Abstract
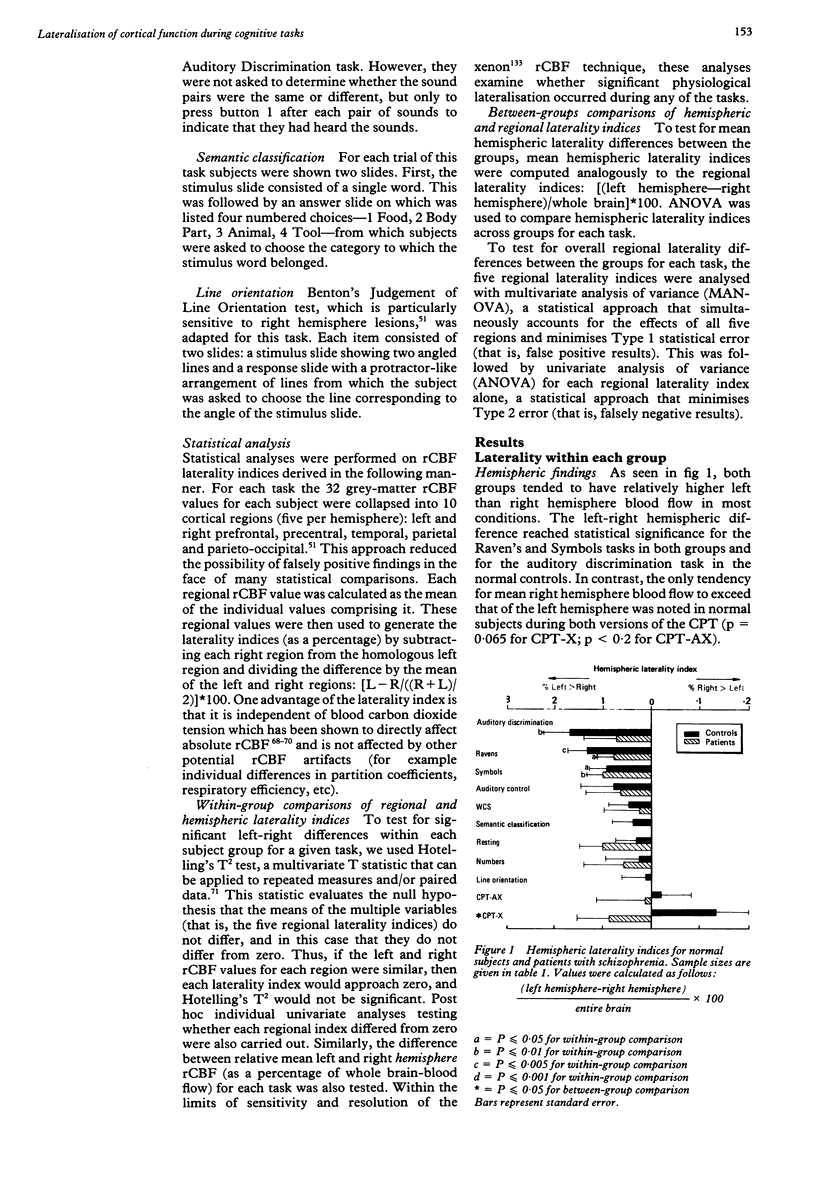
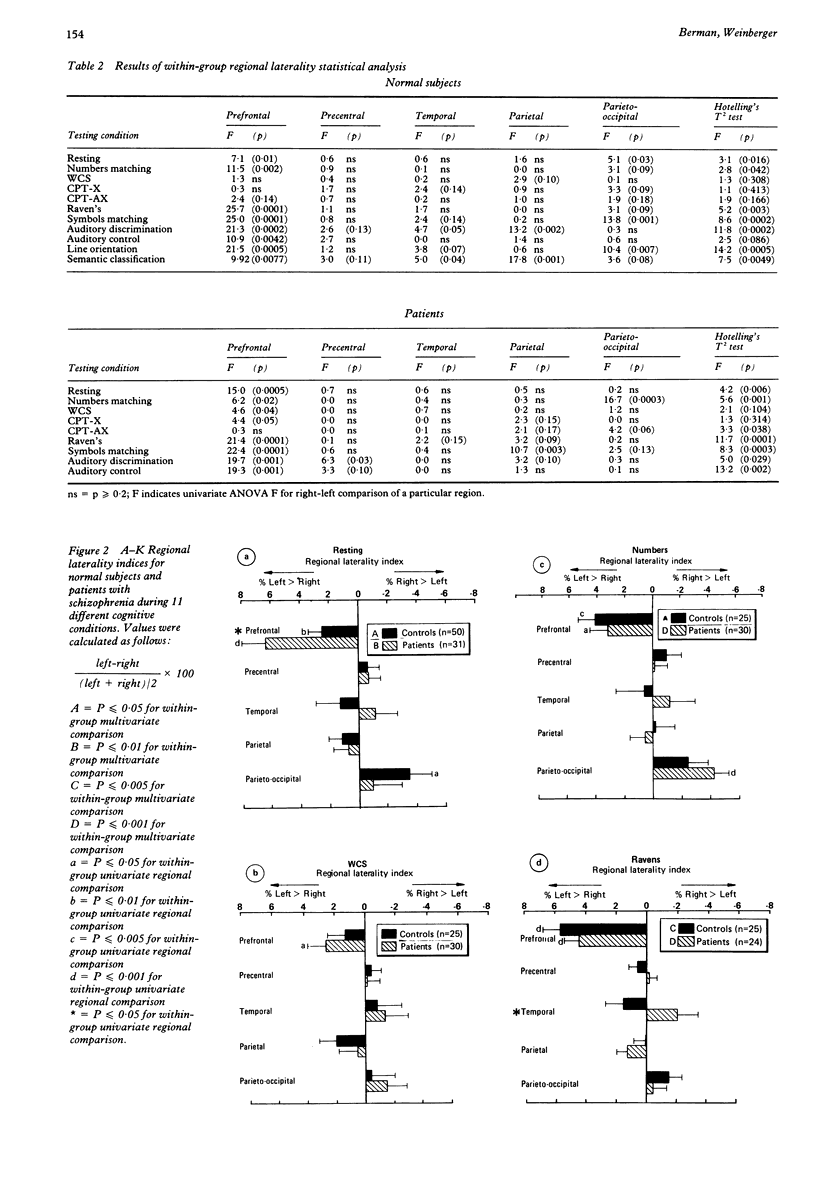
To assess cognitively-related regional asymmetries of brain function, regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) was determined by the xenon inhalation method while normal subjects performed 10 different tasks and also while they were at rest. In addition to healthy subjects, patients with schizophrenia were also studied. A total of 447 rCBF studies were carried out during the following conditions: the Wisconsin Card Sort Test, a numbers matching test, a symbols matching test, Raven's Progressive Matrices, an auditory discrimination test, an auditory control task, two versions of a visual continuous performance task, line orientation, semantic classification, and resting. On the whole, those tasks that seem to require or allow for internal verbalisation resulted in the greatest activation of the left hemisphere compared with the right; right hemisphere activation predominated only in the two tasks primarily involving attention and vigilance. Furthermore, a consistent regional topography of normal cerebral functional laterality was seen: under most conditions left prefrontal cortical activity exceeded that of right prefrontal cortex; during all non-auditory tasks, parieto-occipital cortical activity had an opposite pattern-greater right than left. During most conditions the schizophrenic patients displayed the same pattern. While several cognitively specific between-group differences were found, no single cortical region was consistently implicated and no specific direction of abnormal asymmetry predominated. These data suggest that there is a predominant task-independent functional pattern of cortical activity emphasising relatively greater left anterior and right posterior activation. This pattern may reflect the verbal and attentional primacy of these areas, respectively.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECK L. H., BRANSOME E. D., Jr, MIRSKY A. F., ROSVOLD H. E., SARASON I. A continuous performance test of brain damage. J Consult Psychol. 1956 Oct;20(5):343–350. doi: 10.1037/h0043220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. G., Dimond S. J. Brain disconnection and schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;123(577):661–662. doi: 10.1192/bjp.123.6.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berker E. A., Berker A. H., Smith A. Translation of Broca's 1865 report. Localization of speech in the third left frontal convolution. Arch Neurol. 1986 Oct;43(10):1065–1072. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520100069017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman K. F., Illowsky B. P., Weinberger D. R. Physiological dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. IV. Further evidence for regional and behavioral specificity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Jul;45(7):616–622. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800310020002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman K. F., Zec R. F., Weinberger D. R. Physiologic dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. II. Role of neuroleptic treatment, attention, and mental effort. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1986 Feb;43(2):126–135. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1986.01800020032005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher J. Hand preference in autistic children and their parents. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1977 Jun;7(2):177–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01537728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchsbaum M. S., Ingvar D. H., Kessler R., Waters R. N., Cappelletti J., van Kammen D. P., King A. C., Johnson J. L., Manning R. G., Flynn R. W. Cerebral glucography with positron tomography. Use in normal subjects and in patients with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982 Mar;39(3):251–259. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290030001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman L. J. Recent advances in the study of schizophrenic cognition. Schizophr Bull. 1979;5(4):568–580. doi: 10.1093/schbul/5.4.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damasio A. R., Damasio H., Chui H. C. Neglect following damage to frontal lobe or basal ganglia. Neuropsychologia. 1980;18(2):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(80)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. M., Ackerman R. H., Correia J. A., Alpert N. M., Chang J., Buonanno F., Kelley R. E., Rosner B., Taveras J. M. Cerebral blood flow and cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity in stroke-age normal controls. Neurology. 1983 Apr;33(4):391–399. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duara R., Gross-Glenn K., Barker W. W., Chang J. Y., Apicella A., Loewenstein D., Boothe T. Behavioral activation and the variability of cerebral glucose metabolic measurements. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Jun;7(3):266–271. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor-Henry P. Lateralized temporal-limbic dysfunction and psychopathology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;280:777–797. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb25541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor-Henry P. Psychosis and temporal lobe epilepsy. A controlled investigation. Epilepsia. 1969 Sep;10(3):363–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1969.tb03853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galaburda A. M., LeMay M., Kemper T. L., Geschwind N. Right-left asymmetrics in the brain. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):852–856. doi: 10.1126/science.341314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gevins A. S., Morgan N. H., Bressler S. L., Cutillo B. A., White R. M., Illes J., Greer D. S., Doyle J. C., Zeitlin G. M. Human neuroelectric patterns predict performance accuracy. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):580–585. doi: 10.1126/science.3810158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. Defective interhemispheric transfer in schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol. 1978 Oct;87(5):472–480. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.87.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruzelier J. H. Bilateral asymmetry of skin conductance orienting activity and levels in schizophrenics. Biol Psychol. 1973;1(1):21–41. doi: 10.1016/0301-0511(73)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruzelier J. H., Venables P. H. Skin conductance orienting activity in a heterogeneous sample of schizophrenics. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1972 Oct;155(4):277–287. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197210000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gur R. C., Gur R. E., Obrist W. D., Hungerbuhler J. P., Younkin D., Rosen A. D., Skolnick B. E., Reivich M. Sex and handedness differences in cerebral blood flow during rest and cognitive activity. Science. 1982 Aug 13;217(4560):659–661. doi: 10.1126/science.7089587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gur R. E., Gur R. C., Skolnick B. E., Caroff S., Obrist W. D., Resnick S., Reivich M. Brain function in psychiatric disorders. III. Regional cerebral blood flow in unmedicated schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 Apr;42(4):329–334. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790270015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gur R. E. Left hemisphere dysfunction and left hemisphere overactivation in schizophrenia. J Abnorm Psychol. 1978 Apr;87(2):226–238. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.87.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gur R. E., Skolnick B. E., Gur R. C., Caroff S., Rieger W., Obrist W. D., Younkin D., Reivich M. Brain function in psychiatric disorders. I. Regional cerebral blood flow in medicated schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1983 Nov;40(11):1250–1254. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1983.01790100096013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman K. M., Van Den Abell T. Right hemisphere dominance for attention: the mechanism underlying hemispheric asymmetries of inattention (neglect). Neurology. 1980 Mar;30(3):327–330. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman K. M., Van Den Abell T. Right hemispheric dominance for mediating cerebral activation. Neuropsychologia. 1979;17(3-4):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(79)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingvar D. H., Cronqvist S., Ekberg R., Risberg J., Hoedt-Rasmussen K. Normal values of regional cerebral blood flow in man, including flow and weight estimates of gray and white matter. A preliminary summary. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1965;14:72–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1965.tb01958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingvar D. H., Franzén G. Abnormalities of cerebral blood flow distribution in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1974;50(4):425–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1974.tb09707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingvar D. H. Functional landscapes of the dominant hemisphere. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 30;107(1):181–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kertesz A., Black S. E., Polk M., Howell J. Cerebral asymmetries on magnetic resonance imaging. Cortex. 1986 Mar;22(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(86)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner M. J., Rosenquist A., Alavi A., Rosen M., Dann R., Fazekas F., Bosley T., Greenberg J., Reivich M. Cerebral metabolism and patterned visual stimulation: a positron emission tomographic study of the human visual cortex. Neurology. 1988 Jan;38(1):89–95. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le May M., Kido D. K. Asymmetries of the cerebral hemispheres on computed tomograms. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1978 Sep;2(4):471–476. doi: 10.1097/00004728-197809000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lishman W. A., Toone B. K., Colbourn C. J., McMeekan E. R., Mance R. M. Dichotic listening in psychotic patients. Br J Psychiatry. 1978 Apr;132:333–341. doi: 10.1192/bjp.132.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchins D. J., Weinberger D. R., Wyatt R. J. Schizophrenia and cerebral asymmetry detected by computed tomography. Am J Psychiatry. 1982 Jun;139(6):753–757. doi: 10.1176/ajp.139.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew R. J., Duncan G. C., Weinman M. L., Barr D. L. Regional cerebral blood flow in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1982 Oct;39(10):1121–1124. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1982.04290100001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maximilian V. A., Prohovnik I., Risberg J. Cerebral hemodynamic response to mental activation in normo- and hypercapnia. Stroke. 1980 Jul-Aug;11(4):342–347. doi: 10.1161/01.str.11.4.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M. A cortical network for directed attention and unilateral neglect. Ann Neurol. 1981 Oct;10(4):309–325. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner B. Interhemispheric differences in the localization of psychological processes in man. Br Med Bull. 1971 Sep;27(3):272–277. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlin D. B., Carpenter B., Golden C. J. Hemispheric asymmetries in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 1981 Jun;16(6):561–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrist W. D., Thompson H. K., Jr, King C. H., Wang H. S. Determination of regional cerebral blood flow by inhalation of 133-Xenon. Circ Res. 1967 Jan;20(1):124–135. doi: 10.1161/01.res.20.1.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrist W. D., Thompson H. K., Jr, Wang H. S., Wilkinson W. E. Regional cerebral blood flow estimated by 133-xenon inhalation. Stroke. 1975 May-Jun;6(3):245–256. doi: 10.1161/01.str.6.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orzack M. H., Kornetsky C. Attention dysfunction in chronic schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1966 Mar;14(3):323–326. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1966.01730090099015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prohovnik I., Håkansson K., Risberg J. Observations on the functional significance of regional cerebral blood flow in "resting" normal subjects. Neuropsychologia. 1980;18(2):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(80)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risberg J., Halsey J. H., Wills E. L., Wilson E. M. Hemispheric specialization in normal man studied by bilateral measurements of the regional cerebral blood flow. A study with the 133-Xe inhalation technique. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):511–524. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risberg J., Maximilian A. V., Prohovnik I. Changes of cortical activity patterns during habituation to a reasoning test. A study with the 133Xe inhalation technique for measurement of regional cerebral blood flow. Neuropsychologia. 1977;15(6):793–798. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(77)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risberg J. Regional cerebral blood flow measurements by 133Xe-inhalation: methodology and applications in neuropsychology and psychiatry. Brain Lang. 1980 Jan;9(1):9–34. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(80)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer R. A., Shagass C., Straumanis J. J., Amadeo M. Pattern evoked potential measurements suggesting lateralized hemispheric dysfunction in chronic schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry. 1978 Apr;13(2):185–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland E., Larsen B. Focal increase of cerebral blood flow during stereognostic testing in man. Arch Neurol. 1976 Aug;33(8):551–558. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500080029005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Skinhøj E. Extrastriate cortical areas activated during visual discrimination in man. Brain Res. 1981 Oct 5;222(1):166–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90953-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E., Skinhøj E., Lassen N. A. Focal activations of human cerebral cortex during auditory discrimination. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Jun;45(6):1139–1151. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.6.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland P. E. Somatotopical tuning of postcentral gyrus during focal attention in man. A regional cerebral blood flow study. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Oct;46(4):744–754. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.46.4.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer L. Evidence of right cerebral hemisphere dysfunction in schizophrenic patients with left hemisphere overactivation. Biol Psychiatry. 1982 Jun;17(6):655–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman L. J. Schizophrenia and brain dysfunction: an integration of recent neurodiagnostic findings. Psychol Bull. 1983 Sep;94(2):195–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard G., Gruzelier J., Manchanda R., Hirsch S. R., Wise R., Frackowiak R., Jones T. 15O positron emission tomographic scanning in predominantly never-treated acute schizophrenic patients. Lancet. 1983 Dec 24;2(8365-66):1448–1452. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90798-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry R. W. Hemisphere deconnection and unity in conscious awareness. Am Psychol. 1968 Oct;23(10):723–733. doi: 10.1037/h0026839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., Greenspan B., Abrams R. Lateralized neuropsychological dysfunction in affective disorder and schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 1979 Aug;136(8):1031–1034. doi: 10.1176/ajp.136.8.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., Redfield J., Abrams R. Neuropsychological dysfunction in schizophrenia and affective disease. Biol Psychiatry. 1981 May;16(5):467–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga S., Strandgaard S., Uemura K., Ito K., Kutsuzawa T. Cerebrovascular CO2 reactivity in normotensive and hypertensive man. Stroke. 1976 Sep-Oct;7(5):507–510. doi: 10.1161/01.str.7.5.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villardita C. Raven's colored Progressive Matrices and intellectual impairment in patients with focal brain damage. Cortex. 1985 Dec;21(4):627–634. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(58)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. T., Valenstein E., Heilman K. M. Thalamic neglect. Possible role of the medial thalamus and nucleus reticularis in behavior. Arch Neurol. 1981 Aug;38(8):501–506. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510080063009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger D. R., Berman K. F., Illowsky B. P. Physiological dysfunction of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia. III. A new cohort and evidence for a monoaminergic mechanism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Jul;45(7):609–615. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800310013001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger D. R., Luchins D. J., Morihisa J., Wyatt R. J. Asymmetrical volumes of the right and left frontal and occipital regions of the human brain. Ann Neurol. 1982 Jan;11(1):97–100. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler B. E. Cerebral laterality and psychiatry: a review of the literature. Am J Psychiatry. 1980 Mar;137(3):279–291. doi: 10.1176/ajp.137.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlberg G. W., Kornetsky C. Sustained attention in remitted schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1973 Apr;28(4):533–537. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1973.01750340065011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


