Abstract
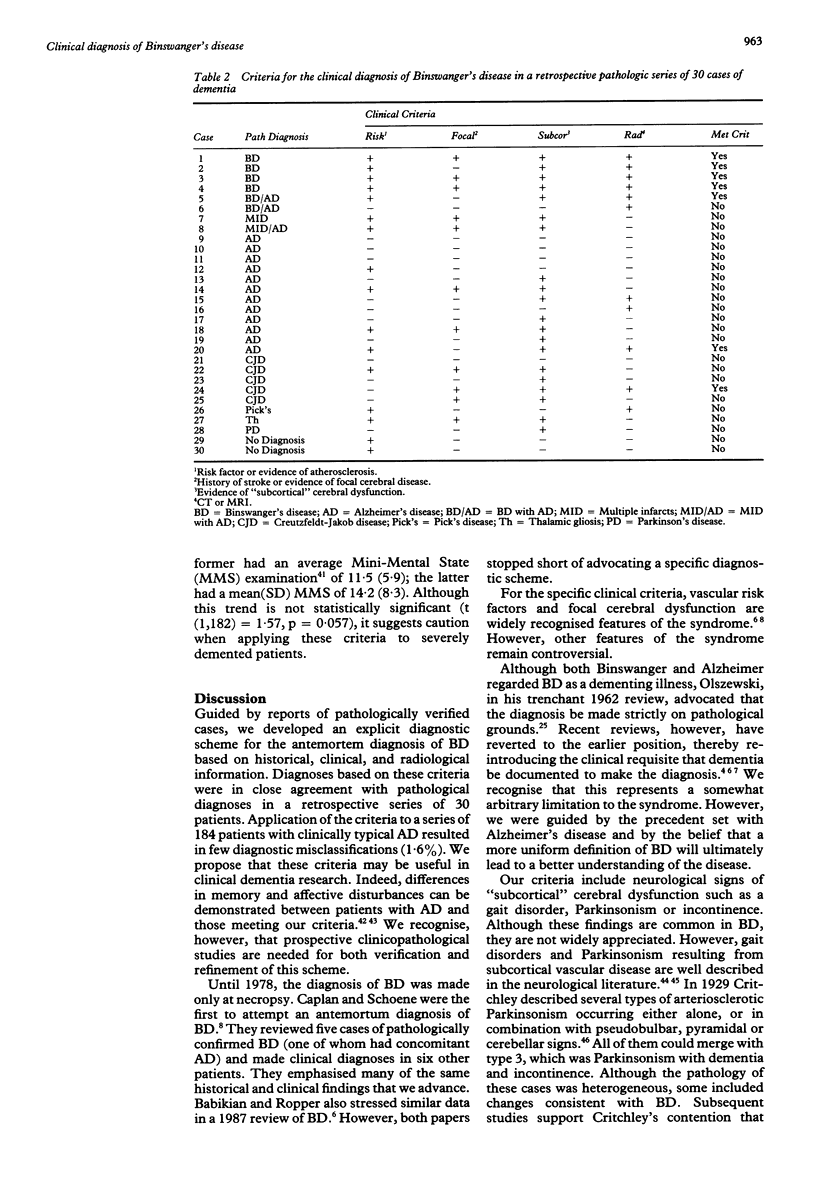
To aid in the prospective study of Binswanger's disease, a poorly understood form of vascular dementia, a standardised criteria for its antemortem diagnosis was proposed. These criteria include dementia, bilateral radiological abnormalities on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and at least two of the following three clinical findings: A) a vascular risk factor or evidence of systemic vascular disease; B) evidence of focal cerebrovascular disease; and C) evidence of "subcortical" cerebral dysfunction. These criteria were validated in two ways. First, by retrospectively applying them to a series of 30 demented patients with various pathological diagnoses. Second, by prospectively applying them to a series of 184 patients with clinically typical Alzheimer's disease. The sensitivity and specificity of the criteria appear adequate for use in clinical research.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson S. M., Perl D. P. Clinical neuropathological conference. A 58-year-old concrete worker was amitted to the hospital because of slowly progressive dementia. Dis Nerv Syst. 1974 Jun;35(6):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awad I. A., Johnson P. C., Spetzler R. F., Hodak J. A. Incidental subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. II. Postmortem pathological correlations. Stroke. 1986 Nov-Dec;17(6):1090–1097. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.6.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awad I. A., Spetzler R. F., Hodak J. A., Awad C. A., Carey R. Incidental subcortical lesions identified on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. I. Correlation with age and cerebrovascular risk factors. Stroke. 1986 Nov-Dec;17(6):1084–1089. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.6.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babikian V., Ropper A. H. Binswanger's disease: a review. Stroke. 1987 Jan-Feb;18(1):2–12. doi: 10.1161/01.str.18.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemond A. On Binswanger's subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy and the possibility of its clinical recognition. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir. 1970 Nov-Dec;73(6):413–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. D., Sumi S. M., Nemens E. J., Nochlin D., Schellenberg G., Lampe T. H., Sadovnick A., Chui H., Miner G. W., Tinklenberg J. Phenotypic heterogeneity in familial Alzheimer's disease: a study of 24 kindreds. Ann Neurol. 1989 Jan;25(1):12–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun A., Englund E. A white matter disorder in dementia of the Alzheimer type: a pathoanatomical study. Ann Neurol. 1986 Mar;19(3):253–262. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brust J. C. Vascular dementia is overdiagnosed. Arch Neurol. 1988 Jul;45(7):799–801. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520310117026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. C., Burch J. G., Kunze U. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). A vascular etiology of dementia. Stroke. 1976 Nov-Dec;7(6):626–631. doi: 10.1161/01.str.7.6.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan L. R., Schoene W. C. Clinical features of subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger disease). Neurology. 1978 Dec;28(12):1206–1215. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.12.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt L. D., Kistler J. P., Miller D. C., Richardson E. P., Jr, Buonanno F. S. NMR-neuropathologic correlation in stroke. Stroke. 1987 Mar-Apr;18(2):342–351. doi: 10.1161/01.str.18.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubas F., Gray F., Roullet E., Escourolle R. Leucoencéphalopathies artériopathiques. (17 cas anatomo-cliniques). Rev Neurol (Paris) 1985;141(2):93–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis M., Brucher J. M., Gonsette R. E. Observation anatomo-clinique d'une encéphalopathie sous-corticale artérioscléreuse ("maladie de Binswanger") avec hypodensité de la substance blanche au scanner cérébral. Acta Neurol Belg. 1984 May-Jul;84(3):131–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvoisin R. C., Golbe L. I. Toward a definition of Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1989 May;39(5):746–746. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.5.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnest M. P., Fahn S., Karp J. H., Rowland L. P. Normal pressure hydrocephalus and hypertensive cerebrovascular disease. Arch Neurol. 1974 Oct;31(4):262–266. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490400076009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erkinjuntti T., Haltia M., Palo J., Sulkava R., Paetau A. Accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of vascular dementia: a prospective clinical and post-mortem neuropathological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Aug;51(8):1037–1044. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.8.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erkinjuntti T., Ketonen L., Sulkava R., Sipponen J., Vuorialho M., Iivanainen M. Do white matter changes on MRI and CT differentiate vascular dementia from Alzheimer's disease? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Jan;50(1):37–42. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. H., Penn R., Clasen R., Martin E., Wilson R., Savoy S. Pathological diagnosis in clinically typical Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 28;313(22):1419–1420. doi: 10.1056/nejm198511283132220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARCIN R., LAPRESLE J., LYON G. [Binswanger's chronic subcortical encephalopathy. Anatomoclinical study of 3 cases]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1960 May;102:423–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Albea E., Cabello A., Franch O. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease): a report of five patients. Acta Neurol Scand. 1987 May;75(5):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1987.tb05450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto K., Ishii N., Fukasawa H. Diffuse white-matter disease in the geriatric population. A clinical, neuropathological, and CT study. Radiology. 1981 Dec;141(3):687–695. doi: 10.1148/radiology.141.3.7302224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray F., Dubas F., Roullet E., Escourolle R. Leukoencephalopathy in diffuse hemorrhagic cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Jul;18(1):54–59. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. R., Naheedy M. H., Young J. C., Ghobrial M., Rubino F. A., Hindo W. Periventricular white matter changes and dementia. Clinical, neuropsychological, radiological, and pathological correlation. Arch Neurol. 1988 Jun;45(6):637–641. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520300057019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson L., Nilsson L. Differential diagnosis of presenile dementia on clinical grounds. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1982 Mar;65(3):194–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1982.tb00840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Iliff L. D., Zilhka E., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol. 1975 Sep;32(9):632–637. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490510088009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey L. A., Modic M. T., Jaffe D. F., Greenough P. G. Natural history of the vascular dementias: a prospective study of seven cases. Can J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;13(4 Suppl):559–565. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K., Wu L., Luo Y. Binswanger's disease: progressive subcortical encephalopathy or multi-infarct dementia? Can J Neurol Sci. 1985 May;12(2):88–94. doi: 10.1017/s031716710004676x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz B. J., Heyman A., Burger P. C., Drayer B. P. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Report of a case simulating psychiatric disease and normal pressure hydrocephalus. N C Med J. 1987 Apr;48(4):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino H., Higashi H., Hayahara T., Ikeda H., Otsuki S. A case of subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1972 Jan;26(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1972.tb01110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JELGERSMA H. C. A CASE OF ENCEPHALOPATHIA SUBCORTICALIS CHRONICA (BINSWANGER'S DISEASE). Psychiatr Neurol (Basel) 1964;147:81–89. doi: 10.1159/000128890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janota I. Dementia, deep white matter damage and hypertension: 'Binswanger's disease'. Psychol Med. 1981 Feb;11(1):39–48. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700053265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkel W. R., Jacobs L., Polachini I., Bates V., Heffner R. R., Jr Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Computed tomographic, nuclear magnetic resonance, and clinical correlations. Arch Neurol. 1985 Oct;42(10):951–959. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060090033010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koto A., Rosenberg G., Zingesser L. H., Horoupian D., Katzman R. Syndrome of normal pressure hydrocephalus: possible relation to hypertensive and arteriosclerotic vasculopathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Jan;40(1):73–79. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotsoris H., Barclay L. L., Kheyfets S., Hulyalkar A., Dougherty J. Urinary and gait disturbances as markers for early multi-infarct dementia. Stroke. 1987 Jan-Feb;18(1):138–141. doi: 10.1161/01.str.18.1.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb C., Gandolfo C., Bino G. Intellectual impairment and cerebral lesions in multiple cerebral infarcts. A clinical-computed tomography study. Stroke. 1988 May;19(5):560–565. doi: 10.1161/01.str.19.5.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loizou L. A., Kendall B. E., Marshall J. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: a clinical and radiological investigation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Apr;44(4):294–304. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler M. E., Cummings J. L., Tomiyasu U. Atypical dementia syndrome in an elderly man. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1987 Dec;35(12):1116–1126. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1987.tb04930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancardi G. L., Romagnoli P., Tassinari T., Gandolfo C., Primavera A., Loeb C. Lacunae and cribriform cavities of the brain. Correlations with pseudobulbar palsy and parkinsonism. Eur Neurol. 1988;28(1):11–17. doi: 10.1159/000116220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. S., McClintic K. L., Rogers R. L., Sims P., Mortel K. F. Aetiological considerations and risk factors for multi-infarct dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Dec;51(12):1489–1497. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.12.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikol J. Maladie de Binswanger et formes apparentées. Contribution à l'étude des leucoencéphalopathies artérioscléreuses. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1968 Feb;118(2):111–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Román G. C. Senile dementia of the Binswanger type. A vascular form of dementia in the elderly. JAMA. 1987 Oct 2;258(13):1782–1788. doi: 10.1001/jama.1987.03400130096040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen W. G., Terry R. D., Fuld P. A., Katzman R., Peck A. Pathological verification of ischemic score in differentiation of dementias. Ann Neurol. 1980 May;7(5):486–488. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. A., Kornfeld M., Stovring J., Bicknell J. M. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger): computerized tomography. Neurology. 1979 Aug;29(8):1102–1106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.8.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau P. Binswanger's disease: a cause of dementia in the elderly. South Med J. 1988 Oct;81(10):1329–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel A. B., Duong T. H., Tomiyasu U. Denervation microangiopathy in senile dementia, Alzheimer type. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1987;1(1):19–37. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198701000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinberg P. Dementia due to vascular disease--a multifactorial disorder. Stroke. 1988 Oct;19(10):1291–1299. doi: 10.1161/01.str.19.10.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg B. S., Kokmen E., Okazaki H. Alzheimer's disease and other dementing illnesses in a defined United States population: incidence rates and clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1987 Dec;22(6):724–729. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. D., Marsden C. D. Gait disorder of subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: Binswanger's disease. Mov Disord. 1987;2(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/mds.870020101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Roth M. Observations on the brains of demented old people. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Sep;11(3):205–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeumer H., Schonsky B., Sturm K. W. Predominant white matter involvement in subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger disease). J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1980 Feb;4(1):14–19. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198002000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


