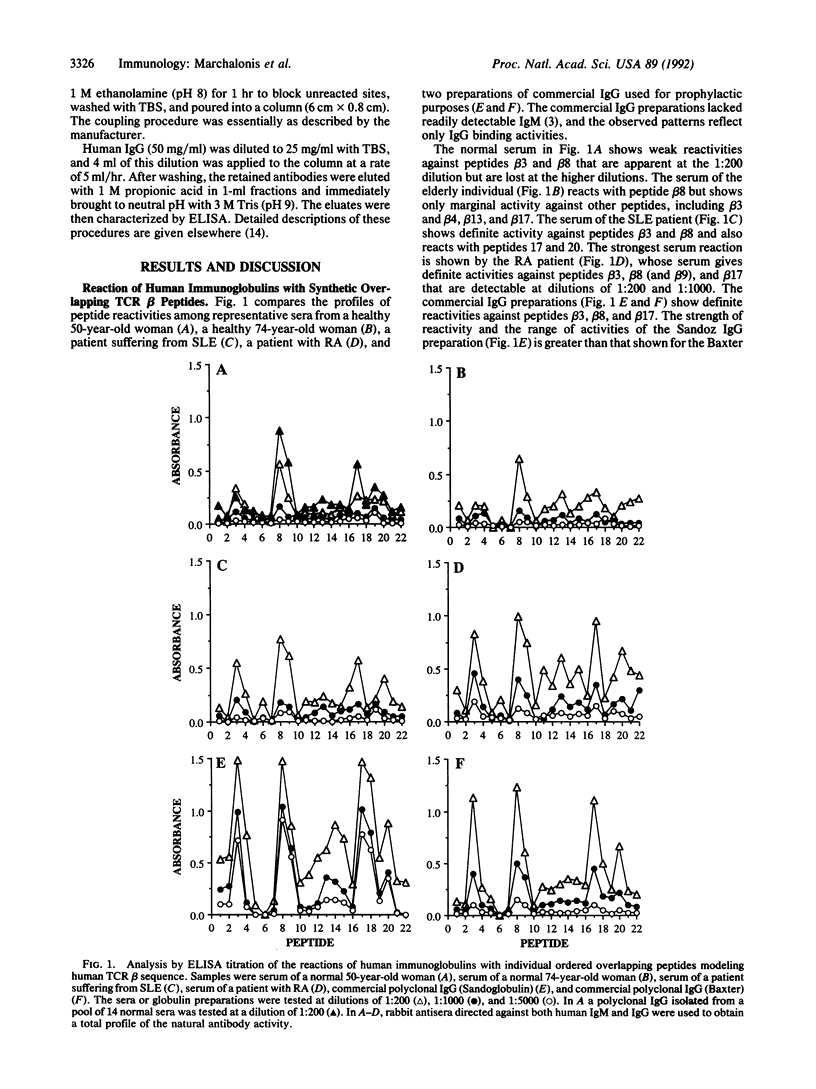
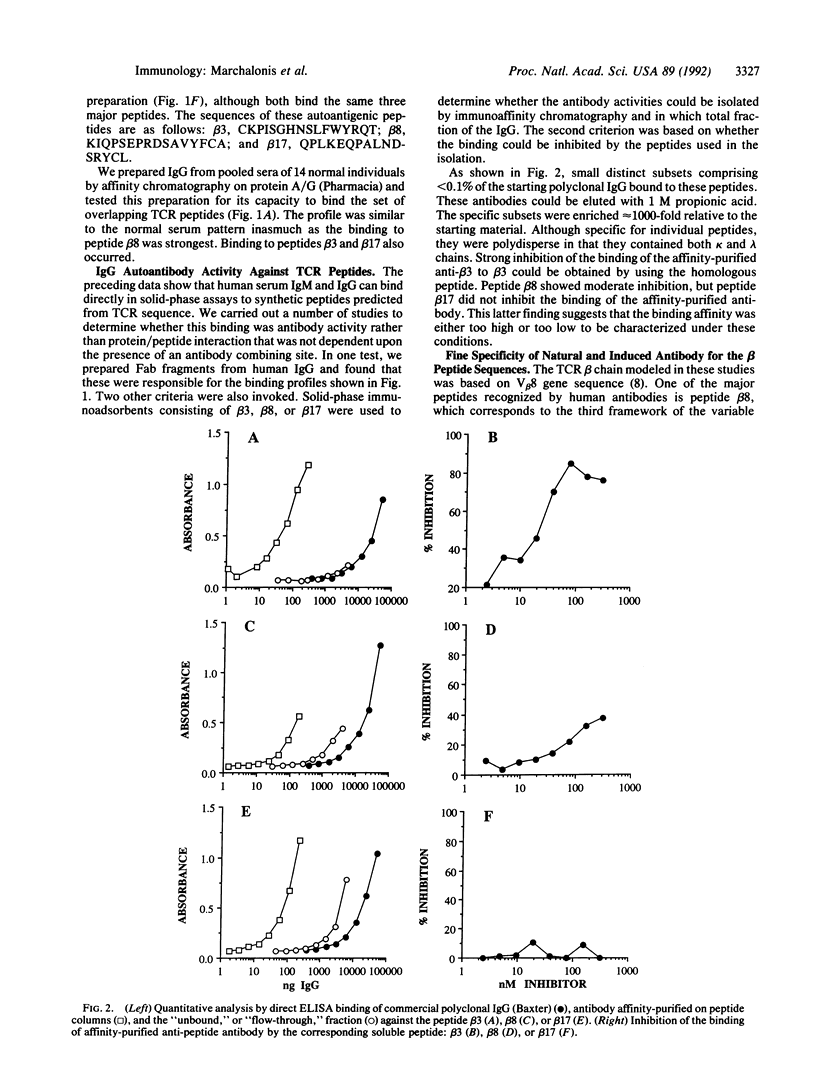
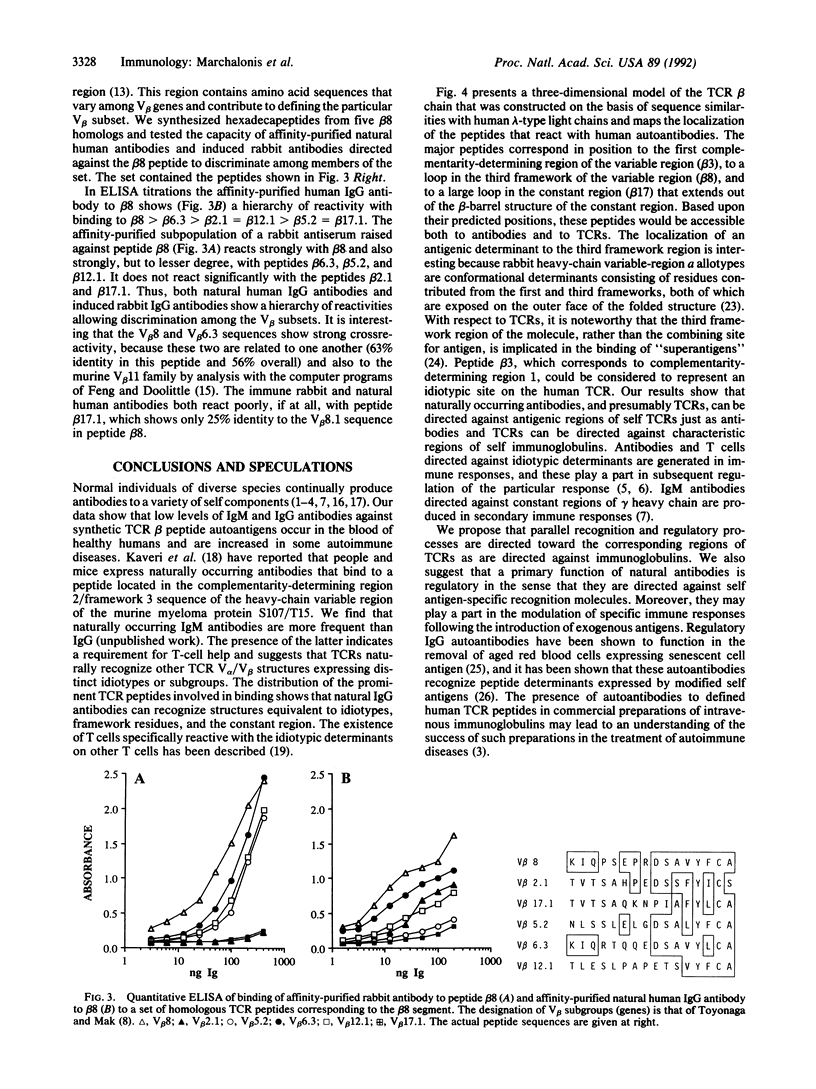
Abstract
We used mapping with synthetic overlapping peptides in combination with molecular modeling to analyze the IgG antibodies that humans naturally produce against human T-cell receptor beta chains and to localize the recognized peptide autoantigens in the three-dimensional structure of the molecule. Healthy individuals produce low levels of antibodies against T-cell receptor peptides, and these can be increased in autoimmune diseases. We characterized the reactivities in detail because IgG molecules reactive with self peptides occur in preparations of intravenous immunoglobulin and can be isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography. Natural IgG antibodies were directed against three major peptides. One corresponds to the first complementarity-determining region of the variable region. A second corresponds to the third framework of the variable region. The third is located in the constant region and is predicted to be a loop that extends out of the beta-barrel structure. This peptide is one that would give a characteristic structural distinction between the beta-chain constant region and the constant regions of immunoglobulin light chains to which beta chains are homologous. The capacity to bind these peptides is found in small fractions of normal polyclonal IgG, which contains both kappa chains and lambda chains. The activity is antibody-like in being confined to the Fab fragment and in its capacity to discriminate among homologous synthetic peptides corresponding to distinct beta-chain variable-region genes. We propose that a recognition and regulatory process naturally occurs that parallels the immune network for the regulation of the production of antibodies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beale D., Coadwell J. Unusual features of the T-cell receptor C domains are revealed by structural comparisons with other members of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;85(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90244-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. A., Chen P. P., Fox R. I., Kipps T. J., Jirik F., Goldfien R. D., Silverman G., Radoux V., Fong S. Rheumatoid factor and immune networks. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:109–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicou E., Nerrière V., Labropoulou V. Naturally occurring antibodies against nerve growth factor in human and rabbit sera: comparison between control and herpes simplex virus-infected patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Nov;34(2-3):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90124-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely K. R., Herron J. N., Harker M., Edmundson A. B. Three-dimensional structure of a light chain dimer crystallized in water. Conformational flexibility of a molecule in two crystal forms. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):601–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert B., Dighiero G., Avrameas S. Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in human sera. I. Detection, isolation and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerne N. K. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974 Jan;125C(1-2):373–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaveri S. V., Dietrich G., Hurez V., Kazatchkine M. D. Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Nov;86(2):192–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05794.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaveri S. V., Kang C. Y., Köhler H. Natural mouse and human antibodies bind to a peptide derived from a germline VH chain. Evidence for evolutionary conserved self-binding locus. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4207–4213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M. Localization of senescent cell antigen on band 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5753–5757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Marchalonis J. J., Hughes J., Watanabe K., Schluter S. F. Definition of a physiologic aging autoantigen by using synthetic peptides of membrane protein band 3: localization of the active antigenic sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazim A. L., Atassi M. Z. A novel and comprehensive synthetic approach for the elucidation of protein antigenic structures. Determination of the full antigenic profile of the alpha-chain of human haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 1;191(1):261–264. doi: 10.1042/bj1910261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Bernstein K. E., McCartney-Francis N., Alexander C. B., Young-Cooper G. O., Padlan E. A., Cohen G. H. The structural and genetic basis for expression of normal and latent VHa allotypes of the rabbit. Mol Immunol. 1984 Nov;21(11):1067–1081. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Schluter S. F. Evolution of variable and constant domains and joining segments of rearranging immunoglobulins. FASEB J. 1989 Nov;3(13):2469–2479. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.13.2509274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. M., Wade T., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Identification of the region of T cell receptor beta chain that interacts with the self-superantigen MIs-1a. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1365–1374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90700-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Dietrich G., Kazatchkine M. D. Anti-idiotypes against autoantibodies in normal immunoglobulins: evidence for network regulation of human autoimmune responses. Immunol Rev. 1989 Aug;110:135–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluter S. F., Marchalonis J. J. Antibodies to synthetic joining segment peptide of the T-cell receptor beta-chain: serological cross-reaction between products of T-cell receptor genes, antigen binding T-cell receptors, and immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1872–1876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy M. S., Dietz M. H., Germain R. N., Benacerraf B., Greene M. I. Antigen- and receptor-driven regulatory mechanisms. IV. Idiotype-bearing I-J+ suppressor T cell factors induce second-order suppressor T cells which express anti-idiotypic receptors. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1183–1195. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyonaga B., Mak T. W. Genes of the T-cell antigen receptor in normal and malignant T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:585–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela F., Andersson A., Dietrich G., Sundblad A., Holmberg D., Kazatchkine M., Coutinho A. Population dynamics of natural antibodies in normal and autoimmune individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5917–5921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor-Kobrin C., Bonilla F. A., Barak Z., Bona C. Structural correlates of a regulatory idiotope. Immunol Rev. 1989 Aug;110:151–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi Y., Yoshikai Y., Leggett K., Clark S. P., Aleksander I., Mak T. W. A human T cell-specific cDNA clone encodes a protein having extensive homology to immunoglobulin chains. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):145–149. doi: 10.1038/308145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



