Abstract
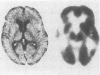
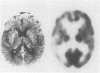
Three cases of slowly progressive speech and language disturbance were studied at various points post onset (three, five and 15 years respectively). Language, neuropsychological and brain imaging (computer tomography and positron emission tomography) evaluations were completed on all three patients. The data suggest that the syndrome of "progressive aphasia": 1) does not involve a uniform symptom complex; 2) does not necessarily develop into a full blown dementia syndrome; 3) varies greatly in rate of progression from case to case; 4) is associated with normal brain structure (on computer tomography); and 5) is associated with abnormal left temporal lobe metabolism as measured by fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET). One patient had histological findings consistent with Alzheimer's disease at necropsy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Canter G. J. Observations on neurogenic stuttering: a contribution to differential diagnosis. Br J Disord Commun. 1971 Oct;6(2):139–143. doi: 10.3109/13682827109011539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawluk J. B., Mesulam M. M., Hurtig H., Kushner M., Weintraub S., Saykin A., Rubin N., Alavi A., Reivich M. Slowly progressive aphasia without generalized dementia: studies with positron emission tomography. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jan;19(1):68–74. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster N. L., Chase T. N. Diffuse involvement in progressive aphasia. Ann Neurol. 1983 Feb;13(2):224–225. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. J., Phelps M. E., Huang S. C. Performance evaluation of a positron tomograph designed for brain imaging. J Nucl Med. 1983 Mar;24(3):245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland A. L., McBurney D. H., Moossy J., Reinmuth O. M. The dissolution of language in Pick's disease with neurofibrillary tangles: a case study. Brain Lang. 1985 Jan;24(1):36–58. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(85)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner H. S., Tanridag O., Thurman L., Whetsell W. O., Jr Progressive aphasia without dementia: two cases with focal spongiform degeneration. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):527–532. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner H. S., Webb W. G., Kelly M. P., Wells C. E. Language disturbance. An initial symptom of cortical degenerations and dementia. Arch Neurol. 1984 May;41(5):491–496. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050170037012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell A. M., Alexander M. P., Carpenter S. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease presenting as isolated aphasia. Neurology. 1989 Jan;39(1):55–58. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M. Primary progressive aphasia--differentiation from Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):533–534. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M. Slowly progressive aphasia without generalized dementia. Ann Neurol. 1982 Jun;11(6):592–598. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metter E. J., Riege W. H., Kameyama M., Kuhl D. E., Phelps M. E. Cerebral metabolic relationships for selected brain regions in Alzheimer's, Huntington's, and Parkinson's diseases. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Dec;4(4):500–506. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. C., Cole M., Banker B. Q., Wright D. Hereditary dysphasic dementia and the Pick-Alzheimer spectrum. Ann Neurol. 1984 Oct;16(4):455–466. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps M. E., Huang S. C., Hoffman E. J., Selin C., Sokoloff L., Kuhl D. E. Tomographic measurement of local cerebral glucose metabolic rate in humans with (F-18)2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose: validation of method. Ann Neurol. 1979 Nov;6(5):371–388. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poeck K., Luzzatti C. Slowly progressive aphasia in three patients. The problem of accompanying neuropsychological deficit. Brain. 1988 Feb;111(Pt 1):151–168. doi: 10.1093/brain/111.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogacar S., Williams R. S. Alzheimer's disease presenting as slowly progressive aphasia. R I Med J. 1984 Apr;67(4):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riege W. H., Metter E. J., Hanson W. R. Verbal and nonverbal recognition memory in aphasic and nonaphasic stroke patients. Brain Lang. 1980 May;10(1):60–70. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(80)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]