Abstract
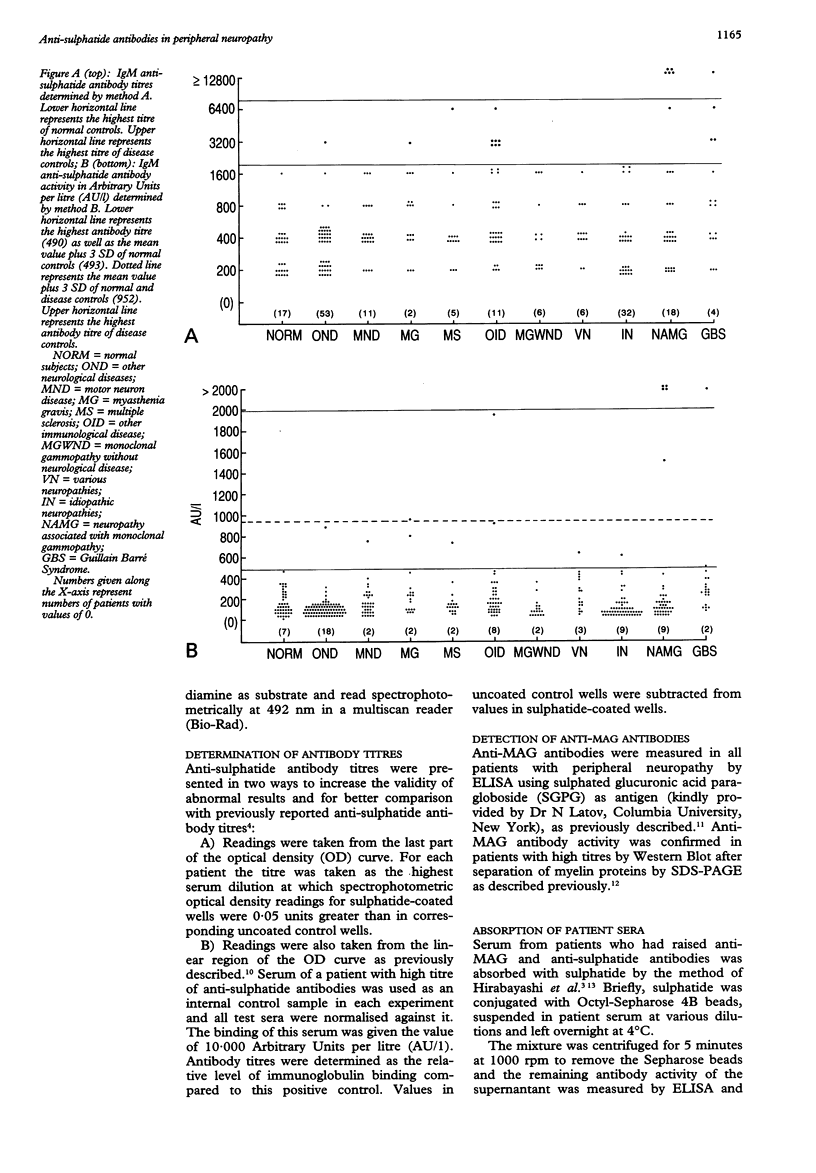
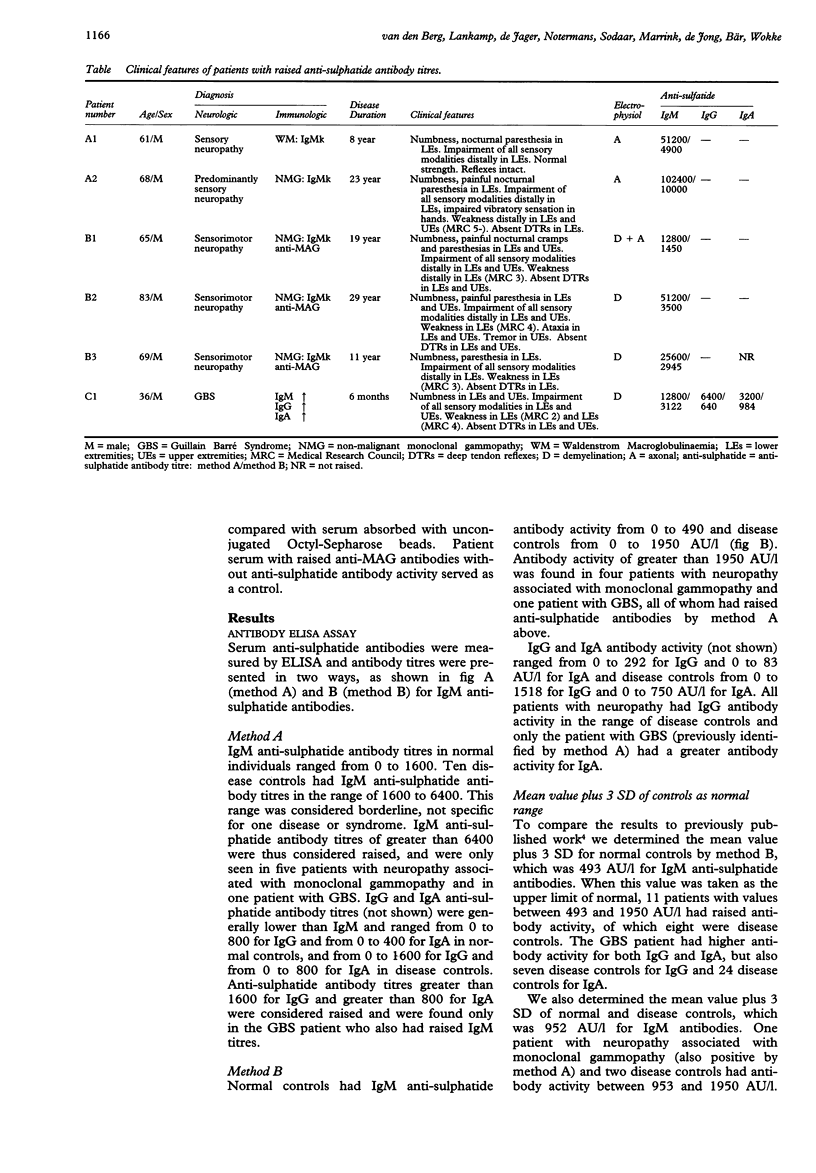
A study was carried out on 135 patients with chronic idiopathic neuropathy (63), neuropathy associated with monoclonal gammopathy (51, including eight with anti-MAG antibody activity) and the Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) (21). Serum IgM, IgG and IgA anti-sulphatide antibody titres were compared with titres in 304 patients with other neurological or immunological diseases and in 50 normal subjects. Titres were presented a) as the highest serum dilution at which reactivity could be detected, and b) in the linear region of the optical density curve. A substantial number of patients with neurological or immunological diseases had higher titres than normal subjects. Compared with normal and disease controls, five patients with neuropathy associated with IgMk monoclonal gammopathy had raised titres of IgM anti-sulphatide antibodies and one patient with GBS had raised IgM, IgG and IgA anti-sulphatide antibodies in the acute phase of the disease. Two patients had a predominantly axonal sensory neuropathy with presenting symptoms of painful paresthesiae and minimal neurological deficit. Three patients had a predominantly demyelinating sensorimotor neuropathy associated with anti-MAG antibody activity. The patient with GBS had extensive sensory loss and antibody titres returned to normal within three weeks. Raised titres of anti-sulphatide antibodies occurred in several types of neuropathy, but all had some degree of sensory impairment and associated immunological abnormality.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fredman P., Vedeler C. A., Nyland H., Aarli J. A., Svennerholm L. Antibodies in sera from patients with inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy react with ganglioside LM1 and sulphatide of peripheral nerve myelin. J Neurol. 1991 Apr;238(2):75–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00315684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi Y., Suzuki T., Suzuki Y., Taki T., Matsumoto M., Higashi H., Kato S. A new method for purification of anti-glycosphingolipid antibody. Avian anti-hematoside (NeuGc) antibody. J Biochem. 1983 Jul;94(1):327–330. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas A. A., Cook S. D., Dalakas M. C., Mithen F. A. Anti-MAG IgM paraproteins from some patients with polyneuropathy associated with IgM paraproteinemia also react with sulfatide. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90158-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas A. A., Mithen F. A., Dalakas M. C., Wargo M., Chen Z. W., Bielory L., Cook S. D. Antibodies to sulfated glycolipids in Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Sep;105(1):108–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90126-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latov N., Hays A. P., Sherman W. H. Peripheral neuropathy and anti-MAG antibodies. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1988;3(4):301–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis S., Kohriyama T., Yu R. K., Pesce M. A., Latov N. Antibodies to sulfated glucuronic acid containing glycosphingolipids in neuropathy associated with anti-MAG antibodies and in normal subjects. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Jan;17(2):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestronk A., Li F., Griffin J., Feldman E. L., Cornblath D., Trotter J., Zhu S., Yee W. C., Phillips D., Peeples D. M. Polyneuropathy syndromes associated with serum antibodies to sulfatide and myelin-associated glycoprotein. Neurology. 1991 Mar;41(3):357–362. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryberg B. Multiple specificities of antibrain antibodies in multiple sclerosis and chronic myelopathy. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Oct;38(3):357–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Fredman P. Antibody detection in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990;27 (Suppl):S36–S40. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda G., Ikeda Y., Kashiwagi M., Iwamori M., Oka H. Hepatocyte plasma membrane glycosphingolipid reactive with sera from patients with autoimmune chronic active hepatitis: its identification as sulfatide. Hepatology. 1990 Oct;12(4 Pt 1):664–670. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vliet H. H., Kappers-Klunne M. C., van der Hel J. W., Abels J. Antibodies against glycosphingolipids in sera of patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 1987 Sep;67(1):103–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg L. H., Marrink J., de Jager A. E., de Jong H. J., van Imhoff G. W., Latov N., Sadiq S. A. Anti-GM1 antibodies in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Jan;55(1):8–11. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg L. H., Sadiq S. A., Thomas F. P., Latov N. Characterization of HNK-1 bearing glycoproteins in human peripheral nerve myelin. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Mar;25(3):295–299. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490250305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


