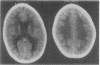
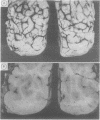
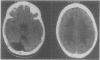
Abstract
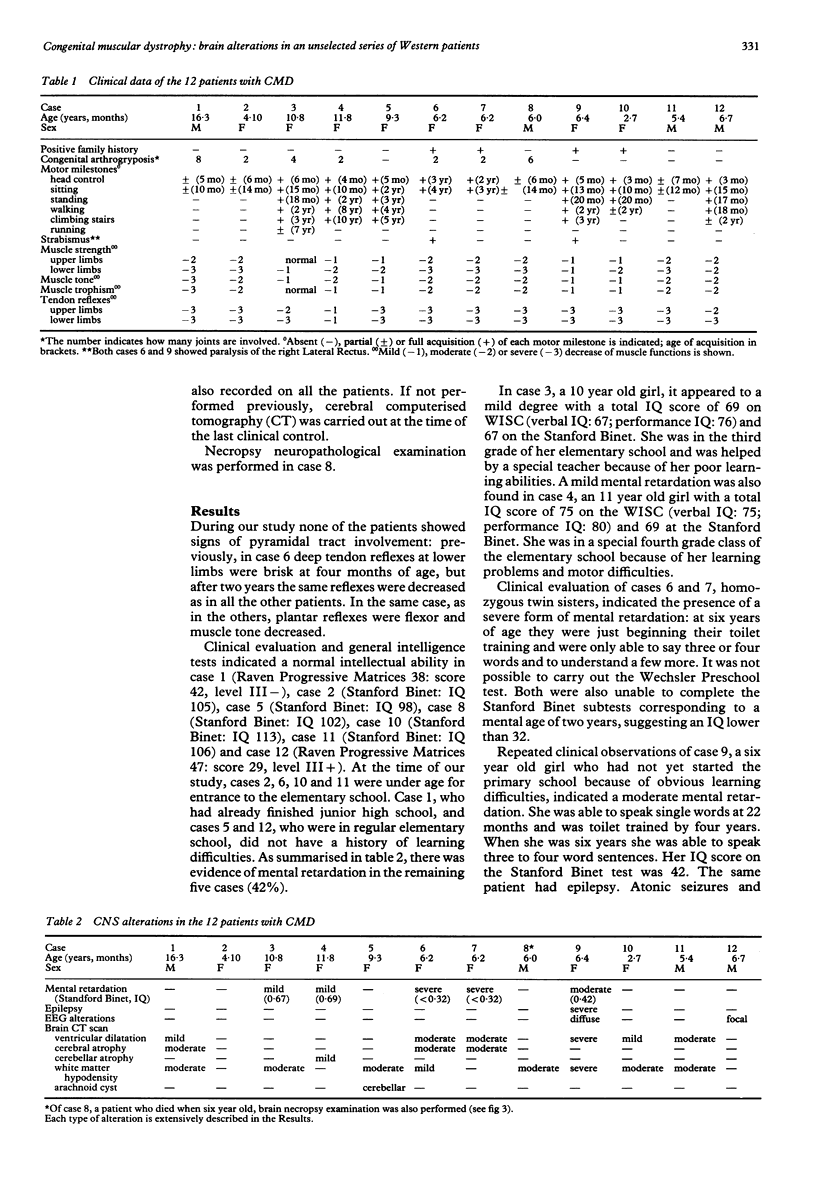
The typical form of congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) described in Western countries is generally considered different from its Japanese variant because of the absence of CNS involvement. Evaluations from both a clinical and a neuroradiological point of view were made of the CNS functions of 12 unselected Western children affected by CMD. In five patients, clinical observation and intelligence tests showed a mild to severe mental retardation. One of these patients suffered also from a severe form of epilepsy. In the same five patients, various degrees of white matter hypodensity, ventricular enlargement and cerebral atrophy were also detected. Similar neuroradiological abnormalities were also found in five of the seven children who did not have clinical symptoms or signs of CNS involvement. In one of these cases, necropsy neuropathological examination showed the gyral anomalies characteristic of the Japanese type of CMD. This study clearly indicates the high frequency of subclinical CNS alterations in typical Western CMD, suggesting that it should be considered a type of myoencephalopathy like its Japanese counterpart.
Full text
PDF
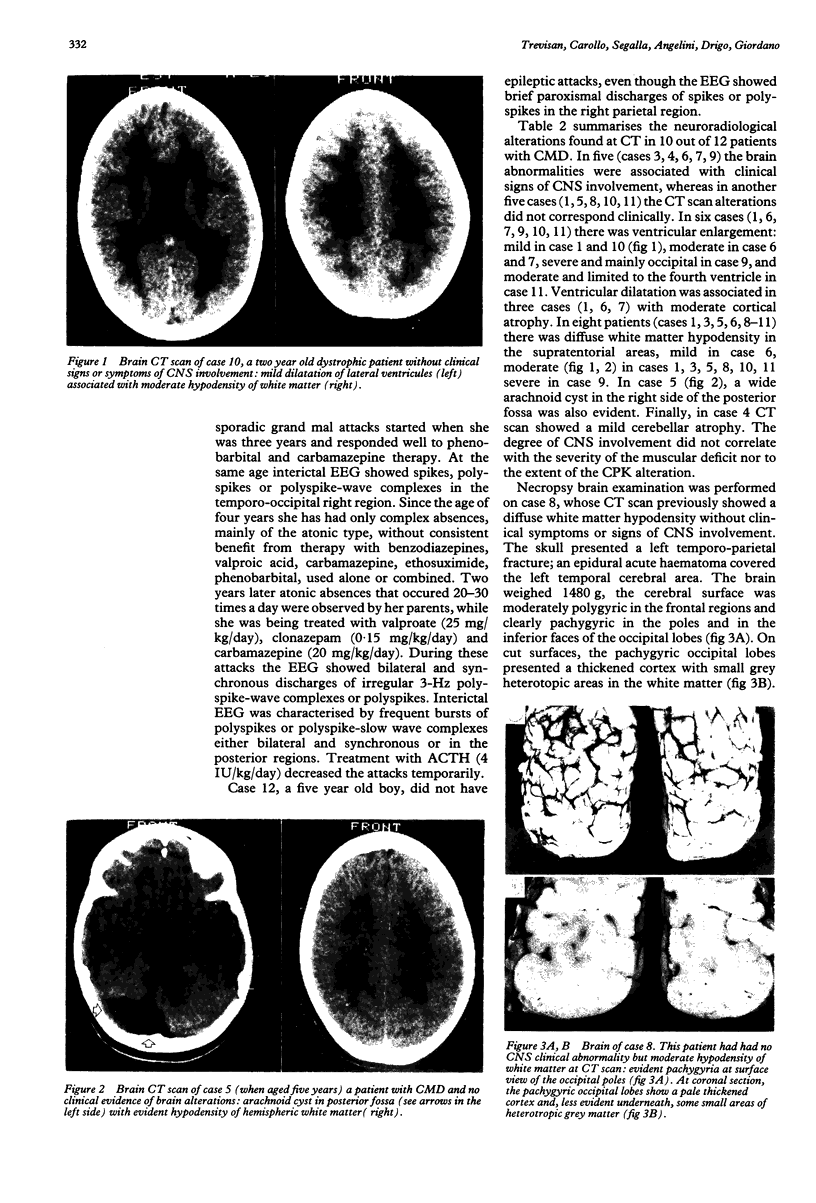


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernier J. P., Brooke M. H., Naidich T. P., Carroll J. E. Myoencephalopathy: cerebral hypomyelination revealed by CT scan of the head in a muscle disease. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1979;104:244–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambska M., Wisniewski K., Sher J., Solish G. Cerebro-oculo-muscular syndrome: a variant of Fukuyama congenital cerebromuscular dystrophy. Clin Neuropathol. 1982;1(3):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner M., Rapola J., Somer H. Congenital muscular dystrophy: a clinico-pathological and follow-up study of 15 patients. Neuropadiatrie. 1975 Aug;6(3):239–258. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1091666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echenne B., Arthuis M., Billard C., Campos-Castello J., Castel Y., Dulac O., Fontan D., Gauthier A., Kulakowski S., De Meuron G. Congenital muscular dystrophy and cerebral CT scan anomalies. Results of a collaborative study of the Société de Neurologie Infantile. J Neurol Sci. 1986 Aug;75(1):7–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egger J., Kendall B. E., Erdohazi M., Lake B. D., Wilson J., Brett E. M. Involvement of the central nervous system in congenital muscular dystrophies. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1983 Feb;25(1):32–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1983.tb13719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama Y., Osawa M., Suzuki H. Congenital progressive muscular dystrophy of the Fukuyama type - clinical, genetic and pathological considerations. Brain Dev. 1981;3(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(81)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gobernado J. M., Gimeno A. Changes in cerebral white matter in a case of congenital muscular dystrophy. Pediatr Radiol. 1982;12(4):201–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00999311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel H. H., Fidzianska A., Lenard H. G., Osse G., Hori A. A morphological study of non-Japanese congenital muscular dystrophy associated with cerebral lesions. Brain Dev. 1983;5(3):292–301. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(83)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson O., Kristensson K., Lycke E., Solymar L., Sourander P. Generalized myopathy and cerebral malformations possibly related to an enteroviral infection. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 Nov;64(6):881–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb03942.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. A Case of Congenital Defect of the Muscular System (Dystrophia muscularis congenita) and its Association with Congenital Talipes equino-varus. Proc R Soc Med. 1908;1(PATHOL):157–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERVIS G. A. Progressive muscular dystrophy with extensive demyelination of the brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1955 Oct;14(4):376–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamoshita S., Konishi Y., Segawa M., Fukuyama Y. Congenital muscular dystrophy as a disease of the central nervous system. Arch Neurol. 1976 Jul;33(7):513–516. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500070055011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korinthenberg R., Palm D., Schlake W., Klein J. Congenital muscular dystrophy, brain malformation and ocular problems (muscle, eye and brain disease) in two German families. Eur J Pediatr. 1984 Apr;142(1):64–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00442595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krijgsman J. B., Barth P. G., Stam F. C., Slooff J. L., Jaspar H. H. Congenital muscular dystrophy and cerebral dysgenesis in a Dutch family. Neuropadiatrie. 1980 May;11(2):108–120. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1071382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli P., Gabellini A. S., Ciucci G., Govoni E., Vitali S., Gullì M. R. Congenital muscular dystrophy with central nervous system involvement: case report. Eur Neurol. 1987;26(1):17–22. doi: 10.1159/000116307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMenamin J. B., Becker L. E., Murphy E. G. Congenital muscular dystrophy: a clinicopathologic report of 24 cases. J Pediatr. 1982 May;100(5):692–697. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80566-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogen A. G. Congenital muscle disease and abnormal findings on computerized tomography. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1980 Oct;22(5):658–663. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1980.tb04381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney K. K., Miller R. G. Inflammatory infiltration in Fukuyama type congenital muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Jan;6(1):75–77. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. C., Bots G. T., Roos R. A., van Gelderen H. H. Fukuyama type congenital muscular dystrophy--two Dutch siblings. Brain Dev. 1984;6(4):406–416. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(84)80117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitta C., Lamminen M., Santavuori P., Leisti J. Ophthalmological findings in a new syndrome with muscle, eye and brain involvement. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1978 Jun;56(3):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1978.tb05700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Fukuyama Y., Ogata T., Oya A. Experimental intrauterine infection of akabane virus. Pathological studies of skeletal muscles and central nervous system of newborn hamsters with relevances to the Fukuyama type congenital muscular dystrophy. Brain Dev. 1981;3(1):65–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towfighi J., Sassani J. W., Suzuki K., Ladda R. L. Cerebro-ocular dysplasia-muscular dystrophy (COD-MD) syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;65(2):110–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00690464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassella F., Mumenthaler M., Rossi E., Moser H., Wiesmann U. Die kongenitale Muskeldystrophie. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1967;190(4):349–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vles J. S., de Krom M. C., Visser R., Höweler C. J. Two Dutch siblings with congenital muscular dystrophy (Fukuyama type). Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1983;85(3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0303-8467(83)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka M., Okuno T., Honda Y., Nakano Y. Central nervous system involvement in progressive muscular dystrophy. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Aug;55(8):589–594. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.8.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka M., Okuno T., Ito M., Konishi Y., Itagaki Y., Sakamoto Y. Congenital muscular dystrophy (Fukuyama type). Repeated CT studies in 19 children. Comput Tomogr. 1981 Jan-Mar;5(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0363-8235(81)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zellweger H., Afifi A., McCormick W. F., Mergner W. Severe congenital muscular dystrophy. Am J Dis Child. 1967 Dec;114(6):591–602. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090270047003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]