Abstract
A syndrome has previously been recognized, which is characterized by recurrent episodes of loss of consciousness, some of which end fatally. The electrocardiogram in affected subjects shows prolongation of the QT interval.
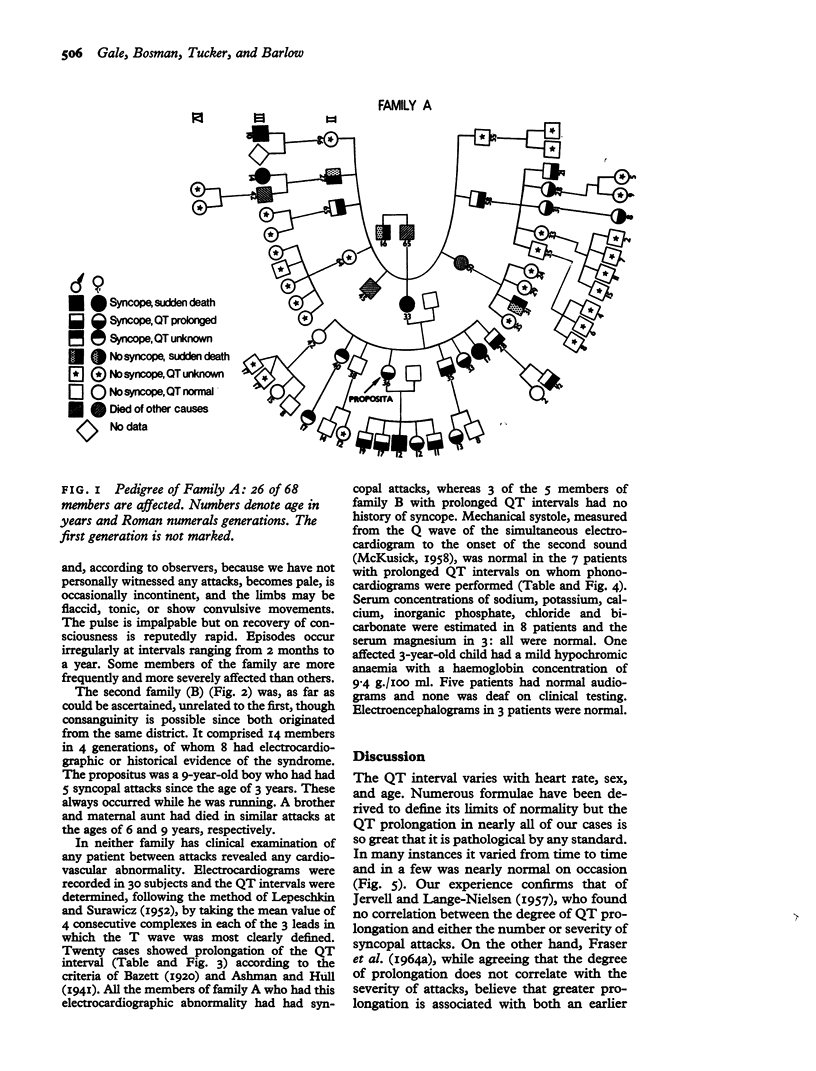
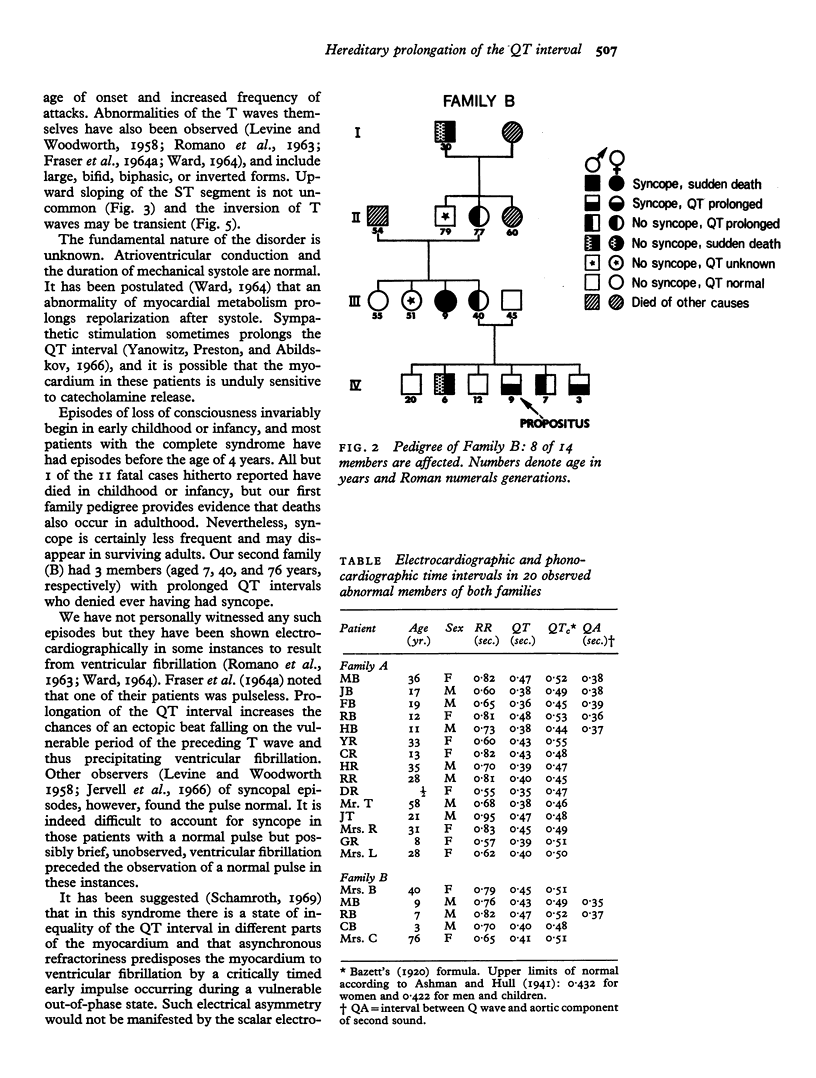
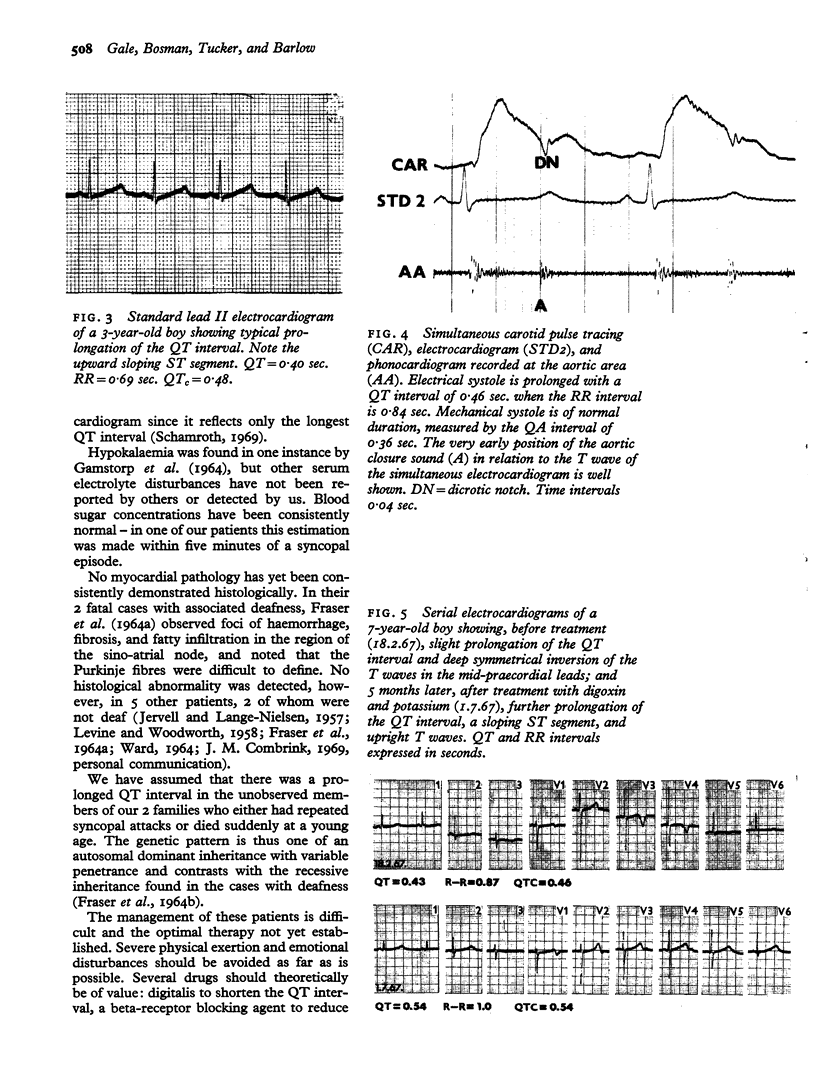
In the present study, 2 unrelated families with a total membership of 82 were investigated; 30 living subjects were examined and 20 were found to be affected. A further 14 members, 11 of whom died suddenly, were presumed from their histories to have been affected. The condition seems to be much more common, at least in South Africa, than the small number of previously reported cases would suggest.
In contrast to the similar syndrome in which congenital deafness is also a feature and in which the disorder is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner, analysis of the present data reveals an autosomal dominant inheritance with variable penetrance. The fundamental nature of the disorder remains unknown. Though treatment is generally unsatisfactory, beta-adrenergic blocking agents may be of value.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLES R. B., SIMPSON W. T., WILKINSON D. S. DEQUALINIUM: A POSSIBLE COMPLICATION OF ITS USE IN BALANITIS. Lancet. 1964 Sep 5;2(7358):531–531. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90485-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. R., FROGGATT P., JAMES T. N. CONGENITAL DEAFNESS ASSOCIATED WITH ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES, FAINTING ATTACKS AND SUDDEN DEATH. A RECESSIVE SYNDROME. Q J Med. 1964 Jul;33:361–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER G. R., FROGGATT P., MURPHY T. GENETICAL ASPECTS OF THE CARDIO-AUDITORY SYNDROME OF JERVELL AND LANGE-NIELSEN (CONGENITAL DEAFNESS AND ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES). Ann Hum Genet. 1964 Nov;28:133–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1964.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAMSTORP I., NILSEN R., WESTLING H. CONGENITAL CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA. Lancet. 1964 Oct 31;2(7366):965–965. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90902-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERVELL A., LANGE-NIELSEN F. Congenital deaf-mutism, functional heart disease with prolongation of the Q-T interval and sudden death. Am Heart J. 1957 Jul;54(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(57)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James T. N. QT prolongation and sudden death. Mod Concepts Cardiovasc Dis. 1969 Jul;38(7):35–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jervell A., Thingstad R., Endsjö T. O. The surdo-cardiac syndrome: three new cases of congenital deafness with syncopal attacks and Q-T prolongation in the electrocardiogram. Am Heart J. 1966 Nov;72(5):582–593. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(66)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPESCHKIN E., SURAWICZ B. The measurement of the Q-T interval of the electrocardiogram. Circulation. 1952 Sep;6(3):378–388. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.6.3.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S. A., WOODWORTH C. R. Congenital deaf-mutism, prolonged QT interval, syncopal attacks and sudden death. N Engl J Med. 1958 Aug 28;259(9):412–417. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195808282590902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANO C., GEMME G., PONGIGLIONE R. ARITMIE CARDIACHE RARE DELL'ETA' PEDIATRICA. II. ACCESSI SINCOPALI PER FIBRILLAZIONE VENTRICOLARE PAROSSISTICA. (PRESENTAZIONE DEL PRIMO CASO DELLA LETTERATURA PEDIATRICA ITALIANA) Clin Pediatr (Bologna) 1963 Sep;45:656–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schamroth L. Fundamental mechanisms in the genesis and evolution of myocardial fibrillation. S Afr Med J. 1969 May 24;43(21):631–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD O. C. A NEW FAMILIAL CARDIAC SYNDROME IN CHILDREN. J Ir Med Assoc. 1964 Apr;54:103–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanowitz F., Preston J. B., Abildskov J. A. Functional distribution of right and left stellate innervation to the ventricles. Production of neurogenic electrocardiographic changes by unilateral alteration of sympathetic tone. Circ Res. 1966 Apr;18(4):416–428. doi: 10.1161/01.res.18.4.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]