Abstract
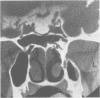
Positive contrast cisternography with digital subtraction of fluoroscopy images before computed tomography (CT) was employed in the investigation of eight patients with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) rhinorrhoea. Fistulae were visualised by preliminary digital subtraction cisternography (DSC) in six patients and in five patients the sites of leakage were confirmed at surgery. Fluoroscopy facilitated interpretation of CT in all the positive studies and in two patients provided information which could not be deduced from CT cisternography (CTC) alone. The combined technique is recommended for the investigation of patients with recurrent and post operative CSF rhinorrhoea and when CTC alone fails to identify the site of leakage.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmadi J., Weiss M. H., Segall H. D., Schultz D. H., Zee C. S., Giannotta S. L. Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea by metrizamide computed tomographic cisternography. Neurosurgery. 1985 Jan;16(1):54–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadbridge A. T., Bayliss S. G., Brayshaw C. I. The effect of intrathecal iohexol on visual evoked response latency: a comparison including incidence of headache with iopamidol and metrizamide in myeloradiculography. Clin Radiol. 1987 Jan;38(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(87)80413-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow J. M., Goodman D., Mafee M. F. Evaluation of CSF rhinorrhea by computerized tomography with metrizamide. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989 Feb;100(2):99–105. doi: 10.1177/019459988910000204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. Cerebrospinal fluid fistula involving the sphenoid sinus. Neurosurgery. 1987 Jan;20(1):31–32. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198701000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Chiro G., Ommaya A. K., Ashburn W. L., Briner W. H. Isotope cisternography in the diagnosis and follow-up of cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea. J Neurosurg. 1968 Jun;28(6):522–529. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.28.6.0522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer B. P., Rosenbaum A. E. Studies of the third circulation. Amipaque CT cisternography and ventriculography. J Neurosurg. 1978 Jun;48(6):946–956. doi: 10.3171/jns.1978.48.6.0946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer B. P., Wilkins R. H., Boehnke M., Horton J. A., Rosenbaum A. E. Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea demonstrated by metrizamide CT cisternography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977 Jul;129(1):149–151. doi: 10.2214/ajr.129.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckert L. G., Mathog R. H. Diagnosis in persistent cerebrospinal fluid fistulas. Laryngoscope. 1977 Jan;87(1):18–25. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197701000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHOURALAL S., MYERS P. W., CAMPBELL E. Persistent cerebrospinal rhinorrhea originating in a fracture through the petrous bone and cured by muscle graft; report of a case. J Neurosurg. 1956 Mar;13(2):205–207. doi: 10.3171/jns.1956.13.2.0205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. L., McDonald T. J., Pearson B. W., Laws E. R., Jr Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea: evolving concepts in diagnosis and surgical management based on the Mayo Clinic experience from 1970 through 1981. Neurosurgery. 1985 Mar;16(3):314–321. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198503000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRCHNER F. R., PROUD G. O. Method for the identification and localization of cerebrospinal fluid, rhinorrhea and otorrhea. Laryngoscope. 1960 Jul;70:921–931. doi: 10.1288/00005537-196007000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman B., Nulsen F. E., Weiss M. H., Brodkey J. S., White R. J., Sykora G. F. Acquired spontaneous, nontraumatic normal-pressure cerebrospinal fluid fistulas originating from the middle fossa. Radiology. 1977 Feb;122(2):379–387. doi: 10.1148/122.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGee E. E., Cauthen J. C., Brackett C. E. Meningitis following acute traumatic cerebrospinal fluid fistula. J Neurosurg. 1970 Sep;33(3):312–316. doi: 10.3171/jns.1970.33.3.0312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manelfe C., Cellerier P., Sobel D., Prevost C., Bonafé A. Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea: evaluation with metrizamide cisternography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982 Mar;138(3):471–476. doi: 10.2214/ajr.138.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manelfe C., Guiraud B., Tremoulet M. Diagnosis of C.S.F. rhinorrhoea by computerised cisternography using metrizamide. Lancet. 1977 Nov 19;2(8047):1073–1073. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91902-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naidich T. P., Moran C. J. Precise anatomic localization of atraumatic sphenoethmoidal cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea by metrizamide CT cisternography. J Neurosurg. 1980 Aug;53(2):222–228. doi: 10.3171/jns.1980.53.2.0222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ommaya A. K., Di Chiro G., Baldwin M., Pennybacker J. B. Non-traumatic cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Jun;31(3):214–225. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ommaya A. K. Spinal fluid fistulae. Clin Neurosurg. 1976;23:363–392. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/23.cn_suppl_1.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribram H. F., Hass A. C., Nishioka H. Radiographic localization of a spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid fistula. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1966 Jun;24(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.3171/jns.1966.24.6.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCKETT F. X., WITTENBORG M. H., SHILLITO J., Jr, MATSON D. D. PANTOPAQUE VISUALIZATION OF A CONGENITAL DURAL DEFECT OF THE INTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS CAUSING RHINORRHEA. REPORT OF A CASE. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1964 Mar;91:640–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovit R. L., Schechter M. M., Nelson K. Spontaneous "high-pressure cerebrospinal rhinorrhea" due to lesions obstructing flow of cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurosurg. 1969 Apr;30(4):406–412. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.30.4.0406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spetzler R. F., Wilson C. B. Management of recurrent CSF rhinorrhea of the middle and posterior fossa. J Neurosurg. 1978 Sep;49(3):393–397. doi: 10.3171/jns.1978.49.3.0393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Mutsuga N., Aoki T., Handa T., Tanoi C., Yoshida J., Kobayashi T. Localization of dural fistulas using metrizamide digital subtraction fluoroscopic cisternography. J Neurosurg. 1988 May;68(5):721–725. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.68.5.0721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmore G. A., Whittam D. E. Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhoea and its management. Br J Surg. 1982 Aug;69(8):489–492. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800690821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]