evolved to resist infection. Because developing transitional cells exhibit a broad range of BCR specificities, including self-, poly- and foreign reactivity, we predict that direct activation of this unique subset may contribute to rapid, TACI-dependent, T cell-independent, antibody responses against blood-borne or other systemic infections.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under award numbers: R01HL075453 (DJR), R01AI084457 (DJR), R01AI071163 (DJR), DP3DK097672 (DJR) and K08AI112993 (SWJ). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. Additional support provided by the Benaroya Family Gift Fund (DJR); by the ACR REF Rheumatology Scientist Development Award (SWJ); and by the Arnold Lee Smith Endowed Professorship for Research Faculty Development (SWJ).
Abbreviations
- AID
activation-induced cytidine deaminase
- ANA
anti-nuclear antibodies
- AutoAb
autoantibodies
- BAFF
B cell activating factor of the TNF family
- BAFF-R
BAFF receptor
- BAFF-Tg
BAFF transgenic
- BCR
B cell receptor
- CDR
Complementary determining regions
- CSR
class-switch recombination
- FM
follicular mature
- Ig
immunoglobulin
- KREC
kappa-deleting recombination excision circle
- MZ
marginal zone
- PC
phosphorylcholine
- SHM
somatic hypermutation
- TACI
transmembrane activator and CAML interactor
- T1 / T2
transitional 1 / 2
Footnotes
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists
REFERENCES
- 1.Mackay F, Schneider P. Cracking the BAFF code. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:491–502. doi: 10.1038/nri2572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thompson JS, Bixler SA, Qian F, Vora K, Scott ML, Cachero TG, Hession C, Schneider P, Sizing ID, Mullen C, Strauch K, Zafari M, Benjamin CD, Tschopp J, Browning JL, Ambrose C. BAFF-R, a newly identified TNF receptor that specifically interacts with BAFF. Science. 2001;293:2108–2111. doi: 10.1126/science.1061965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Figgett WA, Deliyanti D, Fairfax KA, Quah PS, Wilkinson-Berka JL, Mackay F. Deleting the BAFF receptor TACI protects against systemic lupus erythematosus without extensive reduction of B cell numbers. J Autoimmun. 2015 doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ueda Y, Liao D, Yang K, Patel A, Kelsoe G. T-independent activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression, class-switch recombination, and antibody production by immature/transitional 1 B cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:3593–3601. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.6.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Giltiay NV, Chappell CP, Sun X, Kolhatkar N, Teal TH, Wiedeman AE, Kim J, Tanaka L, Buechler MB, Hamerman JA, Imanishi-Kari T, Clark EA, Elkon KB. Overexpression of TLR7 promotes cell-intrinsic expansion and autoantibody production by transitional T1 B cells. J Exp Med. 2013;210:2773–2789. doi: 10.1084/jem.20122798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.MacLennan I, Vinuesa C. Dendritic cells, BAFF, and APRIL: innate players in adaptive antibody responses. Immunity. 2002;17:235–238. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(02)00398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gavin AL, Duong B, Skog P, Ait-Azzouzene D, Greaves DR, Scott ML, Nemazee D. deltaBAFF, a splice isoform of BAFF, opposes full-length BAFF activity in vivo in transgenic mouse models. J Immunol. 2005;175:319–328. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.von Bulow GU, van Deursen JM, Bram RJ. Regulation of the T-independent humoral response by TACI. Immunity. 2001;14:573–582. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(01)00130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sasaki Y, Casola S, Kutok JL, Rajewsky K, Schmidt-Supprian M. TNF family member B cell-activating factor (BAFF) receptor-dependent and -independent roles for BAFF in B cell physiology. J Immunol. 2004;173:2245–2252. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.4.2245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yu W, Nagaoka H, Jankovic M, Misulovin Z, Suh H, Rolink A, Melchers F, Meffre E, Nussenzweig MC. Continued RAG expression in late stages of B cell development and no apparent re-induction after immunization. Nature. 1999;400:682–687. doi: 10.1038/23287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zikherman J, Parameswaran R, Weiss A. Endogenous antigen tunes the responsiveness of naive B cells but not T cells. Nature. 2012;489:160–164. doi: 10.1038/nature11311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jackson SW, Scharping NE, Kolhatkar NS, Khim S, Schwartz MA, Li QZ, Hudkins KL, Alpers CE, Liggitt D, Rawlings DJ. Opposing impact of B cell-intrinsic TLR7 and TLR9 signals on autoantibody repertoire and systemic inflammation. J Immunol. 2014;192:4525–4532. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van Zelm MC, Szczepanski T, van der Burg M, van Dongen JJ. Replication history of B lymphocytes reveals homeostatic proliferation and extensive antigen-induced B cell expansion. J Exp Med. 2007;204:645–655. doi: 10.1084/jem.20060964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schwartz MA, Kolhatkar NS, Thouvenel C, Khim S, Rawlings DJ. CD4+ T cells and CD40 participate in selection and homeostasis of peripheral B cells. J Immunol. 2014;193:3492–3502. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Groom JR, Fletcher CA, Walters SN, Grey ST, Watt SV, Sweet MJ, Smyth MJ, Mackay CR, Mackay F. BAFF and MyD88 signals promote a lupuslike disease independent of T cells. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1959–1971. doi: 10.1084/jem.20062567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rawlings DJ, Schwartz MA, Jackson SW, Meyer-Bahlburg A. Integration of B cell responses through Toll-like receptors and antigen receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:282–294. doi: 10.1038/nri3190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.He B, Santamaria R, Xu W, Cols M, Chen K, Puga I, Shan M, Xiong H, Bussel JB, Chiu A, Puel A, Reichenbach J, Marodi L, Doffinger R, Vasconcelos J, Issekutz A, Krause J, Davies G, Li X, Grimbacher B, Plebani A, Meffre E, Picard C, Cunningham-Rundles C, Casanova JL, Cerutti A. The transmembrane activator TACI triggers immunoglobulin class switching by activating B cells through the adaptor MyD88. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:836–845. doi: 10.1038/ni.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yan M, Wang H, Chan B, Roose-Girma M, Erickson S, Baker T, Tumas D, Grewal IS, Dixit VM. Activation and accumulation of B cells in TACI-deficient mice. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:638–643. doi: 10.1038/89790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Seshasayee D, Valdez P, Yan M, Dixit VM, Tumas D, Grewal IS. Loss of TACI causes fatal lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity, establishing TACI as an inhibitory BLyS receptor. Immunity. 2003;18:279–288. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lesley R, Xu Y, Kalled SL, Hess DM, Schwab SR, Shu HB, Cyster JG. Reduced competitiveness of autoantigen-engaged B cells due to increased dependence on BAFF. Immunity. 2004;20:441–453. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(04)00079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Allman D, Lindsley RC, DeMuth W, Rudd K, Shinton SA, Hardy RR. Resolution of three nonproliferative immature splenic B cell subsets reveals multiple selection points during peripheral B cell maturation. J Immunol. 2001;167:6834–6840. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.12.6834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rubtsov AV, Rubtsova K, Fischer A, Meehan RT, Gillis JZ, Kappler JW, Marrack P. Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7)-driven accumulation of a novel CD11c(+) B-cell population is important for the development of autoimmunity. Blood. 2011;118:1305–1315. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fairfax KA, Tsantikos E, Figgett WA, Vincent FB, Quah PS, LePage M, Hibbs ML, Mackay F. BAFF-driven autoimmunity requires CD19 expression. J Autoimmun. 2015;62:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Treml LS, Carlesso G, Hoek KL, Stadanlick JE, Kambayashi T, Bram RJ, Cancro MP, Khan WN. TLR stimulation modifies BLyS receptor expression in follicular and marginal zone B cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:7531–7539. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.7531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gerth AJ, Lin L, Peng SL. T-bet regulates T-independent IgG2a class switching. Int Immunol. 2003;15:937–944. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxg093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wardemann H, Yurasov S, Schaefer A, Young JW, Meffre E, Nussenzweig MC. Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science. 2003;301:1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.1086907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lopes-Carvalho T, Kearney JF. Development and selection of marginal zone B cells. Immunol Rev. 2004;197:192–205. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.0112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mackay F, Woodcock SA, Lawton P, Ambrose C, Baetscher M, Schneider P, Tschopp J, Browning JL. Mice transgenic for BAFF develop lymphocytic disorders along with autoimmune manifestations. J Exp Med. 1999;190:1697–1710. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.11.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Thien M, Phan TG, Gardam S, Amesbury M, Basten A, Mackay F, Brink R. Excess BAFF rescues self-reactive B cells from peripheral deletion and allows them to enter forbidden follicular and marginal zone niches. Immunity. 2004;20:785–798. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.