Abstract
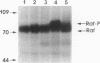
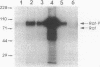
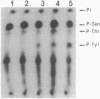
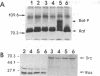
The raf genes encode a family of cytoplasmic proteins with intrinsic protein-serine/threonine kinase activity. The c-raf gene is the cellular homolog of v-raf, the transforming gene of murine sarcoma virus 3611. The constitutive kinase activity of the v-Raf protein has been implicated in transformation and mitogenesis. The activity of Raf-1, the protein product of the c-raf gene, is normally suppressed by a regulatory N-terminal domain. Activation of various tyrosine-kinase growth factor receptors results in activation of Raf-1 and its hyperphosphorylation. Further, Raf-1 has been shown to act either downstream or independently of the p21ras protein, as indicated by experiments involving microinjection of anti-Ras antibodies. To investigate the potential role of p21ras in the activation of Raf-1 by tyrosine kinases, we have used the baculovirus/Sf9 cell system to overproduce various wild-type and mutant forms of pp60src, p21ras, and Raf-1 proteins. We show that either pp60v-src or p21c-ras can independently activate the autokinase activity of Raf-1, but only to a limited extent. Surprisingly, both pp60v-src and p21c-ras are required to fully activate Raf-1. Analysis of the Raf-1 autokinase activity in vitro shows that Raf-1 autophosphorylation sites are distributed equally on serine and threonine residues. When Raf-1 is analyzed by immunoblotting, as previously reported for mammalian cell experiments, a marked increase in the apparent molecular weight of Raf-1 is seen only when it is coexpressed with both pp60v-src and p21ras.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- App H., Hazan R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Rapp U. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates association and kinase activity of Raf-1 with the EGF receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):913–919. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccarini M., Sabatini D. M., App H., Rapp U. R., Stanley E. R. Colony stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) stimulates temperature dependent phosphorylation and activation of the RAF-1 proto-oncogene product. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3649–3657. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Kerby S. B., Sutrave P., Gunnell M. A., Mark G., Rapp U. R. Structure and biological activity of human homologs of the raf/mil oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1400–1407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brott B. K., Decker S., Shafer J., Gibbs J. B., Jove R. GTPase-activating protein interactions with the viral and cellular Src kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. P., Clark-Lewis I., Rapp U. R., May W. S. Interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mediate rapid phosphorylation and activation of cytosolic c-raf. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19812–19817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnsworth C. L., Feig L. A. Dominant inhibitory mutations in the Mg(2+)-binding site of RasH prevent its activation by GTP. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4822–4829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Pan B. T., Roberts T. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation of ras GTP-binding mutants using an in situ colony-binding assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker G., Huleihel M., Cleveland J. L., Kolch W., Beck T. W., Lloyd P., Pawson T., Rapp U. R. Mutational activation of c-raf-1 and definition of the minimal transforming sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2503–2512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huleihel M., Goldsborough M., Cleveland J., Gunnell M., Bonner T., Rapp U. R. Characterization of murine A-raf, a new oncogene related to the v-raf oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2655–2662. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Tamemoto H., Nagao M., Kadowaki T., Takaku F., Kasuga M. Insulin and platelet-derived growth factor stimulate phosphorylation of the c-raf product at serine and threonine residues in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7933–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamal S., Ziff E. Transactivation of c-fos and beta-actin genes by raf as a step in early response to transmembrane signals. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):463–466. doi: 10.1038/344463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Fukumoto Y., Oku N., Hori Y., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Takai Y. Activation of the serum response element and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate response element by the activated c-raf-1 protein in a manner independent of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20855–20858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Lloyd P., Rapp U. R. Raf-1 protein kinase is required for growth of induced NIH/3T3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):426–428. doi: 10.1038/349426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacina K. S., Yonezawa K., Brautigan D. L., Tonks N. K., Rapp U. R., Roth R. A. Insulin activates the kinase activity of the Raf-1 proto-oncogene by increasing its serine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12115–12118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Bell R. M. The lipid binding, regulatory domain of protein kinase C. A 32-kDa fragment contains the calcium- and phosphatidylserine-dependent phorbol diester binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14867–14870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Wood K., Mamon H., Haser W., Roberts T. Raf-1: a kinase currently without a cause but not lacking in effects. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):479–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90228-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S., Daya-Makin M. Protein kinase cascades in meiotic and mitotic cell cycle control. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;68(12):1297–1330. doi: 10.1139/o90-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Williams N. G., Cheng S. H., Roberts T. M. Regulation of pp60c-src and its interaction with polyomavirus middle T antigen in insect cells. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):61–68. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.61-68.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine and threonine in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Yum S., Cuddy M. P., Turner B. C., Rapp U. R. Differential regulation of the p72-74 RAF-1 kinase in 3T3 fibroblasts expressing ras or src oncogenes. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 May;2(5):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban E., Mitchell T., Kufe D. Expression of the c-raf protooncogene in human hematopoietic cells and cell lines. Blood. 1987 May;69(5):1437–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Copeland T. D., Mark G. E., Rapp U. R., Oroszlan S. Detection of the myristylated gag-raf transforming protein with raf-specific antipeptide sera. Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):78–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R., Kung H. F. Induction of transformation and DNA synthesis after microinjection of raf proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3828–3833. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Tsai M. H., Yu C. L., Smith J. K. Critical role of cellular ras proteins in proliferative signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):871–881. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton V. P., Jr, Cooper G. M. Activation of human raf transforming genes by deletion of normal amino-terminal coding sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1171–1179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton V. P., Jr, Nichols D. W., Laudano A. P., Cooper G. M. Definition of the human raf amino-terminal regulatory region by deletion mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):639–647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B., Rapp U., App H., Greene M., Dobashi K., Reed J. Interleukin 2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of p72-74 Raf-1 kinase in a T-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B., Heidecker G., Huleihel M., Rapp U. R. Expression of raf oncogenes activates the PEA1 transcription factor motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2247–2250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., DeClue J. E., Vass W. C., Papageorge A. G., McCormick F., Lowy D. R. Suppression of c-ras transformation by GTPase-activating protein. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):754–756. doi: 10.1038/346754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]