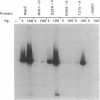
Abstract
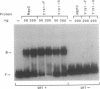
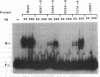
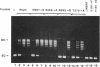
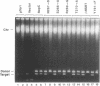
The replication initiator proteins encoded by the pT181 and related plasmids have sequence-specific DNA binding and topoisomerase activities. These proteins create a site-specific nick in one strand of the DNA at the origin of replication that serves as a primer for the initiation of replication. To define the regions of the pT181-encoded initiator protein, RepC, that are involved in its DNA binding, topoisomerase, and replication activities, we have carried out site-directed mutagenesis of the repC gene. Analysis of mutant RepC proteins in vitro and in vivo has identified the amino acids that are critical for its various biochemical activities. The DNA binding domain of RepC was found to be located near its C-terminal region and was different from the domain involved in its sequence-specific topoisomerase activity. These studies also showed that the DNA topoisomerase activity of the initiator protein can be uncoupled from its tight noncovalent DNA binding and replication activities.
Full text
PDF


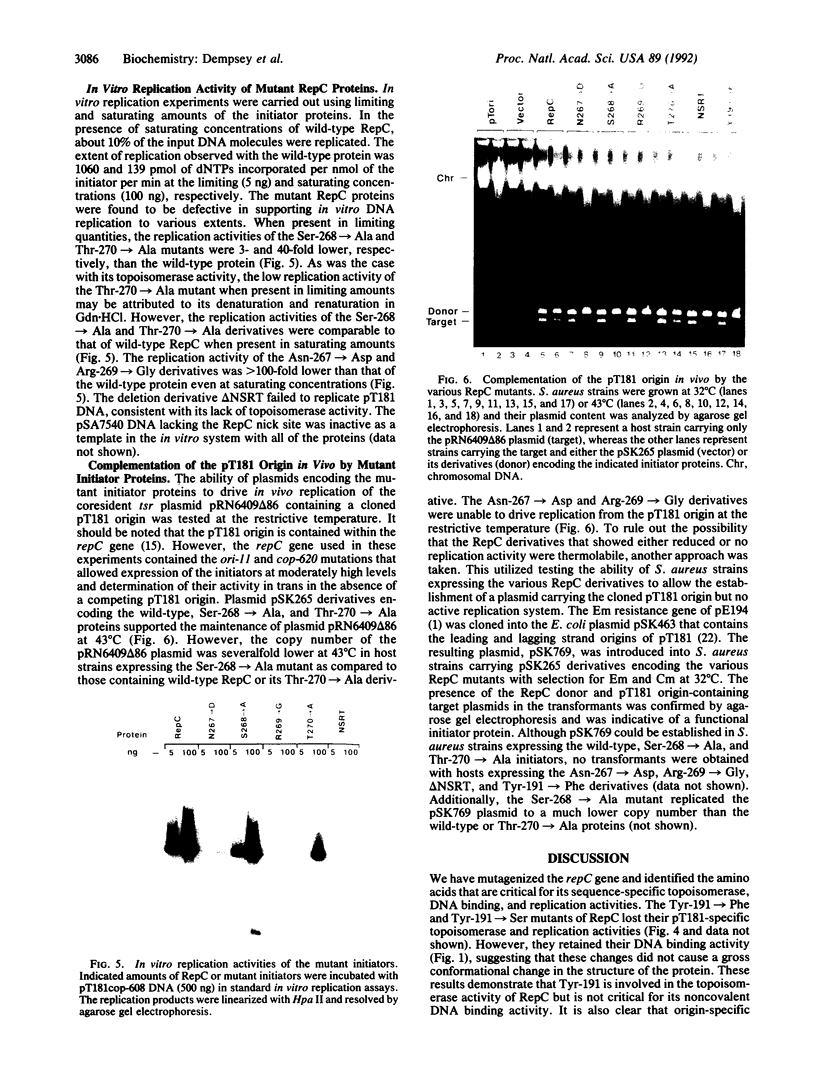

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birch P., Khan S. A. Replication of single-stranded plasmid pT181 DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):290–294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compagnone-Post P., Malyankar U., Khan S. A. Role of host factors in the regulation of the enterotoxin B gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1827–1830. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1827-1830.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Kornberg A. Purification and characterization of phiX174 gene A protein. A multifunctional enzyme of duplex DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5328–5332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennaro M. L., Iordanescu S., Novick R. P., Murray R. W., Steck T. R., Khan S. A. Functional organization of the plasmid pT181 replication origin. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss A., Ehrlich S. D. The family of highly interrelated single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):231–241. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.231-241.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iordanescu S. Specificity of the interactions between the Rep proteins and the origins of replication of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids pT181 and pC221. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):481–487. doi: 10.1007/BF02464921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. A., Novick R. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of pT181, a tetracycline-resistance plasmid from Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Khan S. A. Cleavage of single-stranded DNA by plasmid pT181-encoded RepC protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4085–4097. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Khan S. A. Static and initiator protein-enhanced bending of DNA at a replication origin. Science. 1986 Sep 19;233(4770):1316–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.3749879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Murray R. W., Khan S. A. Sequence-specific interaction between the replication initiator protein of plasmid pT181 and its origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5484–5488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Murray R. W., Rosenblum W. D., Khan S. A. Purification of pT181-encoded repC protein required for the initiation of plasmid replication. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8571–8577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepsel R. R., Murray R. W., Rosenblum W. D., Khan S. A. The replication initiator protein of plasmid pT181 has sequence-specific endonuclease and topoisomerase-like activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6845–6849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. W., Koepsel R. R., Khan S. A. Synthesis of single-stranded plasmid pT181 DNA in vitro. Initiation and termination of DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1051–1057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noirot P., Bargonetti J., Novick R. P. Initiation of rolling-circle replication in pT181 plasmid: initiator protein enhances cruciform extrusion at the origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8560–8564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Staphylococcal plasmids and their replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:537–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Projan S. J., Kornblum J., Moghazeh S. L., Edelman I., Gennaro M. L., Novick R. P. Comparative sequence and functional analysis of pT181 and pC221, cognate plasmid replicons from Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(3):452–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00330758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. D., Balson D. F., Shaw W. V. In vitro studies of the initiation of staphylococcal plasmid replication. Specificity of RepD for its origin (oriD) and characterization of the Rep-ori tyrosyl ester intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5519–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Electrophoretic assay for DNA-binding proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Horiuchi K. Multiregulatory element of filamentous bacteriophages. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):101–106. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.101-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zock J. M., Birch P., Khan S. A. Specificity of RepC protein in plasmid pT181 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3484–3488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]