Abstract
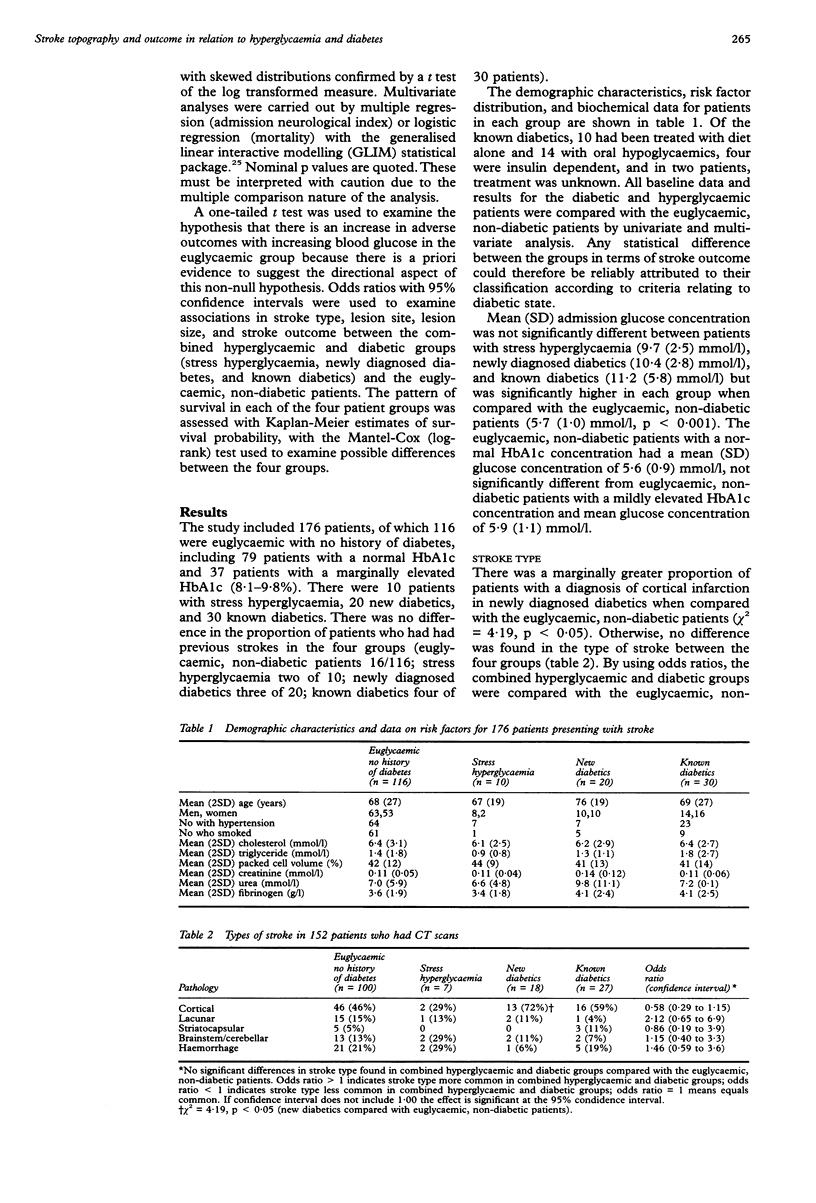
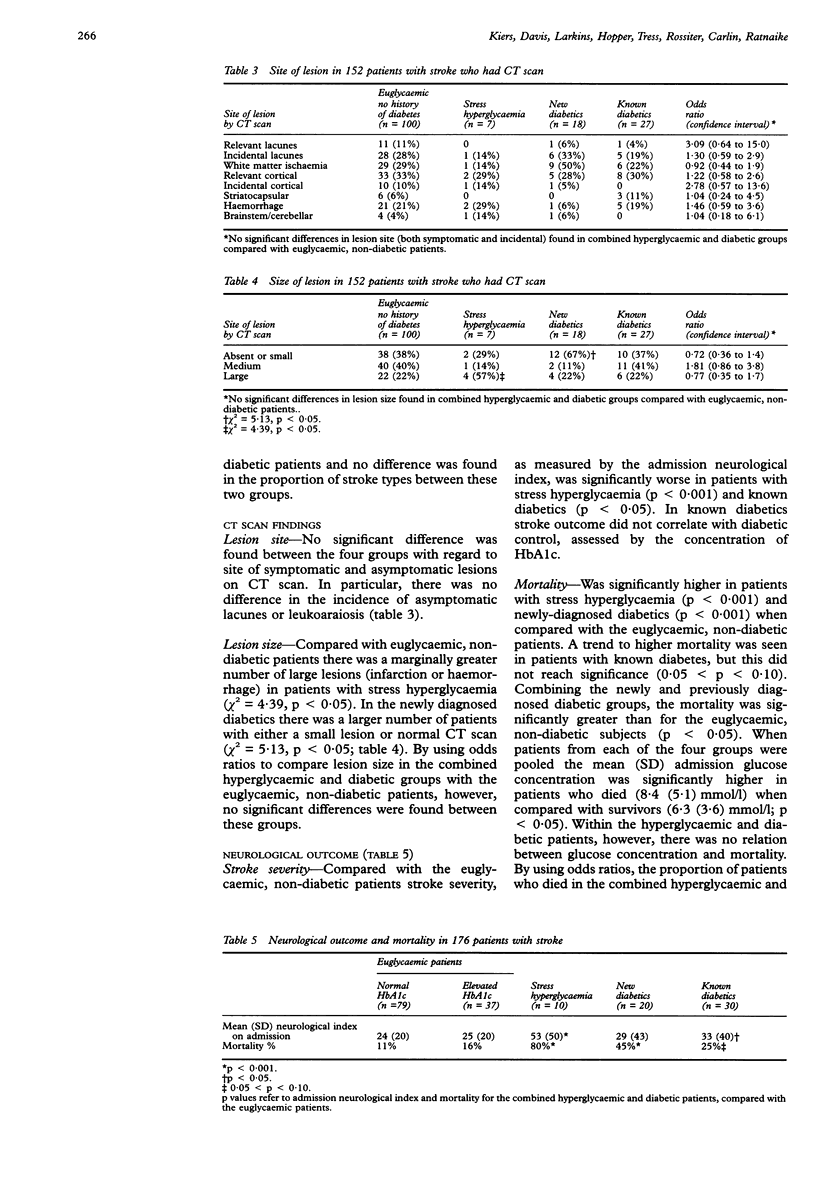
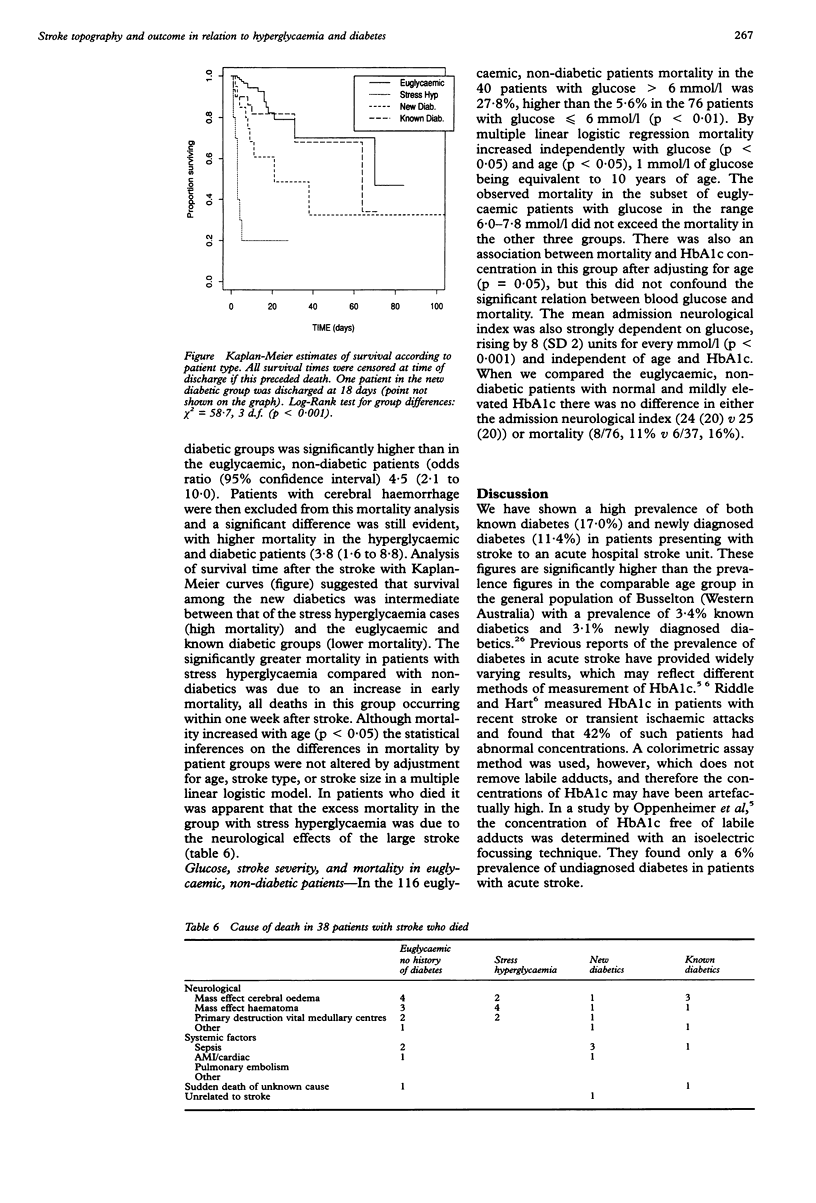
In a prospective study to analyse stroke topography and outcome in diabetics and to determine the prognostic value of blood glucose and glycosylated haemoglobin estimation, we evaluated 176 patients with acute stroke. The patients were classified into four groups on the basis of history, fasting glucose, and glycosylated haemoglobin: euglycaemic patients with no history of diabetes, stress hyperglycaemia, newly diagnosed diabetics, and known diabetics. A high prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes was shown. No difference was found in the type or site of stroke between the four groups. No difference was found in the site of symptomatic or incidental lesions on computerised axial tomography. Patients with stress hyperglycaemia and known diabetics had more severe strokes. Mortality was higher in patients with stress hyperglycaemia, newly diagnosed diabetics, and the combined diabetes groups. This increased mortality was evident in the hyperglycaemic and diabetic groups, even after excluding patients with cerebral haemorrhage. Stroke severity and mortality also increased independently with blood glucose in the euglycaemic group. We conclude that there is a correlation between admission glucose concentration, diabetes, and poor stroke outcome, which may not be attributed to stroke type or location.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEX M., BARON E. K., GOLDENBERG S., BLUMENTHAL H. T. An autopsy study of cerebrovascular accident in diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 1962 Apr;25:663–673. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.25.4.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asplund K., Hägg E., Helmers C., Lithner F., Strand T., Wester P. O. The natural history of stroke in diabetic patients. Acta Med Scand. 1980;207(5):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1980.tb09749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes A. J., Locke P., Scudder P. R., Dormandy T. L., Dormandy J. A., Slack J. Is hyperviscosity a treatable component of diabetic microcirculatory disease? Lancet. 1977 Oct 15;2(8042):789–791. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90724-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentsen N., Larsen B., Lassen N. A. Chronically impaired autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in long-term diabetics. Stroke. 1975 Sep-Oct;6(5):497–502. doi: 10.1161/01.str.6.5.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brott T., Marler J. R., Olinger C. P., Adams H. P., Jr, Tomsick T., Barsan W. G., Biller J., Eberle R., Hertzberg V., Walker M. Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: lesion size by computed tomography. Stroke. 1989 Jul;20(7):871–875. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.7.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candelise L., Landi G., Orazio E. N., Boccardi E. Prognostic significance of hyperglycemia in acute stroke. Arch Neurol. 1985 Jul;42(7):661–663. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060070051014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers B. R., Norris J. W., Shurvell B. L., Hachinski V. C. Prognosis of acute stroke. Neurology. 1987 Feb;37(2):221–225. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox N. H., Lorains J. W. The prognostic value of blood glucose and glycosylated haemoglobin estimation in patients with stroke. Postgrad Med J. 1986 Jan;62(723):7–10. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.62.723.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. H., Dambrosia J. M., Schoenberg B. S., Schoenberg D. G., Pritchard D. A., Lilienfeld A. M., Whisnant J. P. Risk factors for ischemic stroke: a prospective study in Rochester, Minnesota. Ann Neurol. 1987 Sep;22(3):319–327. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson C., Wright K., Maynard A. Determining value for money in day hospital care for the elderly. Age Ageing. 1986 Jan;15(1):1–7. doi: 10.1093/ageing/15.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka S., Yeh H., Mandybur T. I., Tew J. M., Jr Effect of insulin on acute experimental cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Stroke. 1989 Mar;20(3):396–399. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller J. H., Shipley M. J., Rose G., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Mortality from coronary heart disease and stroke in relation to degree of glycaemia: the Whitehall study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 24;287(6396):867–870. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6396.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia M. J., McNamara P. M., Gordon T., Kannel W. B. Morbidity and mortality in diabetics in the Framingham population. Sixteen year follow-up study. Diabetes. 1974 Feb;23(2):105–111. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatthaar C., Welborn T. A., Stenhouse N. S., Garcia-Webb P. Diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. A prevalence estimate based on the Busselton 1981 survey. Med J Aust. 1985 Nov 11;143(10):436–440. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb123131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. S., Taylor R., French J. M., Alberti K. G., Venables G. S., James O. F., Shaw D. A., Cartlidge N. E., Bates D. The prognostic value of stress hyperglycaemia and previously unrecognized diabetes in acute stroke. Diabet Med. 1987 May-Jun;4(3):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1987.tb00870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C. R., Kase C. S., Mohr J. P., Cunningham S. C., Baker W. E. Stroke in south Alabama: incidence and diagnostic features--a population based study. Stroke. 1984 Mar-Apr;15(2):249–255. doi: 10.1161/01.str.15.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Potter P., Merskey H. Leuko-araiosis. Arch Neurol. 1987 Jan;44(1):21–23. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520130013009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helgason C. M. Blood glucose and stroke. Stroke. 1988 Aug;19(8):1049–1053. doi: 10.1161/01.str.19.8.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., McGee D. L. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979 May 11;241(19):2035–2038. doi: 10.1001/jama.241.19.2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMay D. R., Gehua L., Zelenock G. B., D'Alecy L. G. Insulin administration protects neurologic function in cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1988 Nov;19(11):1411–1419. doi: 10.1161/01.str.19.11.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan D. E., Utterback N. G., La Puma J. Reduced erythrocyte deformability in diabetes. Diabetes. 1978 Sep;27(9):895–901. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.9.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed E. Reactive hyperglycaemia in patients with acute stroke. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Oct;29(2-4):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr J. P., Caplan L. R., Melski J. W., Goldstein R. J., Duncan G. W., Kistler J. P., Pessin M. S., Bleich H. L. The Harvard Cooperative Stroke Registry: a prospective registry. Neurology. 1978 Aug;28(8):754–762. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.8.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. E., Yamaguchi S. Nervous system effects of cardiac arrest in monkeys. Preservation of vision. Arch Neurol. 1977 Feb;34(2):65–74. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500140019003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer S. M., Hoffbrand B. I., Oswald G. A., Yudkin J. S. Diabetes mellitus and early mortality from stroke. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Oct 12;291(6501):1014–1015. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6501.1014-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peress N. S., Kane W. C., Aronson S. M. Central nervous system findings in a tenth decade autopsy population. Prog Brain Res. 1973;40(0):473–483. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)60707-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum F. What causes infarction in ischemic brain?: The Robert Wartenberg Lecture. Neurology. 1983 Feb;33(2):222–233. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.2.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulsinelli W. A., Levy D. E., Sigsbee B., Scherer P., Plum F. Increased damage after ischemic stroke in patients with hyperglycemia with or without established diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1983 Apr;74(4):540–544. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)91007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulsinelli W. A., Waldman S., Rawlinson D., Plum F. Moderate hyperglycemia augments ischemic brain damage: a neuropathologic study in the rat. Neurology. 1982 Nov;32(11):1239–1246. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.11.1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulsinelli W., Waldman S., Sigsbee B., Rawlinson D., Scherer P., Plum F. Experimental hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus worsen stroke outcome. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1980;105:21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle M. C., Hart J. Hyperglycemia, recognized and unrecognized, as a risk factor for stroke and transient ischemic attacks. Stroke. 1982 May-Jun;13(3):356–359. doi: 10.1161/01.str.13.3.356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. S., Grossman R. G. Protection against spinal cord ischemia with insulin-induced hypoglycemia. J Neurosurg. 1987 Nov;67(5):739–744. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.5.0739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemkowicz E., Gjedde A. Post-ischemic coma in rat: effect of different pre-ischemic blood glucose levels on cerebral metabolic recovery after ischemia. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Nov;110(3):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemkowicz E., Hansen A. J. Clinical restitution following cerebral ischemia in hypo-, normo- and hyperglycemic rats. Acta Neurol Scand. 1978 Jul;58(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Special report from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Classification of cerebrovascular diseases III. Stroke. 1990 Apr;21(4):637–676. doi: 10.1161/01.str.21.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyama K., Neriishi S., Kawamoto S., Kato H., Miyake S., Nagataki S. Risk factors of cerebro-cardiovascular disorders in mild diabetes. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1983 Dec;141 (Suppl):535–540. doi: 10.1620/tjem.141.suppl_535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wautier J. L., Paton R. C., Wautier M. P., Pintigny D., Abadie E., Passa P., Caen J. P. Increased adhesion of erythrocytes to endothelial cells in diabetes mellitus and its relation to vascular complications. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 30;305(5):237–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107303050501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo J., Lam C. W., Kay R., Wong A. H., Teoh R., Nicholls M. G. The influence of hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus on immediate and 3-month morbidity and mortality after acute stroke. Arch Neurol. 1990 Nov;47(11):1174–1177. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1990.00530110028011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


