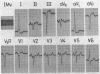
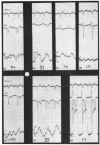
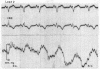
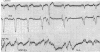
Full text
PDF
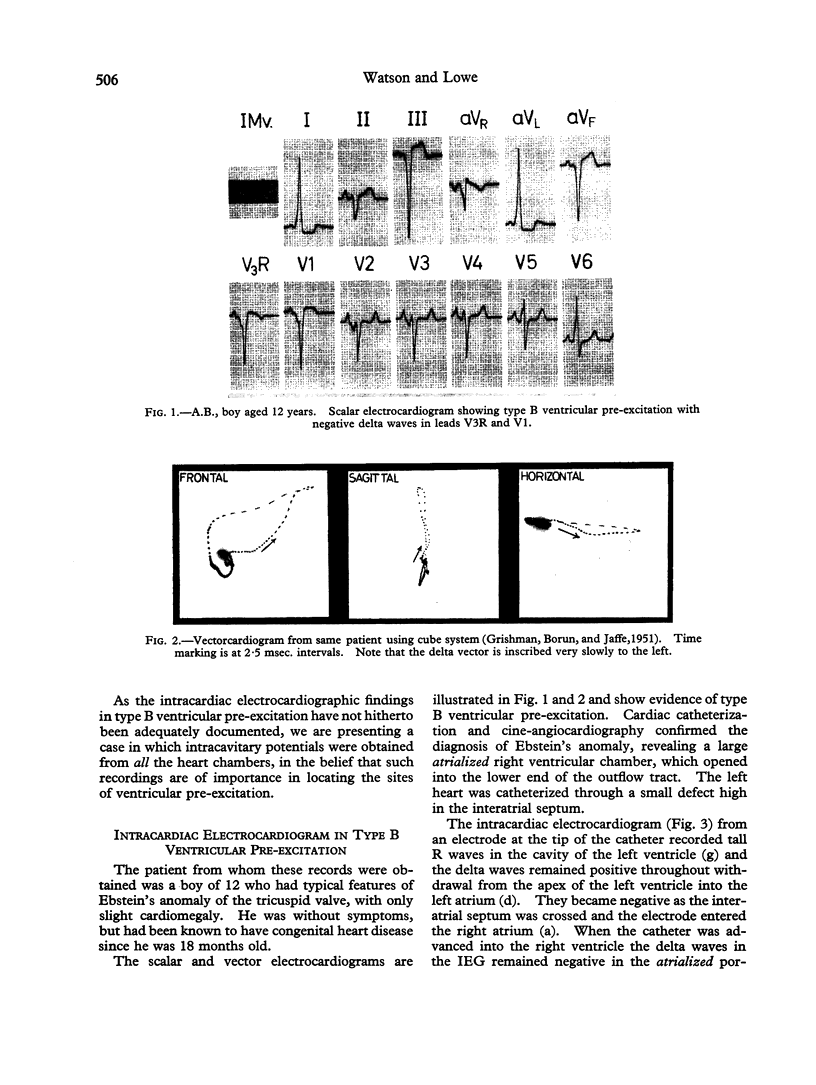

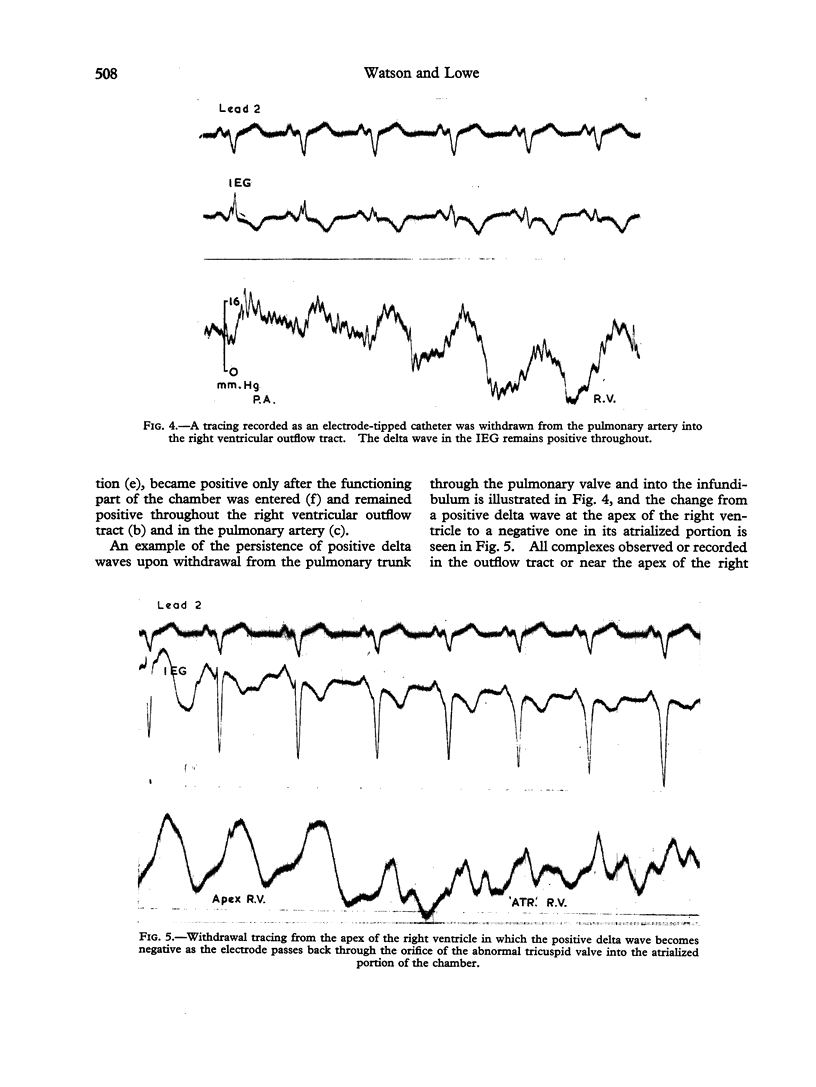
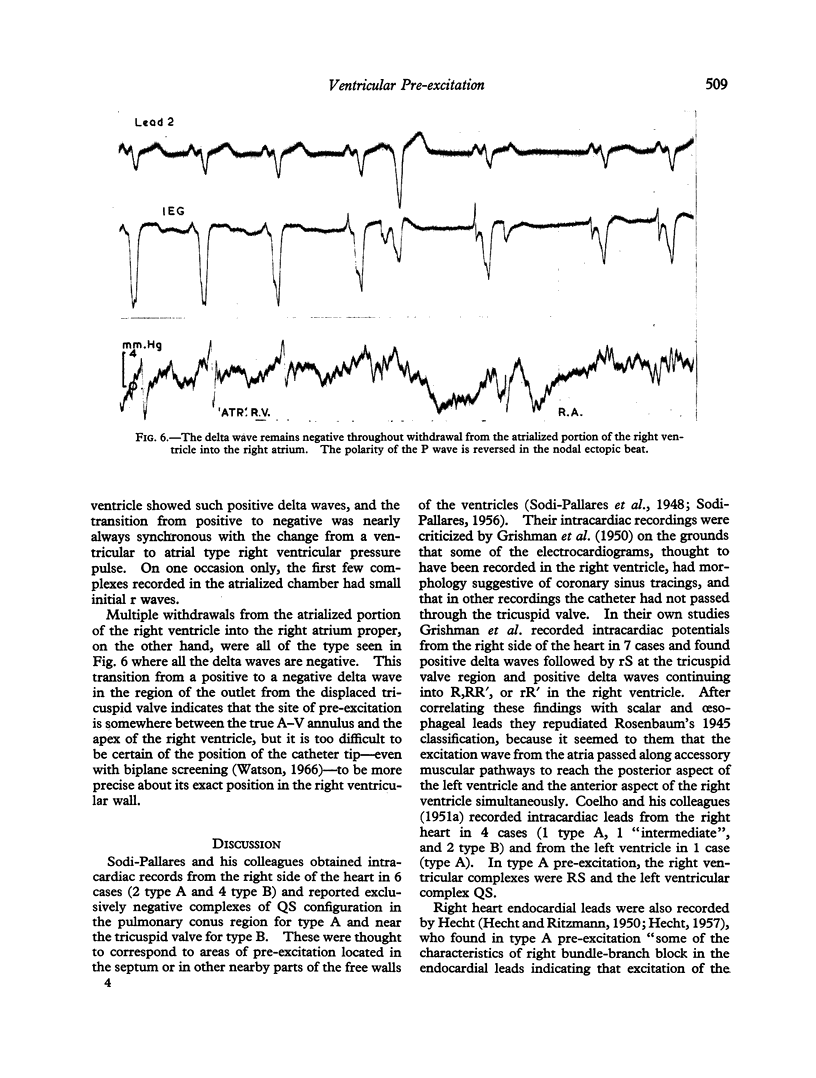


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLEIFER S., KAHN M., GRISHMAN A., DONOSO E. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: a vectorcardiographic, electrocardiographic and clinical study. Am J Cardiol. 1959 Sep;4:321–333. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(59)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COELHO E., FONSECA J. M., BORGES A. S., NUNES A., PAIVA E. Etude des dérivations intra-cavitaires du syndrome de Wolff-Parkinson-White et son déclenchement au moyen de l'excitation de la cloison inter-ventriculaire. Sem Hop. 1951 Jan 2;27(1):8–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COELHO E., FONSECA J. M., NUNES A., PADUA F., SERRAS PEREIRA J. Les potentiels intracavitaires du coeur gauche de l'homme dans différentes cardiopathies. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1951 Nov;44(11):961–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAU G., AGOSTONI A. [The electrocardiogram in Ebstein's disease. Morphology, genesis and diagnostic importance. Description of 2 new cases and a review of 124 other cases reported in the literature]. Folia Cardiol. 1959 Jun 30;18:223–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAMBOA R., PENALOZA D., SIME F., BANCHERO N. The role of the right and left ventricles in the ventricular pre-excitation (WPW) syndrome. An experimental study in man. Am J Cardiol. 1962 Nov;10:650–656. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(62)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRISHMAN A., BORUN E. R., JAFFE H. L. Spatial vectorcardiography: technique for the simultaneous recording of the frontal, sagittal, and horizontal projections. I. Am Heart J. 1951 Apr;41(4):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(51)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRISHMAN A., KROOP I. G., STEINBERG M. F. The course of the excitation wave in patients with electrocardiograms showing short P-R intervals and wide QRS complexes (Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome). Am Heart J. 1950 Oct;40(4):554–572. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(50)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHT H. H., RITZMANN L. Potential variations of the epicardial and endocardial surfaces in anomalous atrioventricular excitation. Am J Med. 1950 Apr;8(4):527–527. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON P. G., EMSLIE-SMITH D., LOWE K. G., WATSON H. THE ASSOCIATION OF TYPE B VENTRICULAR PRE-EXCITATION AND RIGHT BUNDLE-BRANCH BLOCK. Br Heart J. 1963 Nov;25:755–762. doi: 10.1136/hrt.25.6.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRANCHESI J., GUIMARAES A. C., TEIXEIRA V., PILEGGI F. Vectorial interpretation of the ventricular complex in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1959 Sep;4:334–340. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(59)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson H. Electrode catheters and the diagnosis of Ebstein's anomaly of the tricuspid valve. Br Heart J. 1966 Mar;28(2):161–171. doi: 10.1136/hrt.28.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]