Abstract
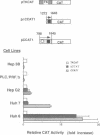
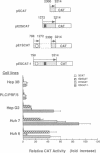
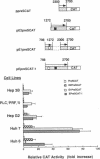
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection causes acute and chronic hepatitis and is closely associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. The principal site of HBV infection is liver, and HBV actively replicates in hepatocytes. Two regions of the HBV genome have been shown previously to display properties of a transcriptional enhancer. In this study, we show that either of the two HBV enhancers can activate all three major HBV promoters in several human hepatoma lines, and the cooperative action of the two enhancers ultimately affects overall activity of the three promoters. In addition, our data suggest that HBV gene expression may be differentially regulated by its enhancers. HBV infection causes chronic liver inflammation and hepatocyte regeneration. It has been proposed that progressive accumulation of mutations during the regenerative hyperplasia may lead to alterations in the differentiation state of hepatocytes. Thus, the development of two differentially regulated enhancers may reflect a strategy of HBV to replicate efficiently in less differentiated hepatocytes during hepatocyte regeneration or hepatocarcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Levy R., Faktor O., Berger I., Shaul Y. Cellular factors that interact with the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1804–1809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Klopchin K., Moriyama T., Pasquinelli C., Dunsford H. A., Sell S., Pinkert C. A., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1145–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90770-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Gray P., Valenzuela P., Rall L. B., Rutter W. J. Integration of hepatitis B virus sequences and their expression in a human hepatoma cell. Nature. 1980 Jul 31;286(5772):535–538. doi: 10.1038/286535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourel G., Trepo C., Bougueleret L., Henglein B., Ponzetto A., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Frequent activation of N-myc genes by hepadnavirus insertion in woodchuck liver tumours. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):294–298. doi: 10.1038/347294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Multiple liver-specific factors bind to the hepatitis B virus core/pregenomic promoter: trans-activation and repression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Marchio A., Etiemble J., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Rearrangement and enhanced expression of c-myc in hepatocellular carcinoma of hepatitis virus infected woodchucks. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):276–279. doi: 10.1038/324276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raney A. K., Milich D. R., Easton A. J., McLachlan A. Differentiation-specific transcriptional regulation of the hepatitis B virus large surface antigen gene in human hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2360–2368. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2360-2368.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Rutter W. J., Laub O. A human hepatitis B viral enhancer element. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):427–430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sureau C., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Mullins J. I., Essex M. Production of hepatitis B virus by a differentiated human hepatoma cell line after transfection with cloned circular HBV DNA. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):37–47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W. Hepatocellular carcinoma and the hepatitis B virus: evidence for a causal association. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:40–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognoni A., Cattaneo R., Serfling E., Schaffner W. A novel expression selection approach allows precise mapping of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7457–7472. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Fujiyama A., Matsubara K. Stable expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in an integrated state in a human hepatoma cell line transfected with the cloned viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):444–448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twist E. M., Clark H. F., Aden D. P., Knowles B. B., Plotkin S. A. Integration pattern of hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in human hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):239–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.239-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Schloemer R. H. Transcriptional trans-activating function of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3448–3453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3448-3453.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee J. K. A liver-specific enhancer in the core promoter region of human hepatitis B virus. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):658–661. doi: 10.1126/science.2554495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]